Abstract
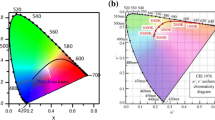
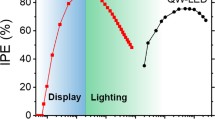
Advances in image quality in recent decades have made it necessary to develop new technologies for producing displays to meet remarkably stricter standards. The display market is governed mainly by liquid crystal display and light-emitting diode (LED) technology; however, it suffers from limitations that can be overcome by developing the next generation of electroluminescent displays. The introduction of colloidal quantum dots (QDs) as down-converters has enabled the production of displays with extremely high color purity and gamut. Therefore, colloidal nanocrystals are excellent candidates for the preparation of electroluminescent devices, which represent a straightforward approach to the development of unprecedented high-quality displays. We synthesized light-emitting QDs covering the entire visible spectrum with high fluorescence quantum yields and color purity, and produced high-brightness single-color LEDs with external quantum efficiencies of 0.39%, 1.04%, 2.10%, and 1.30% for red-, orange-, green-, and blue-emitting dots, respectively. Additionally, white LEDs were prepared by mixing QDs; they showed color temperatures of 5,300 K and color rendering indices exceeding 80%. Very importantly, we exhaustively characterized the LED performance, including the response time, stability, and evolution of the light characteristics, thus providing crucial information toward the development of high-quality electroluminescent displays.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekimov, A. I.; Onushchenko, A. A. Quantum size effect in three-dimensional microscopic semiconductor crystals. J. Exp. Theoret. Phys. Lett. 1981, 34, 345.
Derfus, A. M.; Chan, W. C. W.; Bhatia, S. N. Probing the cytotoxicity of semiconductor quantum dots. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 11–18.
Jamieson, T.; Bakhshi, R.; Petrova, D.; Pocock, R.; Imani, M.; Seifalian, A. M. Biological applications of quantum dots. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4717–4732.
Ko, D. K.; Maurano, A.; Suh, S. K.; Kim, D.; Hwang, G. W.; Grossman, J. C.; Bulovic, V.; Bawendi, M. G. Photovoltaic performance of PBS quantum dots treated with metal salts. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3382–3388.
Li, X. M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S. L.; Cai, B.; Gu, Y.; Song, J. Z.; Zeng, H. B. Quantum dots: CsPbX3 quantum dots for lighting and displays: Room-temperature synthesis, photoluminescence superiorities, underlying origins and white light-emitting diodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2584.
Liu, M. X.; Voznyy, O.; Sabatini, R.; de Arquer, F. P. G.; Munir, R.; Balawi, A. H.; Lan, X. Z.; Fan, F. J.; Walters, G.; Kirmani, A. R. et al. Hybrid organic–inorganic inks flatten the energy landscape in colloidal quantum dot solids. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 258–263.
Liu, M. X.; de Arquer, F. P. G.; Li, Y. Y.; Lan, X. Z.; Kim, G. H.; Voznyy, O.; Jagadamma, L. K.; Abbas, A. S.; Hoogland, S.; Lu, Z. H. et al. Double-sided junctions enable high-performance colloidal-quantum-dot photovoltaics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4142–4148.
Kim, G. H.; de Arquer, F. P. G.; Yoon, Y. J.; Lan, X. Z.; Liu, M. X.; Voznyy, O.; Yang, Z. Y.; Fan, F. J.; Ip, A. H.; Kanjanaboos, P. et al. High-efficiency colloidal quantum dot photovoltaics via robust self-assembled monolayers. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 7691–7696.
Rekemeyer, P. H.; Chang, S.; Chuang, C. H. M.; Hwang, G. W.; Bawendi, M. G.; Gradecak, S. Enhanced photocurrent in pbs quantum dot photovoltaics via ZnO nanowires and band alignment engineering. Advanced Energy Materials 2016, 6, 1600848.
Sargent, E.; McDonald, S. A.; Zhang, S. G.; Levina, L.; Konstantatos, G.; Cyr, P. Three-dimensional bicontinuous heterostructures, method of making, and their application in quantum dot-polymer nanocomposite photodetectors and photovoltaics. U. S. Patents 20130244366, September 19, 2013.
Lhuillier, E.; Scarafagio, M.; Hease, P.; Nadal, B.; Aubin, H.; Xu, X. Z.; Lequeux, N.; Patriarche, G.; Ithurria, S.; Dubertret, B. Infrared photodetection based on colloidal quantum-dot films with high mobility and optical absorption up to thz. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1282–1286.
Hwang, D. K.; Lee, Y. T.; Lee, H. S.; Lee, Y. J.; Shokouh, S. H.; Kyhm, J. h.; Lee, J.; Kim, H. H.; Yoo, T. H.; Nam, S. H. et al. Ultrasensitive pbs quantum-dot-sensitized InGaZnO hybrid photoinverter for near-infrared detection and imaging with high photogain. NPG Asia Mater. 2016, 8, e233.
Gao, J. B.; Nguyen, S. C.; Bronstein, N. D.; Alivisatos, A. P. Solution-processed, high-speed, and high-quantum-efficiency quantum dot infrared photodetectors. ACS Photonics 2016, 3, 1217–1222.
Mashford, B. S.; Stevenson, M.; Popovic, Z.; Hamilton, C.; Zhou, Z. Q.; Breen, C.; Steckel, J.; Bulovic, V.; Bawendi, M.; Coe-Sullivan, S. et al. High-efficiency quantum-dot lightemitting devices with enhanced charge injection. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 407–412.
Lee, K. H.; Lee, J. H.; Song, W. S.; Ko, H.; Lee, C.; Lee, J. H.; Yang, H. Highly efficient, color-pure, color-stable blue quantum dot light-emitting devices. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7295–7302.
Lee, K. H.; Lee, J. H.; Kang, H. D.; Park, B.; Kwon, Y.; Ko, H.; Lee, C.; Lee, J.; Yang, H. Over 40 cd/a efficient green quantum dot electroluminescent device comprising uniquely large-sized quantum dots. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4893–4901.
Zhang, H.; Wang, S. T.; Sun, X. W.; Chen, S. M. Solutionprocessed vanadium oxide as an efficient hole injection layer for quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 817–823.
Dai, X. L.; Zhang, Z. X.; Jin, Y. Z.; Niu, Y.; Cao, H. J.; Liang, X. Y.; Chen, L. W.; Wang, J. P.; Peng, X. G. Solutionprocessed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature 2014, 515, 96–99.
Sanchez, R. S.; Binetti, E.; Torre, J. A.; Garcia-Belmonte, G.; Striccoli, M.; Mora-Sero, I. All solution processed low turn-on voltage near infrared leds based on core–shell PbS-CdS quantum dots with inverted device structure. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8551–8555.
Anikeeva, P. O.; Halpert, J. E.; Bawendi, M. G.; Bulovic, V. Quantum dot light-emitting devices with electroluminescence tunable over the entire visible spectrum. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2532–2536.
Moreels, I.; Justo, Y.; de Geyter, B.; Haustraete, K.; Martins, J. C.; Hens, Z. Size-tunable, bright, and stable PbS quantum dots: A surface chemistry study. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2004–2012.
Steckel, J. S.; Ho, J.; Hamilton, C.; Xi, J. Q.; Breen, C.; Liu, W. H.; Allen, P.; Coe-Sullivan, S. Quantum dots: The ultimate down-conversion material for LCD displays. J. Soc. Inf. Display 2015, 23, 294–305.
Shirasaki, Y.; Supran, G. J.; Bawendi, M. G.; Bulovic, V. Emergence of colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting technologies. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 13–23.
Yang, Y. X.; Zheng, Y.; Cao, W. R.; Titov, A.; Hyvonen, J.; Manders, J. R.; Xue, J. G.; Holloway, P. H.; Qian, L. Highefficiency light-emitting devices based on quantum dots with tailored nanostructures. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 259–266.
Lee, K. H.; Han, C. Y.; Kang, H. D.; Ko, H.; Lee, C.; Lee, J.; Myoung, N.; Yim, S. Y.; Yang, H. Highly efficient, color-reproducible full-color electroluminescent devices based on red/green/blue quantum dot-mixed multilayer. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 10941–10949.
Han, J.; Bong, J.; Lim, T.; Lee, K. H.; Yang, H.; Ju, S. Water repellent spray-type encapsulation of quantum dot light-emitting diodes using super-hydrophobic self-assembled nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 353, 338–341.
Qian, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, J. G.; Holloway, P. H. Stable and efficient quantum-dot light-emitting diodes based on solution-processed multilayer structures. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 543–548.
Bae, W. K.; Park, Y. S.; Lim, J.; Lee, D.; Padilha, L. A.; McDaniel, H.; Robel, I.; Lee, C.; Pietryga, J. M.; Klimov, V. I. Controlling the influence of auger recombination on the performance of quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2661.
Caruge, J. M.; Halpert, J. E.; Wood, V.; Bulovic, V.; Bawendi, M. G. Colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with metal-oxide charge transport layers. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 247–250.
Anikeeva, P. O.; Halpert, J. E.; Bawendi, M. G.; Bulovic, V. Electroluminescence from a mixed red-green-blue colloidal quantum dot monolayer. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2196–2200.
Kim, T. H.; Cho, K. S.; Lee, E. K.; Lee, S. J.; Chae, J.; Kim, J. W.; Kim, D. H.; Kwon, J. Y.; Amaratunga, G.; Lee, S. Y. et al. Full-colour quantum dot displays fabricated by transfer printing. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 176–182.
Wood, V.; Panzer, M. J.; Chen, J. L.; Bradley, M. S.; Halpert, J. E.; Bawendi, M. G.; Bulovic, V. Inkjet-printed quantum dot-polymer composites for full-color ac-driven displays. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2151–2155.
Kim, K.; Woo, J. Y.; Jeong, S.; Han, C. S. Photoenhancement of a quantum dot nanocomposite via uv annealing and its application to white leds. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 911–914.
Bae, W. K.; Char, K.; Hur, H.; Lee, S. Single-step synthesis of quantum dots with chemical composition gradients. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 531–539.
Rurack, K.; Spieles, M. Fluorescence quantum yields of a series of red and near-infrared dyes emitting at 600–1,000 nm. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 1232–1242.
Bender, V. C.; Marchesan, T. B.; Alonso, J. M. Solid-state lighting: A concise review of the state of the art on led and oled modeling. IEEE Ind. Electronics Mag. 2015, 9, 6–16.
Chen, H. T.; Hui, S. Y. Dynamic prediction of correlated color temperature and color rendering index of phosphor-coated white light-emitting diodes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electronics 2014, 61, 784–797.
Shimizu, K. T.; Woo, W. K.; Fisher, B. R.; Eisler, H. J.; Bawendi, M. G. Surface-enhanced emission from single semiconductor nanocrystals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 117401.
Murase, S.; Yang, Y. Solution processed moo3 interfacial layer for organic photovoltaics prepared by a facile synthesis method. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2459–2462.
Cho, A.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Cho, W.; Park, C.; Kim, F. S.; Kim, J. H. Influence of imidazole-based acidity control of PEDOT:PSS on its electrical properties and environmental stability. J. Polym. Sci. B: Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 1530–1536.
Jasieniak, J. J.; Seifter, J.; Jo, J.; Mates, T.; Heeger, A. J. A solution-processed MoOx anode interlayer for use within organic photovoltaic devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2594–2605.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by MINECO of Spain (No. MAT2016-76892-C3-1-R) and by Generalitat Valenciana (No. PROMETEOII/2014/020). B. C. H. is grateful to the support of the National Council of Technological and Scientific Development (CNPq), Brazil, through the Science without Borders program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hames, B.C., Mora-Seró, I. & Sánchez, R.S. Device performance and light characteristics stability of quantum-dot-based white-light-emitting diodes. Nano Res. 11, 1575–1588 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1773-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1773-2