Abstract
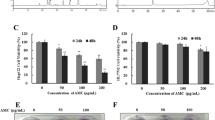
Ginseng’s major active components, ginsenosides, have been known to show anti-cancer, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory activities. Ultrasonication processed Panax ginseng berry extract (UGB) contains various ginsenosides. The components are different from Panax ginseng berry extract (GBE). This study was aimed to investigate the cytotoxic mechanism of UGB in HepG2 cells, human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. HepG2 cells were treated with UGB (0, 10, 20 μg/ml). Cell growth and cellular apoptosis were evaluated by MTT assay and Annexin V/Pi staining, respectively. Intracellular Reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were also determined by 2′, 7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate (DCFDA) staining. The expressions of Bax, Bcl-2 and caspase-3, the apoptotic markers, were evaluated by Western Blot. UGB dose-dependently inhibited cell growth and induced apoptotic cell death. Intracellular ROS levels were increased. UGB increased the expression of the cleaved form of caspase-3. Furthermore, UGB induced apoptosis of HepG2 cells through Bax activation and Bcl-2 inhibition. In conclusion, UGB induced apoptosis through an intrinsic pathway in HepG2 cells suggesting that UGB might play a role as a novel substance for anti-cancer effect.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boxer LA, Harris RE, Baehner RL (1979) Regulation of membrane peroxidation in health and disease. Pediatrics 64:713–718
Chen B, Shen YP, Zhang DF, Cheng J, Jia XB (2013) The apoptosis-inducing effect of ginsenoside F4 from steamed notoginseng on human lymphocytoma JK cells. Nat Prod Res 27:2351–2354
Choi K, Yoon J, Lim HK, Ryoo S (2014) Korean red ginseng water extract restores impaired endothelial function by inhibiting arginase activity in aged mice. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 18:95–101
Debatin KM, Krammer PH (2004) Death receptors in chemotherapy and cancer. Oncogene 23:2950–2966
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516
Elrod HA, Sun SY (2008) PPARgamma and apoptosis in cancer. PPAR Res 2008:704165
Fadeel B, Orrenius S (2005) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in human disease. J Intern Med 258:479–517
Fuchs Y, Steller H (2011) Programmed cell death in animal development and disease. Cell 147:742–758
Gross A, Jockel J, Wei MC, Korsmeyer SJ (1998) Enforced dimerization of BAX results in its translocation, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. EMBO J 17:3878–3885
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:770–776
Hsu YT, Wolter KG, Youle RJ (1997) Cytosol-to-membrane redistribution of Bax and Bcl-X(L) during apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:3668–3672
Kim YS, Jin SH (2004) Ginsenoside Rh2 induces apoptosis via activation of caspase-1 and -3 and up-regulation of Bax in human neuroblastoma. Arch Pharm Res 27:834–839
Kim YS, Jin SH, Lee YH, Kim SI, Park JD (1999) Ginsenoside Rh2 induces apoptosis independently of Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, or Bax in C6Bu-1 cells. Arch Pharm Res 22:448–453
Kim HJ, Mun JY, Chun YJ, Choi KH, Ham SW, Kim MY (2003) Effects of a naphthoquinone analog on tumor growth and apoptosis induction. Arch Pharm Res 26:405–410
Kim YJ, Kwon HC, Ko H, Park JH, Kim HY, Yoo JH, Yang HO (2008) Anti-tumor activity of the ginsenoside Rk1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through inhibition of telomerase activity and induction of apoptosis. Biol Pharm Bull 31:826–830
Leung KW, Yung KK, Mak NK, Chan YS, Fan TP, Wong RN (2007) Neuroprotective effects of ginsenoside-Rg1 in primary nigral neurons against rotenone toxicity. Neuropharmacology 52:827–835
Li D, Ueta E, Kimura T, Yamamoto T, Osaki T (2004) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) control the expression of Bcl-2 family proteins by regulating their phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Cancer Sci 95:644–650
Li N, Liu B, Dluzen DE, Jin Y (2007) Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg2 against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. J Ethnopharmacol 111:458–463
Lim HJ, Lee HY, Lim DY (2014) Inhibitory effects of ginsenoside-rb2 on nicotinic stimulation-evoked catecholamine secretion. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 18:431–439
Mao Z, Xia W, Wang J, Chen T, Zeng Q, Xu B, Li W, Chen X, Xu S (2013) Perfluorooctane sulfonate induces apoptosis in lung cancer A549 cells through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrion-dependent pathway. J Appl Toxicol 33:1268–1276
Martinou JC, Youle RJ (2011) Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell 21:92–101
Nechushtan A, Smith CL, Hsu YT, Youle RJ (1999) Conformation of the Bax C-terminus regulates subcellular location and cell death. EMBO J 18:2330–2341
Oh GS, Pae HO, Choi BM, Seo EA, Kim DH, Shin MK, Kim JD, Kim JB, Chung HT (2004) 20(S)-Protopanaxatriol, one of ginsenoside metabolites, inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expressions through inactivation of nuclear factor-kappaB in RAW 264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Cancer Lett 205:23–29
Ola MS, Nawaz M, Ahsan H (2011) Role of Bcl-2 family proteins and caspases in the regulation of apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 351:41–58
Park EK, Choo MK, Han MJ, Kim DH (2004) Ginsenoside Rh1 possesses antiallergic and anti-inflammatory activities. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 133:113–120
Park MY, Jeong YJ, Kang GC, Kim MH, Kim SH, Chung HJ, Jung JY, Kim WJ (2014) Nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of human dental pulp cells is mediated by the mitochondria-dependent pathway. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 18:25–32
Porter AG, Janicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:99–104
Shroff EH, Snyder C, Chandel NS (2007) Role of Bcl-2 family members in anoxia induced cell death. Cell Cycle 6:807–809
Shuangyan W, Ruowu S, Hongli N, Bei Z, Yong S (2012) Protective effects of Rg2 on hypoxia-induced neuronal damage in hippocampal neurons. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol 40:142–145
Steller H (1995) Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science 267:1445–1449
Sun HQ, Zhou ZY (2010) Effect of ginsenoside-Rg3 on the expression of VEGF and TNF-alpha in retina with diabetic rats. Int J Ophthalmol 3:220–223
Tode T, Kikuchi Y, Hirata J, Kita T, Imaizumi E, Nagata I (1993) Inhibitory effects of oral administration of ginsenoside Rh2 on tumor growth in nude mice bearing serous cyst adenocarcinoma of the human ovary. Nihon Sanka Fujinka Gakkai Zasshi 45:1275–1282
Victor VM, Rocha M, De la Fuente M (2004) Immune cells: free radicals and antioxidants in sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol 4:327–347
Wei X, Su F, Su X, Hu T, Hu S (2012) Stereospecific antioxidant effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on oxidative stress induced by cyclophosphamide in mice. Fitoterapia 83:636–642
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A, Xi XG, Youle RJ (1997) Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 139:1281–1292
Xu TM, Cui MH, Xin Y, Gu LP, Jiang X, Su MM, Wang DD, Wang WJ (2008) Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rg3 on ovarian cancer metastasis. Chin Med J (Engl) 121:1394–1397
Zhang G, Liu A, Zhou Y, San X, Jin T, Jin Y (2008) Panax ginseng ginsenoside-Rg2 protects memory impairment via anti-apoptosis in a rat model with vascular dementia. J Ethnopharmacol 115:441–448
Zhang C, Liu L, Yu Y, Chen B, Tang C, Li X (2012) Antitumor effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Mol Med Rep 5:1295–1298
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by High Value-added Food Technology Development program, Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (113021-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, H., Bae, J., Ko, S.K. et al. Ultrasonication processed Panax ginseng berry extract induces apoptosis through an intrinsic apoptosis pathway in HepG2 cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 39, 855–862 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0760-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0760-6