Abstract
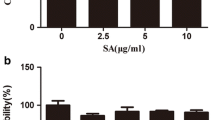
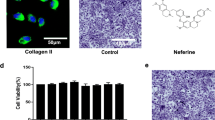
Matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) plays a critical role in degrading major collagens in human cartilage under some pathological conditions such as osteoarthritis. To establish the therapeutic potential against cartilage degradation, the effects of 12 naturally-occurring triterpenoids and steroids on MMP-13 induction were examined in the human chondrocyte cell line, SW1353. They included coreanoside F1, suavissimoside R1, spicatoside A, 25(S)-ruscogenin, methyl protogracillin, hederagenin, loniceroside A, loniceroside B, loniceroside C, smilaxin A, smilaxin C, and ursolic acid. Among these, only spicatoside A and 25(S)-ruscogenin were found to inhibit MMP-13 expression in IL-1β-treated SW1353 cells at a pharmacologically-relevant concentration of 10 μM. These effects were also supported by the finding that spicatoside A (20 μM) reduced glycosaminoglycan release from IL-1α-treated rabbit joint cartilage culture to some degree. When the cellular mechanisms of action of spicatoside A in MMP-13 inhibition were investigated, the blocking point was not found among the MMP-13 signaling molecules examined such as mitogen-activated protein kinases, activator protein-1, and nuclear transcription factor-κB. Instead, spicatoside A was found to reduce MMP-13 mRNA stability. All of these findings suggest that spicatoside A and 25(S)-ruscogenin have a therapeutic potential for protecting against cartilage breakdown in arthritic disorders.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S., N. Wang, M. Lalonde, V.M. Goldberg, and T.M. Haqqi. 2004. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) differentially inhibits interleukin-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -13 in human chondrocytes. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 308: 767–773.
Caton, J., and M.E. Ryan. 2011. Clinical studies on the management of periodontal diseases utilizing subantimicrobial dose doxycycline (SDD). Pharmacological Research 63: 114–120.
Corps, A.N., V.A. Curry, D.J. Buttle, B.L. Hazleman, and G.P. Riley. 2004. Inhibition of interleukin-1-stimulated collagenase and stromelysin expression in human tendon fibroblasts by epigallocatechin gallate ester. Matrix Biology 23: 163–169.
Hadler-Olsen, E., B. Fadnes, I. Sylte, L. Uhlin-Hansen, and J.O. Winberg. 2011. Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase activity in health and disease. FEBS Journal 278: 28–45.
Hur, J., P. Lee, E. Moon, I. Kang, S.H. Kim, M.S. Oh, and S.Y. Kim. 2009. Neurite outgrowth induced by spicatoside A, a steroidal saponin, via the tyrosine kinase A receptor pathway. European Journal of Pharmacology 620: 9–15.
Kim, S.Y., K.H. Son, H.W. Chang, S.S. Kang, and H.P. Kim. 1999. Inhibition of mouse ear edema by steroidal and triterpenoid saponins. Archives of Pharmacal Research 22: 313–316.
Kwak, W.J., C.K. Han, H.W. Chang, H.P. Kim, S.S. Kang, and K.H. Son. 2003. Loniceroside C, an anti-inflammatory saponin from Lonicera japonica. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 51: 333–335.
Kwon, G., H.E. Lee, D.H. Lee, H. Woo, S.J. Park, Q. Gao, Y.J. Ahn, K.H. Son, and J.H. Ryu. 2014. Spicatoside A enhances memory consolidation through the brain-derived neurotrophic factor in mice. Neuroscience Letters 572: 58–62.
Lee, J.H., H. Lim, O. Shehzad, Y.S. Kim, and H.P. Kim. 2014. Ginsenosides from Korean red ginseng inhibit matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in articular chondrocytes and prevent cartilage degradation. European Journal of Pharmacology 724: 145–151.
Lee, Y.C., J.C. Lee, Y.B. Seo, and Y.B. Kook. 2005. Liriopis tuber inhibit OVA-induced airway inflammation and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in murine model of asthma. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 101: 144–152.
Lim, H., and H.P. Kim. 2011. Matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in IL-1β-treated chondrocytes by activation of the p38 MAPK/c-Fos/AP-1 and JAK/STAT pathways. Archives of Pharmacal Research 34: 109–117.
Lim, H., H. Park, and H.P. Kim. 2011. Effects of flavonoids on matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression of interleukin-1-treated articular chondrocytes and their cellular mechanisms: Inhibition of c-Fos/AP-1 and JAK/STAT signaling pathways. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 116: 221–231.
Little, C.B., A. Barai, D. Burkhardt, S.M. Smith, A.J. Fosang, Z. Werb, M. Shah, and E.W. Thopson. 2009. Matrix metalloproteinase 13-deficient mice are resistant to osteoarthritic cartilage erosion but not chondrocyte hypertrophy or osteophyte development. Arthritis and Rheumatism 60: 3723–3733.
Mengshol, J.A., M.P. Vincent, C.I. Coon, A. Barchowsky, and C.E. Brinckehoff. 2000. Interleukin-1 induction of collagenase 3 (matrix metalloproteinase-13) gene expression in chondrocytes requires p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and nuclear factor κB: Differential regulation of collagenase a and collagenase 3. Arthritis and Rheumatism 43: 801–811.
Mitchell, P.G., H.A. Magna, L.M. Reeves, L.L. Lopresti-Morrow, S.A. Yocum, P.J. Rosner, K.F. Geoghegan, and J.E. Hambor. 1996. Cloning, expression, and type II collagenolytic activity of matrix metalloproteinase-13 from human osteoarthritic cartilage. Journal of Clinical Investigation 97: 761–768.
Mossman, T. 1983. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxic assays. Journal of Immunological Methods 65: 55–56.
Park, H.Y., H. Lim, H.P. Kim, and Y.S. Kwon. 2011. Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-13 by the root extract of Cyathula officinalis Kuan and its constituents in IL-1β-treated chondrocytes. Planta Medica 77: 1528–1530.
Park, S.H., H.J. Lee, J. Ryu, K.H. Son, S.Y. Kwon, S.K. Lee, Y.S. Kim, J.H. Hong, J.H. Seok, and C.J. Lee. 2014. Effects of ophiopogonin D and spicatoside A derived from Liriope Tuber on secretion and production of mucin from airway epithelial cells. Phytomedicine 21: 172–176.
Pei, Y., A. Harvey, X.P. Yu, S. Chandrasekhar, and K. Thirunavukkarasu. 2006. Differential regulation of cytokine-induced MMP-1 and MMP-13 expression by p38 kinase inhibitors in human chondrosarcoma cells; potential role of Runx2 in mediating p38 effects. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 14: 749–758.
Takaishi, H., T. Kimura, S. Dalah, Y. Okada, and J. D’Armiento. 2008. Joint disease and matrix metalloproteinases: A role for MMP-13. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 9: 47–54.
Yadav, V.R., S. Prasad, B. Sung, R. Kannappan, and B.B. Aggarwal. 2010. Targeting inflammatory pathways by triterpenoids for prevention and treatment of cancer. Toxins 2: 2428–2466.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by BK21-plus Project from the Korean Ministry of Education. The bioassay facility of New Drug Res. Institute (KNU) was used and greatly acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
The authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, H., Min, D.S., Kang, Y. et al. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in IL-1β-treated articular chondrocytes by a steroidal saponin, spicatoside A, and its cellular mechanisms of action. Arch. Pharm. Res. 38, 1108–1116 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0581-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-015-0581-z