Abstract
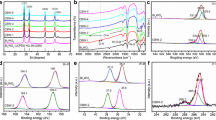
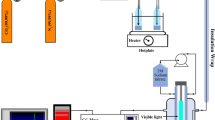
The photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to energy-rich hydrocarbon fuels is a promising and sustainable method of addressing global warming and the imminent energy crisis concomitantly. However, a vast majority of the existing photocatalysts are only capable of harnessing ultraviolet (UV) or/and visible light (Vis), whereas the near-infrared (NIR) region still remains unexplored. In this study, carbon quantum dots (CQDs)-decorated ultrathin Bi2WO6 nanosheets (UBW) were demonstrated to be an efficient photocatalyst for CO2 photoreduction over the Vis–NIR broad spectrum. It is noteworthy that the synthesis procedure of the CQDs/UBW hybrid nanocomposites was highly facile, involving a one-pot hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB)-assisted hydrothermal process. Under visible light irradiation, the optimized 1CQDs/UBW (1 wt.% CQD content) exhibited a remarkable 9.5-fold and 3.1-fold enhancement of CH4 production over pristine Bi2WO6 nanoplatelets (PBW) and bare UBW, respectively. More importantly, the photocatalytic responsiveness of CQDs/UBW was successfully extended to the NIR region, which was achieved without involving any rare earth or noble metals. The realization of NIR-driven CO2 reduction could be attributed to the synergistic effects of (i) the ultrathin nanostructures and highly exposed {001} active facets of UBW, (ii) the excellent spectral coupling of UBW and CQDs, where UBW could be excited by the up-converted photoluminescence of CQDs, and (iii) the electron-withdrawing nature of the CQDs to trap the photogenerated electrons and retard the recombination of charge carriers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
White, J. L.; Baruch, M. F.; Pander, J. E., III; Hu, Y.; Fortmeyer, I. C.; Park, J. E.; Zhang, T.; Liao, K.; Gu, J.; Yan, Y. et al. Light-driven heterogeneous reduction of carbon dioxide: Photocatalysts and photoelectrodes. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12888–12935.
Tu, W. G.; Zhou, Y.; Zou, Z. G. Photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuels: State-of-the-art accomplishment, challenges, and prospects. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 4607–4626.
Li, K.; Peng, B. S.; Peng, T. Y. Recent advances in heterogeneous photocatalytic CO2 conversion to solar fuels. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 7485–7527.
Inoue, T.; Fujishima, A.; Konishi, S.; Honda, K. Photoelectrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide in aqueous suspensions of semiconductor powders. Nature 1979, 277, 637–638.
Wang, W. J.; Li, Y. C.; Kang, Z. W.; Wang, F.; Yu, J. C. A NIR-driven photocatalyst based on α-NaYF4:Yb, Tm@TiO2 core–shell structure supported on reduced graphene oxide. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 182, 184–192.
Tou, M. J.; Mei, Y. Y.; Bai, S.; Luo, Z. G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Q. Depositing CdS nanoclusters on carbon-modified NaYF4:Yb,Tm upconversion nanocrystals for NIR-light enhanced photocatalysis. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 553–562.
Tang, Y. N.; Di, W. H.; Zhai, X. S.; Yang, R. Y.; Qin, W. P. NIR-responsive photocatalytic activity and mechanism of NaYF4:Yb,Tm@TiO2 core−shell nanoparticles. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 405–412.
Zheng, Z. K.; Tachikawa, T.; Majima, T. Single-particle study of Pt-modified Au nanorods for plasmon-enhanced hydrogen generation in visible to near-infrared region. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6870–6873.
Chen, C. K.; Chen, H. M.; Chen, C.-J.; Liu, R.-S. Plasmonenhanced near-infrared-active materials in photoelectrochemical water splitting. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7917–7919.
Li, H. T.; Liu, R. H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Yu, H.; Ming, H.; Lian, S. Y.; Lee, S.-T.; Kang, Z. H. Carbon quantum dots/Cu2O composites with protruding nanostructures and their highly efficient (near) infrared photocatalytic behavior. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17470–17475.
Lim, S. Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Q. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381.
Li, H. T.; Kang, Z. H.; Liu, Y.; Lee, S. T. Carbon nanodots: Synthesis, properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24230–24253.
Yu, H. J.; Shi, R.; Zhao, Y. F.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Wu, L.-Z.; Tung, C.-H.; Zhang T. R. Smart utilization of carbon dots in semiconductor photocatalysis. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9454–9477.
Liu, Q.; Chen, T. X.; Guo, Y. R.; Zhang, Z. G.; Fang, X. M. Environmental ultrathin g-C3N4 nanosheets coupled with carbon nanodots as 2D/0D composites for efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 193, 248–258.
Hou, J. G.; Cheng, H. J.; Yang, C.; Takeda, O.; Zhu, H. M. Hierarchical carbon quantum dots/hydrogenated-γ-TaON heterojunctions for broad spectrum photocatalytic performance. Nano Energy 2015, 18, 143–153.
Ge, L.; Han, C. C.; Liu, J. Novel visible light-induced g-C3N4/Bi2WO6 composite photocatalysts for efficient degradation of methyl orange. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 108–109, 100–107.
Zhang, N.; Ciriminna, R.; Pagliaro, M.; Xu, Y.-J. Nanochemistry-derived Bi2WO6 nanostructures: Towards production of sustainable chemicals and fuels induced by visible light. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5276–5287.
Zhou, Y.; Tian, Z. P.; Zhao, Z. Y.; Liu, Q.; Kou, J. H.; Chen, X. Y.; Gao, J.; Yan, S. C.; Zou, Z. G. High-yield synthesis of ultrathin and uniform Bi2WO6 square nanoplates benefitting from photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuel under visible light. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3594–3601.
Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. G.; Wu, Q. S. High {001} facets dominated BiOBr lamellas: Facile hydrolysis preparation and selective visible-light photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 8622–8629.
Zhang, M.; Sun, R. Z.; Li, Y. J.; Shi, Q. M.; Xie, L. H.; Chen, J. S.; Xu, X. H.; Shi, H. X.; Zhao, W. R. High H2 evolution from quantum Cu(II) nanodot-doped two-dimensional ultrathin TiO2 nanosheets with dominant exposed {001} facets for reforming glycerol with multiple electron transport pathways. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 10746–10756.
Kong, X. Y.; Lee, W. P. C.; Ong, W.-J.; Chai, S.-P.; Mohamed, A. R. Oxygen-deficient BiOBr as a highly stable photocatalyst for efficient CO2 reduction into renewable carbon-neutral fuels. ChemCatChem 2016, 8, 3074–3081.
Kong, X. Y.; Choo, Y. Y.; Chai, S.-P.; Soh, A. K.; Mohamed, A. R. Oxygen vacancy induced Bi2WO6 for the realization of photocatalytic CO2 reduction over the full solar spectrum: From the UV to the NIR region. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 14242–14245.
Ong, W.-J.; Tan, L.-L.; Chai, S.-P.; Yong, S.-T.; Mohamed, A. R. Surface charge modification via protonation of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) for electrostatic self-assembly construction of 2D/2D reduced graphene oxide (rGO)/g-C3N4 nanostructures toward enhanced photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to methane. Nano Energy 2015, 13, 757–770.
Tan, L.-L.; Ong, W.-J.; Chai, S.-P.; Goh, B. T.; Mohamed, A. R. Visible-light-active oxygen-rich TiO2 decorated 2D graphene oxide with enhanced photocatalytic activity toward carbon dioxide reduction. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 179, 160–170.
Ong, W.-J.; Tan, L.-L.; Chai, S.-P.; Yong, S.-T.; Mohamed, A. R. Self-assembly of nitrogen-doped TiO2 with exposed {001} facets on a graphene scaffold as photo-active hybrid nanostructures for reduction of carbon dioxide to methane. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1528–1547.
Zhang, G.; Hu, Z. Y.; Sun, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L. M.; Liu, H. J.; Huang, C. P.; Qu, J. H.; Li, J. H. Formation of Bi2WO6 bipyramids with vacancy pairs for enhanced solar-driven photoactivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3726–3734.
Di, J.; Xia, J. X.; Ge, Y. P.; Li, H. P.; Ji, H. Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H. M.; Li, M. N. Novel visible-light-driven CQDs/Bi2WO6 hybrid materials with enhanced photocatalytic activity toward organic pollutants degradation and mechanism insight. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 168–169, 51–61.
Sun, Z. H.; Guo, J. J.; Zhu, S. M.; Mao, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D. A high-performance Bi2WO6–graphene photocatalyst for visible light-induced H2 and O2 generation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 2186–2193.
Di, J.; Xia, J. X.; Ji, M. X.; Wang, B.; Yin, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z. G.; Li, H. M. Carbon quantum dots modified BiOCl ultrathin nanosheets with enhanced molecular oxygen activation ability for broad spectrum photocatalytic properties and mechanism insight. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20111–20123.
Liu, C. M.; Liu, J. W.; Zhang, G. Y.; Zhang, J. B.; Wu, Q. S.; Xu, Y. Y.; Sun, Y.-Q. Facile room-temperature precipitation strategy for Ag2O/Bi2WO6 heterojunction with high simulated sunlight photocatalytic performance via bi-directed electron migration mechanism. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32333–32342.
Pan, D. Y.; Zhang, J. C.; Li, Z.; Wu, C.; Yan, X. M.; Wu, M. H. Observation of pH-, solvent-, spin-, and excitationdependent blue photoluminescence from carbon nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3681–3683.
Xia, X. Y.; Deng, N.; Cui, G. W.; Xie, J. F.; Shi, X. F.; Zhao, Y. Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Tang, B. NIR light induced H2 evolution by a metal-free photocatalyst. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10899–10902.
Ortega-Liebana, M. C.; Hueso, J. L.; Larrea, A.; Sebastian, V.; Santamaria, J. Feroxyhyte nanoflakes coupled to up-converting carbon nanodots: A highly active, magnetically recoverable, Fenton-like photocatalyst in the visible-NIR range. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16625–166288.
Li, H. P.; Liu, J. Y.; Liang, X. F.; Hou, W. G.; Tao, X. T. Enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of bismuth oxybromide lamellas with decreasing lamella thicknesses. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8926–8932.
Acknowledgements
The work was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) Malaysia and Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) under NanoMITe Long-term Research Grant Scheme (LRGS) (No. 203/PJKIMIA/6720009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2017_1435_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Harnessing Vis–NIR broad spectrum for photocatalytic CO2 reduction over carbon quantum dots-decorated ultrathin Bi2WO6 nanosheets
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, X.Y., Tan, W.L., Ng, BJ. et al. Harnessing Vis–NIR broad spectrum for photocatalytic CO2 reduction over carbon quantum dots-decorated ultrathin Bi2WO6 nanosheets. Nano Res. 10, 1720–1731 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1435-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1435-4