Abstract
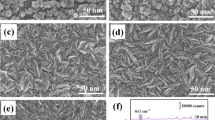
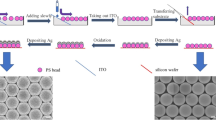
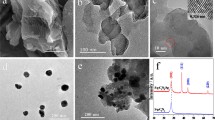
The surface topography of noble metal particles is a significant factor in tailoring surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) properties. Here, we present a simple fabrication route to hexagonally arranged arrays of surface-roughened urchinlike Ag hemispheres (Ag-HSs) decorated with Ag nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) for highly active and reproducible SERS substrates. The urchin-like Ag-HS arrays are achieved by sputtering Ag onto the top surface of a highly ordered porous anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) template to form ordered arrays of smooth Ag-HSs and then by electrodepositing Ag-NPs onto the surface of each Ag-HS. Owing to the ordered arrangement of the Ag-HSs and the improved surface roughness, the urchin-like hierarchical Ag-HS arrays can provide sufficient and uniform “hot spots” for reproducible and highly active SERS effects. Using the urchin-like Ag-HS arrays as SERS substrates, 10−7 M dibutyl phthalate (a member of plasticizers family) and 1.5 × 10−5 M PCB-77 (one congener of polychlorinated biphenyl, a notorious class of pollutants) are identified, showing promising potential for these substrates in the rapid recognition of organic pollutants.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ling, X. Y.; Yan, R. X.; Lo, S.; Hoang, D. T.; Liu, C.; Fardy, M. A.; Khan, S. B.; Asiri, A. M.; Bawaked, S. M.; Yang, P. D. Alumina-coated Ag nanocrystal monolayers as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy platforms for the direct spectroscopic detection of water splitting reaction intermediates. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 132–143.
Schlücker, S. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: Concepts and chemical applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 4756–4795.
Nima, Z. A.; Mahmood, M.; Xu, Y.; Mustafa, T.; Watanabe, F.; Nedosekin, D. A.; Juratli, M. A.; Fahmi, T.; Galanzha, E. I. et al. Circulating tumor cell identification by functionalized silver-gold nanorods with multicolor, super-enhanced SERS and photothermal resonances. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4752.
Huang, Z. L.; Meng, G. W.; Huang, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhou, F.; Hu, X. Y.; Qian, Y. W.; Tang, H. B.; Han, F. M.; Chu, Z. Q. Polyacrylic acid sodium salt film entrapped Ag-nanocubes as molecule traps for SERS detection. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 1177–1187.
You, H. J.; Ji, Y. T.; Wang, L.; Yang, S. C.; Yang, Z. M.; Fang, J. X.; Song, X. P.; Ding, B. J. Interface synthesis of gold mesocrystals with highly roughened surfaces for surfaceenhanced Raman spectroscopy. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1998–2006.
Fang, J. X.; Du, S. Y.; Lebedkin, S.; Li, Z. Y.; Kruk, R.; Kappes, M.; Hahn, H. Gold mesostructures with tailored surface topography and their self-assembly arrays for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 5006–5013.
Pechárroman, C.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Mata-Osoro, G.; Liz-Marzán, L. M.; Mulvaney, P. Redshift of surface plasmon modes of small gold rods due to their atomic roughness and end-cap geometry. Phys. Rev. B 2008, 77, 035418.
Rodríguez-Fernández, J.; Funston, A. M.; Perez-Juste, J.; álvarez-Puebla, R. A.; Liz-Marzán, L. M.; Mulvaney, P. The effect of surface roughness on the plasmonic response of individual sub-micron gold spheres. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 5909–5914.
Bakr, O. M.; Wunsch, B. H.; Stellacci, F. High-yield synthesis of multi-branched urchin-like gold nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 3297–3301.
Wang, H.; Halas, N. J. Mesoscopic Au “meatball” particles. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 820–825.
Liang, H. Y.; Li, Z. P.; Wang, W. Z.; Wu, Y. S.; Xu, H. X. Highly surface-roughened “flower-like” silver nanoparticles for extremely sensitive substrates of surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4614–4618.
Huang, P.; Pandoli, O.; Wang, X. S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z. M.; Zhang, C. L.; Chen, F.; Lin, J.; Cui, D. X.; Chen, X. Y. Chiral guanosine 5’-monophosphate-capped gold nanoflowers: Controllable synthesis, characterization, surface-enhanced Raman scattering activity, cellular imaging and photothermal therapy. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 630–639.
Mulvihill, M. J.; Ling, X. Y.; Henzie, J.; Yang, P. Anisotropic etching of silver nanoparticles for plasmonic structures capable of single-particle SERS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 268–274.
Tang, H. B.; Meng, G. W.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, C. H.; Huang, Z. L.; Li, Z. B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Urchin-like Aunanoparticles@ Ag-nanohemisphere arrays as active SERSsubstrates for recognition of PCBs. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 19654–19657.
Wang, J.; Huang, L. Q.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, L. H.; Feng, X. H.; Zhang, W. W.; Zhai, L. P.; Zhu, J. Silver nanostructure arrays abundant in sub-5nm gaps as highly Raman-enhancing substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3519–3523.
Jaakkola, J. J. K.; Ieromnimon, A.; Jaakkola, M. S. Interior surface materials and asthma in adults: A population-based incident case-control study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 742–749.
Yanagisawa, R.; Takano, H.; Inoue, K. I.; Koike, E.; Sadakane, K.; Ichinose, T. Effects of maternal exposure to di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate during fetal and/or neonatal periods on atopic dermatitis in male offspring. Environ. Health Persp. 2008, 116, 1136–1141.
Kolarik, B.; Naydenov, K.; Larsson, M.; Bornehag, C. G.; Sundell, J. The association between phthalates in dust and allergic diseases among bulgarian children. Environ. Health Persp. 2008, 116, 98–103.
Zheng, T. Z.; Holford, T. R.; Tessari, J.; Mayne, S. T.; Owens, P. H.; Ward, B.; Carter, D.; Boyle, P.; Dubrow, R.; Archibeque-Engle, S. et al. Breast cancer risk associated with congeners of polychlorinated biphenyls. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 152, 50–58.
Rylander, L.; Strömberg, U.; Dyremark, E.; Östman, C.; Nilsson-Ehle, P.; Hagmar, L. Polychlorinated biphenyls in blood plasma among swedish female fish consumers in relation to low birth weight. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 147, 493–502.
Daniels, J. L.; Longnecker, M. P.; Klebanoff, M. A.; Gray, K. A.; Brock, J. W.; Zhou, H. B.; Chen, Z.; Needham, L. L. Prenatal exposure to low-level polychlorinated biphenyls in relation to mental and motor development at 8 months. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 157, 485–492.
Zhou, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ni, J. E.; Li, Z. C.; Zhang, Z. J. Rapid recognition of isomers of monochlorobiphenyls at trace levels by surface-enhanced Raman scattering using Ag nanorods as a substrate. Nano Res. 2010, 3, 423–428.
Li, Y. B.; Zheng, M. J.; Ma, L.; Shen, W. Z. Fabrication of highly ordered nanoporous alumina films by stable highfield anodization. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 5101.
Choi, J.; Luo, Y.; Wehrspohn, R. B.; Hillebrand, R.; Schilling, J.; Gösele, U. Perfect two-dimensional porous alumina photonic crystals with duplex oxide layers. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 4757–4762.
Nielsch, K.; Choi, J.; Schwirn, K.; Wehrspohn, R. B.; Gösele, U. Self-ordering regimes of porous alumina: The 10 porosity rule. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 677–680.
Li, Z. B.; Meng, G. W.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, C. H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. D. Galvanic-cell-induced growth of Ag nanosheetassembled structures as sensitive and reproducible SERS substrates. Chem.—Eur. J. 2012, 18, 14948–14953.
Qian, Y. W.; Meng, G. W.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, C. H.; Huang, Z. L.; Sun, K. X.; Chen, B. Flexible membranes of Agnanosheet grafted polyamide-nanofibers as effective 3D SERS substrates. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 4781–4788.
Duan, G. T.; Cai, W. P.; Luo, Y. Y.; Li, Y.; Lei, Y. Hierarchical surface rough ordered Au particle arrays and their surface enhanced Raman scattering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 181918.
Zhang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W. P.; Shen, L.; Li, Z. C.; Zhang, Z. J. Latticing vertically aligned Ag nanorods to enhance its SERS sensitivity. Mater. Res. Bull. 2012, 47, 921–924.
Zhang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ni, J.; Li, Z. C.; Zhang, Z. J. Surfaceenhanced Raman scattering from a hexagonal lattice of micro-patterns of vertically aligned Ag nanorods. Physica E 2011, 44, 460–463.
Cai, Q.; Lu, S. K.; Liao, F.; Li, Y. Q.; Ma, S. Z.; Shao, M. W. Catalytic degradation of dye molecules and in situ SERS monitoring by peroxidase-like Au/CuS composite. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8117–8123.
Lee, J.; Seo, J.; Kim, D.; Shin, S.; Lee, S.; Mahata, C.; Lee, H. S.; Min, B. W.; Lee, T. Capillary force-induced glue-free printing of Ag nanoparticle arrays for highly sensitive SERS substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 9053–9060.
Huang, G. L.; Sun, H. W.; Song, Z. H. Interactions between dibutyl phthalate and aquatic organisms. B. Environ. Contam. Tox. 1999, 63, 759–765.
Mylchreest, E.; Cattley, R. C.; Foster, P. M. D. Male reproductive tract malformations in rats following gestational and lactational exposure to di(n-butyl) phthalate: An antiandrogenic mechanism? Toxicol. Sci. 1998, 43, 47–60.
Huang, Z. L.; Meng, G. W.; Huang, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhu, C. H.; Zhang, Z. Large-area Ag nanorod array substrates for SERS: AAO template-assisted fabrication, functionalization, and application in detection PCBs. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 240–246.
Hou, C.; Meng, G. W.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, C. H.; Huang, Z. L.; Chen, B.; Sun, K. X. Ag-nanoparticle-decorated Au-fractal patterns on bowl-like-dimple arrays on Al foil as an effective SERS substrate for the rapid detection of PCBs. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 569–571.
Chen, B.; Meng, G. W.; Huang, Q.; Huang, Z. L.; Xu, Q. L.; Zhu, C. H.; Qian, Y. W.; Ding, Y. Green synthesis of largescale highly ordered core@shell nanoporous Au@Ag nanorod arrays as sensitive and reproducible 3D SERS substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2014, 6, 15667–15675.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, H., Meng, G., Li, Z. et al. Hexagonally arranged arrays of urchin-like Ag hemispheres decorated with Ag nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates. Nano Res. 8, 2261–2270 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0737-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0737-7