Abstract
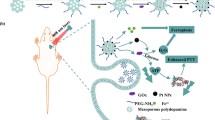
The synergistic therapy of chemotherapy and photothermal therapy (PTT) has been reported as a promising antitumor strategy. To achieve effective combination therapy, developing more suitable candidate nanomaterials with optimal photothermal property and high chemical drug loading capacity is very necessary. Herein, a bimetallic PtPd nanoparticle was synthesized with the merits of excellent photothermal effect and mesoporous structure for doxorubicin (DOX) loading. We further designed PtPd-ethylene glycol (PEG)-folic acid (FA)-doxorubicin (DOX) nanoparticle for chemo-photothermal therapy of MCF-7 tumor with folic acid engineering to achieve active targeting. Moreover, excellent photoacoustic (PA) imaging of PtPd-PEG-FA-DOX nanoparticles facilitated the precise in vivo tracking and further evaluation of nanoparticles’ targeting effect. The in vitro and in vivo results both demonstrated PtPd-PEG-FA-DOX nanoparticles serve as a safe and promising system for effective treatment of MCF-7 tumor.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M. M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin.2011, 61, 69–90.
Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R. A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell2011, 144, 646–674.
Duan, X.; Yang, X.; Dai, C. L.; Tong, T.; Miao, C. X.; Zheng, J. P. One-pot synthesis of camptothecin-loaded glutathione-responsive PEGlyation nanogels as novel antitumor therapeutics. Mater. Express2019, 9, 757–763.
He, Q. J.; Guo, S. R.; Qian, Z. Y.; Chen, X. Y. Development of individualized anti-metastasis strategies by engineering nanomedicines. Chem. Soc. Rev.2015, 44, 6258–6286.
Farokhzad, O. C.; Langer, R. Impact of nanotechnology on drug delivery. ACS Nano2009, 3, 16–20.
Luo, S. L.; Zhang, E. L.; Su, Y. P.; Cheng, T. M.; Shi, C. M. A review of NIR dyes in cancer targeting and imaging. Biomaterials2011, 32, 7127–7138.
Melancon, M. P.; Zhou, M.; Li, C. Cancer theranostics with near-infrared light-activatable multimodal nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res.2011, 44, 947–956.
Cheng, B.; He, H.; Huang, T.; Berr, S. S.; He, J.; Fan, D.; Zhang, J.; Xu, P. Gold nanosphere gated mesoporous silica nanoparticle responsive to near-infrared light and redox potential as a theranostic platform for cancer therapy. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol.2016, 12, 435–449.
Gu, Z. J.; Yan, L.; Tian, G.; Li, S. J.; Chai, Z. F.; Zhao, Y. L. Recent advances in design and fabrication of upconversion nanoparticles and their safe theranostic applications. Adv. Mater.2013, 25, 3758–3779.
Li, J. W.; Lyv, Z. L.; Li, Y. L.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. K.; Zhan, W. J.; Chen, H.; Chen, H. B.; Li, X. M. A theranostic prodrug delivery system based on Pt(IV) conjugated nano-graphene oxide with synergistic effect to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of Pt drug. Biomaterials2015, 51, 12–21.
Sun, X. L.; Cai, W. B.; Chen, X. Y. Positron emission tomography imaging using radiolabeled inorganic nanomaterials. Acc. Chem. Res.2015, 48, 286–294.
Shanmugam, V.; Selvakumar, S.; Yeh, C. S. Near-infrared light-responsive nanomaterials in cancer therapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev.2014, 43, 6254–6287.
Chen, Q.; Liang, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, Z. An imagable and photothermal “Abraxane-like” nanodrug for combination cancer therapy to treat subcutaneous and metastatic breast tumors. Adv. Mater.2015, 27, 903–910.
Lee, N.; Yoo, D.; Ling, D. S.; Cho, M. H.; Hyeon, T.; Cheon, J. Iron oxide based nanoparticles for multimodal imaging and magnetoresponsive therapy. Chem. Rev.2015, 115, 10637–10689.
Jabeen, F.; Najam-ul-Haq, M.; Javeed, R.; Huck, C. W.; Bonn, G. K. Au-nanomaterials as a superior choice for near-infrared photothermal therapy. Molecules2014, 19, 20580–20593.
Biju, V.; Itoh, T.; Anas, A.; Sujith, A.; Ishikawa, M. Semiconductor quantum dots and metal nanoparticles: Syntheses, optical properties, and biological applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem.2008, 391, 2469–2495.
Xiang, H. F.; Cheng, J. H.; Ma, X. F.; Zhou, X. G.; Chruma, J. J. Near-infrared phosphorescence: Materials and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev.2013, 42, 6128–6185.
Daniel, M. C.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles: Assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem. Rev.2004, 104, 293–346.
Zhao, L. L.; Choi, J.; Lu, Y.; Kim, S. Y. Targeted photodynamic therapy activities of surface-enhanced raman scattering-active theranostic system based on folate/hyaluronic acid-fonctionalized gold nanochains. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol.2019, 15, 544–554.
Kolmakov, A.; Klenov, D. O.; Lilach, Y.; Stemmer, S.; Moskovits, M. Enhanced gas sensing by individual SnO2 nanowires and nanobelts functionalized with Pd catalyst particles. Nano Lett.2005, 5, 667–673.
Tang, S. C.; Chen, M.; Zheng, N. F. Sub-10-nm Pd nanosheets with renal clearance for efficient near-infrared photothermal cancer therapy. Small2014, 10, 3139–3144.
Xiao, J. W.; Fan, S. X.; Wang, F.; Sun, L. D.; Zheng, X. Y.; Yan, C. H. Porous Pd nanoparticles with high photothermal conversion efficiency for efficient ablation of cancer cells. Nanoscale2014, 6, 4345–4351.
Chen, H.; Lin, W. Y.; Yuan, L. Construction of a near-infrared fluorescence turn-on and ratiometric probe for imaging palladium in living cells. Org. Biomol. Chem.2013, 11, 1938–1941.
Nie, L. M.; Chen, M.; Sun, X. L.; Rong, P. F.; Zheng, N. F.; Chen, X. Y. Palladium nanosheets as highly stable and effective contrast agents for in vivo photoacoustic molecular imaging. Nanoscale2014, 6, 1271–1276.
Tang, S. H.; Chen, M.; Zheng, N. F. Multifunctional ultrasmall Pd nanosheets for enhanced near-infrared photothermal therapy and chemotherapy of cancer. Nano Res.2015, 8, 165–174.
Alayoglu, S.; Zavalij, P.; Eichhorn, B.; Wang, Q.; Frenkel, A. I.; Chupas, P. Structural and architectural evaluation of bimetallic nanoparticles: A case study of Pt-Ru core-shell and alloy nanoparticles. ACS Nano2009, 3, 3127–3137.
Chen, L. Y.; Chen, N.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Z. C.; Lv, S. H.; Fujita, T.; Jiang, J. H.; Hirata, A.; Chen, M. W. Geometrically controlled nanoporous PdAu bimetallic catalysts with tunable Pd/Au ratio for direct ethanol fuel cells. ACS Catal.2013, 3, 1220–1230.
Fan, N. N.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W. F.; Zhang, L. J.; Chen, W.; Zou, C.; Huang, S. M. Selective etching induces selective growth and controlled formation of various platinum nanostructures by modifying seed surface free energy. ACS Nano2012, 6, 4072–4082.
Wang, S. Y.; Jiang, S. P.; White, T. J.; Guo, J.; Wang, X. Electrocatalytic activity and interconnectivity of Pt nanoparticles on multiwalled carbon nanotubes for fuel cells. J. Phys. Chem. C2009, 113, 18935–18945.
Jain, R. A. The manufacturing techniques of various drug loaded biodegradable poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) devices. Biomaterials2000, 21, 2475–2490.
Ataee-Esfahani, H.; Imura, M.; Yamauchi, Y. All-metalmesoporous nanocolloids: Solution-phase synthesis of core-shellPd@Pt nanoparticles with a designed concave surface. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed.2013, 52, 13611–13615.
Fischer, H. C.; Chan, W. C. W. Nanotoxicity: The growing need for in vivo study. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol.2007, 18, 565–571.
Wang, Y. Z.; Song, Y. J.; Zhu, G. X.; Zhang, D. C.; Liu, X. W. Highly biocompatible BSA-MnO2 nanoparticles as an efficient near-infrared photothermal agent for cancer therapy. Chin. Chem. Lett.2018, 29, 1685–1688.
Ruan, S. B.; Hu, C.; Tang, X.; Cun, X. L.; Xiao, W.; Shi, K. R.; He, Q.; Gao, H. L. Increased gold nanoparticle retention in brain tumors by in situ enzyme-induced aggregation. ACS Nano2016, 10, 10086–10098.
Li, Y. N.; Zhang, H. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for enhanced tumor-targeting treatment. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol.2019, 15, 1–27.
Li, W. T.; Peng, J. R.; Tan, L. W.; Wu, J.; Shi, K.; Qu, Y.; Wei, X. W.; Qian, Z. Y. Mild photothermal therapy/photodynamic therapy/chemotherapy of breast cancer by Lyp-1 modified Docetaxel/IR820 Co-loaded micelles. Biomaterials2016, 106, 119–133.
Yu, Z. H.; Guo, Y. C.; Dai, H.; Zeng, B. F.; Zheng, X.; Yi, C. X.; Jiang, N.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X. On-demand drug release and re-absorption from pirarubicin loaded Fe3O4@ZnO core-shell nanoparticles for targeting infusion chemotherapy for urethral carcinoma. Mater. Express2019, 9, 467–474.
Hao, Y.; Dong, M. L.; Zhang, T. Y.; Peng, J. R.; Jia, Y. P.; Cao, Y. P.; Qian, Z. Y. Novel approach of using near-infrared responsive PEGylated gold nanorod coated poly(L-lactide) microneedles to enhance the antitumor efficiency of docetaxel-loaded MPEG-PDLLA micelles for treating an A431 tumor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces2017, 9, 15317–15327.
Liu, R.; Hu, C.; Yang, Y. Y.; Zhang, J. Q.; Gao H. L. Theranostic nanoparticles with tumor-specific enzyme-triggered size reduction and drug release to perform photothermal therapy for breast cancer treatment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B2019, 9, 410–420.
Melamed, J. R.; Edelstein, R. S.; Day, E. S. Elucidating the fundamental mechanisms of cell death triggered by photothermal therapy. ACS Nano2015, 9, 6–11.
Li, J. L.; Gu, M. Surface plasmonic gold nanorods for enhanced two-photon microscopic imaging and apoptosis induction of cancer cells. Biomaterials2010, 31, 9492–9498.
Pustovalov, V. K.; Smetannikov, A. S.; Zharov, V. P. Photothermal and accompanied phenomena of selective nanophotothermolysis with gold nanoparticlesand laser pulses. Laser Phys. Lett.2008, 5, 775–792.
Tang, X. C.; Tan, L. W.; Shi, K.; Peng, J. R.; Xiao, Y.; Li, W. T.; Chen, L. J.; Yang, Q.; Qian, Z. Y. Gold nanorods together with HSP inhibitor-VER-155008 micelles for colon cancer mild-temperature photothermal therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B2018, 8, 587–601.
Tong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huff, T. B.; Hansen, M. N.; Wei, A.; Cheng J. X. Gold nanorods mediate tumor cell death by compromising membrane integrity. Adv. Mater.2007, 19, 3136–3141.
Tong, L.; Cheng, J. X. Gold nanorod-mediated photothermolysis induces apoptosis of macrophages via damage of mitochondria. Nanomedicine2009, 4, 265–276.
O’Neill, K. L.; Fairbairn, D. W.; Smith M. J.; Poe, B. S. Critical parameters influencing hyperthermia-induced apoptosis in human lymphoid cell lines. Apoptosis1998, 3, 369–375.
Link, S.; El-Sayed, M. A. Shape and size dependence of radiative, non-radiative and photothermal properties of gold nanocrystals. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem.2000, 19, 409–453.
Peng, J. R.; Qi, T. T.; Liao, J. F.; Chu, B. Y.; Yang, Q.; Qu, Y.; Li, W. T.; Li, H.; Luo, F.; Qian, Z. Y. Mesoporous magnetic gold “nanoclusters” as theranostic carrier for chemo-photothermal co-therapy of breast cancer. Theranostics2014, 4, 678–692.
Guo, L. L.; Chen, H.; He, N. Y.; Deng, Y. Effects of surface modifications on the physicochemical properties of iron oxide nanoparticles and their performance as anticancer drug carriers. Chin. Chem. Lett.2018, 29, 1829–1833.
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the help of Dr. Shanling Wang from Analytical & Testing Center in Sichuan University for TEM analysis of our nanoparticles. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31930067, 31525009, 31800797, and 31771096), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Nos. 2017YFC1103502 and 2016YFA0201402), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 2018M631094), the Postdoctoral Innovation Talents Support Program (No. BX20180207), and 1·3·5 project for disciplines of excellence, West China Hospital, Sichuan University (No. ZYGD18002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Song, Y., Qu, Y. et al. Mesoporous PtPd nanoparticles for ligand-mediated and imaging-guided chemo-photothermal therapy of breast cancer. Nano Res. 13, 1739–1748 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2800-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-020-2800-2