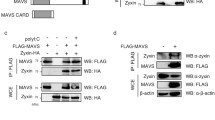
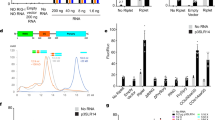
Abstract
RIG-I is a cytosolic receptor recognizing virus-specific RNA structures and initiates an antiviral signaling that induces the production of interferons and proinflammatory cytokines. Because inappropriate RIG-I signaling affects either viral clearance or immune toxicity, multiple regulations of RIG-I have been investigated since its discovery as the viral RNA detector. In this review, we describe the recent progress in research on the regulation of RIG-I activity or abundance. Specifically, we focus on the mechanism that modulates RIG-I-dependent antiviral response through post-translational modifications of or protein-protein interactions with RIG-I.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostolou, E. and Thanos, D. 2008. Virus infection induces NF-κB-dependent interchromosomal associations mediating monoallelic IFN-β gene expression. Cell 134, 85–96.
Arimoto, K., Takahashi, H., Hishiki, T., Konishi, H., Fujita, T., and Shimotohno, K. 2007. Negative regulation of the RIG-I signaling by the ubiquitin ligase RNF125. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 7500–7505.
Choi, S.J., Lee, H.C., Kim, J.H., Park, S.Y., Kim, T.H., Lee, W.K., Jang, D.J., Yoon, J.E., Choi, Y.I., Kim, S., et al. 2016. HDAC6 regulates cellular viral RNA sensing by deacetylation of RIG-I. EMBO J. 35, 429–442.
Choudhary, C., Kumar, C., Gnad, F., Nielsen, M.L., Rehman, M., Walther, T.C., Olsen, J.V., and Mann, M. 2009. Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions. Science 325, 834–840.
Cui, J., Song, Y., Li, Y., Zhu, Q., Tan, P., Qin, Y., Wang, H.Y., and Wang, R.F. 2014. USP3 inhibits type I interferon signaling by deubiquitinating RIG-I-like receptors. Cell Res. 24, 400–416.
Das, A., Dinh, P.X., Panda, D., and Pattnaik, A.K. 2014. Interferoninducible protein IFI35 negatively regulates RIG-I antiviral signaling and supports vesicular stomatitis virus replication. J. Virol. 88, 3103–3113.
Fan, Y., Mao, R., Yu, Y., Liu, S., Shi, Z., Cheng, J., Zhang, H., An, L., Zhao, Y., Xu, X., et al. 2014. USP21 negatively regulates antiviral response by acting as a RIG-I deubiquitinase. J. Exp. Med. 211, 313–328.
Friedman, C.S., O’Donnell, M.A., Legarda-Addison, D., Ng, A., Cardenas, W.B., Yount, J.S., Moran, T.M., Basler, C.F., Komuro, A., Horvath, C.M., et al. 2008. The tumour suppressor CYLD is a negative regulator of RIG-I-mediated antiviral response. EMBO Rep. 9, 930–936.
Gack, M.U., Shin, Y.C., Joo, C.H., Urano, T., Liang, C., Sun, L., Takeuchi, O., Akira, S., Chen, Z., Inoue, S., et al. 2007. TRIM25 RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase is essential for RIG-I-mediated antiviral activity. Nature 446, 916–920.
Hayakawa, S., Shiratori, S., Yamato, H., Kameyama, T., Kitatsuji, C., Kashigi, F., Goto, S., Kameoka, S., Fujikura, D., Yamada, T., et al. 2011. ZAPS is a potent stimulator of signaling mediated by the RNA helicase RIG-I during antiviral responses. Nat. Immunol. 12, 37–44.
He, S., Zhao, J., Song, S., He, X., Minassian, A., Zhou, Y., Zhang, J., Brulois, K., Wang, Y., Cabo, J., et al. 2015. Viral pseudo-enzymes activate RIG-I via deamidation to evade cytokine production. Mol. Cell 58, 134–146.
Hu, J., Sealfon, S.C., Hayot, F., Jayaprakash, C., Kumar, M., Pendleton, A.C., Ganee, A., Fernandez-Sesma, A., Moran, T.M., and Wetmur, J.G. 2007. Chromosome-specific and noisy IFNB1 transcription in individual virus-infected human primary dendritic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 5232–5241.
Hwang, S.Y., Hur, K.Y., Kim, J.R., Cho, K.H., Kim, S.H., and Yoo, J.Y. 2013. Biphasic RLR-IFN-β response controls the balance between antiviral immunity and cell damage. J. Immunol. 190, 1192–1200.
Inn, K.S., Gack, M.U., Tokunaga, F., Shi, M.D., Wong, L.Y., Iwai, K., and Jung, J.U. 2011. Linear ubiquitin assembly complex negatively regulates RIG-I- and TRIM25-mediated type I interferon induction. Mol. Cell 41, 354–365.
Jiang, X., Kinch, L.N., Brautigam, C.A., Chen, X., Du, F., Grishin, N.V., and Chen, Z.J. 2012. Ubiquitin-induced oligomerization of the RNA sensors RIG-I and MDA5 activates antiviral innate immune response. Immunity 36, 959–973.
Jiang, F., Ramanathan, A., Miller, M.T., Tang, G.Q., Gale, M.Jr., Patel, S.S., and Marcotrigiano, J. 2011. Structural basis of RNA recognition and activation by innate immune receptor RIG-I. Nature 479, 423–427.
Kawai, T., Takahashi, K., Sato, S., Coban, C., Kumar, H., Kato, H., Ishii, K.J., Takeuchi, O., and Akira, S. 2005. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat. Immunol. 6, 981–988.
Kim, M.J., Hwang, S.Y., Imaizumi, T., and Yoo, J.Y. 2008. Negative feedback regulation of RIG-I-mediated antiviral signaling by interferon-induced ISG15 conjugation. J. Virol. 82, 1474–1483.
Kok, K.H., Lui, P.Y., Ng, M.H.J., Siu, K.L., Au, S.W.N., and Jin, D.Y. 2011. The double-stranded RNA-binding protein PACT functions as a cellular activator of RIG-I to facilitate innate antiviral response. Cell Host Microbe 9, 299–309.
Kowalinski, E., Lunardi, T., McCarthy, A.A., Louber, J., Brunel, J., Grigorov, B., Gerlier, D., and Cusack, S. 2011. Structural basis for the activation of innate immune pattern-recognition receptor RIG-I by viral RNA. Cell 147, 423–435.
Kuniyoshi, K., Takeuchi, O., Pandey, S., Satoh, T., Iwasaki, H., Akira, S., and Kawai, T. 2014. Pivotal role of RNA-binding E3 ubiquitin ligase MEX3C in RIG-I-mediated antiviral innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 5646–5651.
Li, M.T., Di, W., Xu, H., Yang, Y.K., Chen, H.W., Zhang, F.X., Zhai, Z.H., and Chen, D.Y. 2013. Negative regulation of RIG-I-mediated innate antiviral signaling by SEC14L1. J. Virol. 87, 10037–10046.
Liu, H.M., Loo, Y.M., Horner, S.M., Zornetzer, G.A., Katze, M.G., and Gale, M. 2012. The mitochondrial targeting chaperone 14-3-3 epsilon regulates a RIG-I translocon that mediates membrane association and innate antiviral immunity. Cell Host Microbe 11, 528–537.
Liu, X., Luo, D.Y., and Yang, N. 2015. Cytosolic low molecular weight FGF2 orchestrates RIG-I-mediated innate immune response. J. Immunol. 195, 4943–4952.
Loo, Y.M. and Gale, M.Jr. 2011. Immune signaling by RIG-I-like receptors. Immunity 34, 680–692.
Maharaj, N.P., Wies, E., Stoll, A., and Gack, M.U. 2012. Conventional protein kinase C-α (PKC-α) and PKC-β negatively regulate RIG-I antiviral signal transduction. J. Virol. 86, 1358–1371.
Meylan, E., Curran, J., Hofmann, K., Moradpour, D., Binder, M., Bartenschlager, R., and Tschopp, J. 2005. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature 437, 1167–1172.
Mi, Z., Fu, J., Xiong, Y., and Tang, H. 2010. SUMOylation of RIG-I positively regulates the type I interferon signaling. Protein Cell 1, 275–283.
Miyashita, M., Oshiumi, H., Matsumoto, M., and Seya, T. 2011. DDX60, a DEXD/H box helicase, is a novel antiviral factor promoting RIG-I-like receptor-mediated signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 31, 3802–3819.
Nguyen, N.T.H., Now, H., Kim, W.J., Kim, N., and Yoo, J.Y. 2016. Ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10 attenuates RIG-I mediated antiviral signaling by segregating activated RIG-I from its signaling platform. Sci. Rep. DOI 10.1038/srep23377.
Nistal-Villan, E., Gack, M.U., Martinez-Delgado, G., Maharaj, N.P., Inn, K.S., Yang, H., Wang, R., Aggarwal, A.K., Jung, J.U., and Garcia-Sastre, A. 2010. Negative role of RIG-I serine 8 phosphorylation in the regulation of interferon-β production. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 20252–20261.
Now, H. and Yoo, J.Y. 2011. A protein-kinase, IFN-inducible doublestranded RNA dependent inhibitor and repressor of p58 (PRKRIR) enhances type I IFN-mediated antiviral response through the stability control of RIG-I protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 413, 487–493.
Oshiumi, H., Matsumoto, M., Hatakeyama, S., and Seya, T. 2009. Riplet/RNF135, a RING finger protein, ubiquitinates RIG-I to promote interferon-β induction during the early phase of viral infection. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 807–817.
Oshiumi, H., Miyashita, M., Inoue, N., Okabe, M., Matsumoto, M., and Seya, T. 2010. The ubiquitin ligase Riplet is essential for RIGI-dependent innate immune responses to RNA virus infection. Cell Host Microbe 8, 496–509.
Oshiumi, H., Miyashita, M., Matsumoto, M., and Seya, T. 2013. A distinct role of Riplet-mediated K63-linked polyubiquitination of the RIG-I repressor domain in human antiviral innate immune responses. PLoS Pathog. 9, e1003533.
Patel, J.R., Jain, A., Chou, Y.Y., Baum, A., Ha, T., and Garcia-Sastre, A. 2013. ATPase-driven oligomerization of RIG-I on RNA allows optimal activation of type-I interferon. EMBO Rep. 14, 780–787.
Sun, Z., Ren, H., Liu, Y., Teeling, J.L., and Gu, J. 2011. Phosphorylation of RIG-I by casein kinase II inhibits its antiviral response. J. Virol. 85, 1036–1047.
Wallach, D. and Kovalenko, A. 2013. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the RIG-I-like receptors: a safety latch on a fateful pathway. Immunity 38, 402–403.
Wang, P.H., Arjona, A., Zhang, Y., Sultana, H., Dai, J.F., Yang, L., Le-Blanc, P.M., Doiron, K., Saleh, M., and Fikrig, E. 2010. Caspase-12 controls West Nile virus infection via the viral RNA receptor RIG-I. Nat. Immunol. 11, 912–919.
Wang, Y.T., Tong, X.M., Li, G., Li, J.H., Deng, M., and Ye, X. 2012. Ankrd17 positively regulates RIG-I-like receptor (RLR)-mediated immune signaling. Eur. J. Immunol. 42, 1304–1315.
Wang, L., Zhao, W., Zhang, M., Wang, P., Zhao, K., Zhao, X., Yang, S., and Gao, C. 2013. USP4 positively regulates RIG-I-mediated antiviral response through deubiquitination and stabilization of RIG-I. J. Virol. 87, 4507–4515.
Wies, E., Wang, M.K., Maharaj, N.P., Chen, K., Zhou, S., Finberg, R.W., and Gack, M.U. 2013. Dephosphorylation of the RNA sensors RIG-I and MDA5 by the phosphatase PP1 is essential for innate immune signaling. Immunity 38, 437–449.
Yan, J., Li, Q., Mao, A.P., Hu, M.M., and Shu, H.B. 2014. TRIM4 modulates type I interferon induction and cellular antiviral response by targeting RIG-I for K63-linked ubiquitination. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 154–163.
Yang, Y.K., Qu, H., Gao, D., Di, W., Chen, H.W., Guo, X., Zhai, Z.H., and Chen, D.Y. 2011. ARF-like protein 16 (ARL16) inhibits RIG-I by binding with its C-terminal domain in a GTP-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 10568–10580.
Yoneyama, M., Kikuchi, M., Natsukawa, T., Shinobu, N., Imaizumi, T., Miyagishi, M., Taira, K., Akira, S., and Fujita, T. 2004. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat. Immunol. 5, 730–737.
Zawatzky, R., De Maeyer, E., and De Maeyer-Guignard, J. 1985. Identification of individual interferon-producing cells by in situ hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 1136–1140.
Zhang, X., Yu, H., Zhao, J., Li, X., Li, J., He, J., Xia, Z., and Zhao, J. 2016. IKK negatively regulates RIG-I via direct phosphorylation. J. Med. Virol. 88, 712–718.
Zhao, K., Zhang, Q., Li, X., Zhao, D., Liu, Y., Shen, Q., Yang, M., Wang, C., Li, N., and Cao, X. 2016. Cytoplasmic STAT4 promotes antiviral type I IFN production by blocking CHIP-mediated degradation of RIG-I. J. Immunol. 196, 1209–1217.
Zhao, M., Zhang, J., Phatnani, H., Scheu, S., and Maniatis, T. 2012. Stochastic expression of the interferon-β gene. PLoS Biol. 10, e1001249.
Zhu, J.Z., Zhang, Y.G., Ghosh, A., Cuevas, R.A., Forero, A., Dhar, J., Ibsen, M.S., Schmid-Burgk, J.L., Schmidt, T., Ganapathiraju, M.K., et al. 2014. Antiviral activity of human OASL protein is mediated by enhancing signaling of the RIG-I RNA sensor. Immunity 40, 936–948.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, N., Now, H., Nguyen, N.T.H. et al. Multilayered regulations of RIG-I in the anti-viral signaling pathway. J Microbiol. 54, 583–587 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-016-6322-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-016-6322-2