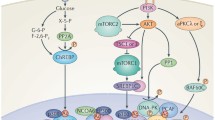
Abstract
Glucose is a primary fuel for generating energy in basic daily activities. Thus, glucose homeostasis is tightly regulated by counter-regulatory hormones such as glucagon, cortisol, and insulin, which affect key organs including liver, skeletal muscle, pancreas, and adipocytes. Among metabolic tissues, liver plays a critical role in controlling glucose production under various hormonal and metabolic cues. Under fasting, acute activation of both glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis is achieved by post-translational modification or allosteric activation of key rate-limiting enzymes, thereby enabling enhanced glucose production from the liver to maintain glucose homeostasis. More prolonged fasting or starvation leads to the chronic activation of gluconeogenesis that requires increased expression of key enzymes in the pathway, which is turned off under feeding conditions by the molecular events that are initiated by insulin. This process is normally achieved by the regulation of gene expression at the level of transcription. Recently, the transcriptional regulators of hepatic gluconeogenesis are considered as potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. In this review, we would like to discuss the current knowledge regarding the key transcriptional activators and inhibitors of hepatic gluconeogenic program to provide the better insight into the control of glycemia in the disease status.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accili, D., and K.C. Arden. 2004. FoxOs at the crossroads of cellular metabolism, differentiation, and transformation. Cell 117: 421–426.
Alberts, A.S., J. Arias, M. Hagiwara, M.R. Montminy, and J.R. Feramisco. 1994. Recombinant cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB) phosphorylated on Ser-133 is transcriptionally active upon its introduction into fibroblast nuclei. Journal of Biological Chemistry 269: 7623–7630.
Altarejos, J.Y., and M. Montminy. 2011. CREB and the CRTC co-activators: sensors for hormonal and metabolic signals. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 12: 141–151.
Aranda, A., and A. Pascual. 2001. Nuclear hormone receptors and gene expression. Physiological Reviews 81: 1269–1304.
Arias, J., A.S. Alberts, P. Brindle, F.X. Claret, T. Smeal, M. Karin, J. Feramisco, and M. Montminy. 1994. Activation of cAMP and mitogen responsive genes relies on a common nuclear factor. Nature 370: 226–229.
Ayala, J.E., R.S. Streeper, J.S. Desgrosellier, S.K. Durham, A. Suwanichkul, C.A. Svitek, J.K. Goldman, F.G. Barr, D.R. Powell, and R.M. O’brien. 1999. Conservation of an insulin response unit between mouse and human glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit gene promoters: transcription factor FKHR binds the insulin response sequence. Diabetes 48: 1885–1889.
Bailey, D., C. Barreca, and P. O’hare. 2007. Trafficking of the bZIP transmembrane transcription factor CREB-H into alternate pathways of ERAD and stress-regulated intramembrane proteolysis. Traffic 8: 1796–1814.
Bailey, D., and P. O’hare. 2007. Transmembrane bZIP transcription factors in ER stress signaling and the unfolded protein response. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 9: 2305–2321.
Bannister, A.J., and T. Kouzarides. 1996. The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature 384: 641–643.
Barthel, A., D. Schmoll, and T.G. Unterman. 2005. FoxO proteins in insulin action and metabolism. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism 16: 183–189.
Bedford, D.C., L.H. Kasper, R. Wang, Y. Chang, D.R. Green, and P.K. Brindle. 2011. Disrupting the CH1 domain structure in the acetyltransferases CBP and p300 results in lean mice with increased metabolic control. Cell Metabolism 14: 219–230.
Bedford, M.T., and S.G. Clarke. 2009. Protein arginine methylation in mammals: who, what, and why. Molecular Cell 33: 1–13.
Behrens, J., J.P. Von Kries, M. Kuhl, L. Bruhn, D. Wedlich, R. Grosschedl, and W. Birchmeier. 1996. Functional interaction of beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature 382: 638–642.
Biggs III, W.H., J. Meisenhelder, T. Hunter, W.K. Cavenee, and K.C. Arden. 1999. Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 96: 7421–7426.
Brown, M.S., and J.L. Goldstein. 2008. Selective versus total insulin resistance: a pathogenic paradox. Cell Metabolism 7: 95–96.
Brunet, A., A. Bonni, M.J. Zigmond, M.Z. Lin, P. Juo, L.S. Hu, M.J. Anderson, K.C. Arden, J. Blenis, and M.E. Greenberg. 1999. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857–868.
Chanda, D., J.H. Park, and H.S. Choi. 2008. Molecular basis of endocrine regulation by orphan nuclear receptor Small Heterodimer Partner. Endocrine Journal 55: 253–268.
Chandak, G.R., C.S. Janipalli, S. Bhaskar, S.R. Kulkarni, P. Mohankrishna, A.T. Hattersley, T.M. Frayling, and C.S. Yajnik. 2007. Common variants in the TCF7L2 gene are strongly associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Indian population. Diabetologia 50: 63–67.
Chin, K.T., H.J. Zhou, C.M. Wong, J.M. Lee, C.P. Chan, B.Q. Qiang, J.G. Yuan, I.O. Ng, and D.Y. Jin. 2005. The liver-enriched transcription factor CREB-H is a growth suppressor protein underexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nucleic Acids Research 33: 1859–1873.
Choi, D., Oh KJ, H.S. Han, Y.S. Yoon, C.Y. Jung, S.T. Kim, and S.H. Koo. 2012a. Protein arginine methyltransferase-1 regulates hepatic glucose production in a FoxO1 dependent manner. Hepatology 56(4): 1546–1556.
Choi, D., K.J. Oh, and S.H. Koo. 2012b. Involvement of multiple protein arginine methyltransferases in hepatic glucose metabolism. Hepatology. doi:10.1002/hep.25939.
Chrivia, J.C., R.P. Kwok, N. Lamb, M. Hagiwara, M.R. Montminy, and R.H. Goodman. 1993. Phosphorylated CREB binds specifically to the nuclear protein CBP. Nature 365: 855–859.
Clevers, H. 2006. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 127: 469–480.
Conkright, M.D., G. Canettieri, R. Screaton, E. Guzman, L. Miraglia, J.B. Hogenesch, and M. Montminy. 2003a. TORCs: Transducers of regulated CREB activity. Molecular Cell 12: 413–423.
Conkright, M.D., E. Guzman, L. Flechner, A.I. Su, J.B. Hogenesch, and M. Montminy. 2003b. Genome-wide analysis of CREB target genes reveals a core promoter requirement for cAMP responsiveness. Molecular Cell 11: 1101–1108.
Daitoku, H., M. Hatta, H. Matsuzaki, S. Aratani, T. Ohshima, M. Miyagishi, T. Nakajima, and A. Fukamizu. 2004. Silent information regulator 2 potentiates Foxo1-mediated transcription through its deacetylase activity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101: 10042–10047.
Denboer, L.M., P.W. Hardy-Smith, M.R. Hogan, G.P. Cockram, T.E. Audas, and R. Lu. 2005. Luman is capable of binding and activating transcription from the unfolded protein response element. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 331: 113–119.
Dentin, R., S. Hedrick, J. Xie, J. Yates III, and M. Montminy. 2008. Hepatic glucose sensing via the CREB coactivator CRTC2. Science 319: 1402–1405.
Erion, D.M., I.D. Ignatova, S. Yonemitsu, Y. Nagai, P. Chatterjee, D. Weismann, J.J. Hsiao, D. Zhang, T. Iwasaki, R. Stark, C. Flannery, M. Kahn, C.M. Carmean, X.X. Yu, S.F. Murray, S. Bhanot, B.P. Monia, G.W. Cline, V.T. Samuel, and G.I. Shulman. 2009. Prevention of hepatic steatosis and hepatic insulin resistance by knockdown of cAMP response element-binding protein. Cell Metabolism 10: 499–506.
Essers, M.A., S. Weijzen, A.M. De Vries-Smits, I. Saarloos, N.D. De Ruiter, J.L. Bos, and B.M. Burgering. 2004. FOXO transcription factor activation by oxidative stress mediated by the small GTPase Ral and JNK. EMBO Journal 23: 4802–4812.
Gonzalez, G.A., and M.R. Montminy. 1989. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell 59: 675–680.
Grant, S.F., G. Thorleifsson, I. Reynisdottir, R. Benediktsson, A. Manolescu, J. Sainz, A. Helgason, H. Stefansson, V. Emilsson, A. Helgadottir, U. Styrkarsdottir, K.P. Magnusson, G.B. Walters, E. Palsdottir, T. Jonsdottir, T. Gudmundsdottir, A. Gylfason, J. Saemundsdottir, R.L. Wilensky, M.P. Reilly, D.J. Rader, Y. Bagger, C. Christiansen, V. Gudnason, G. Sigurdsson, U. Thorsteinsdottir, J.R. Gulcher, A. Kong, and K. Stefansson. 2006. Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nature Genetics 38: 320–323.
Haeusler, R.A., K.H. Kaestner, and D. Accili. 2010. FoxOs function synergistically to promote glucose production. Journal of Biological Chemistry 285: 35245–35248.
Hanson, R.W., and L. Reshef. 1997. Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene expression. Annual Review of Biochemistry 66: 581–611.
Hayashi, T., Y. Iwamoto, K. Kaku, H. Hirose, and S. Maeda. 2007. Replication study for the association of TCF7L2 with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in a Japanese population. Diabetologia 50: 980–984.
He, L., A. Sabet, S. Djedjos, R. Miller, X. Sun, M.A. Hussain, S. Radovick, and F.E. Wondisford. 2009. Metformin and insulin suppress hepatic gluconeogenesis through phosphorylation of CREB binding protein. Cell 137: 635–646.
Helgason, A., S. Palsson, G. Thorleifsson, S.F. Grant, V. Emilsson, S. Gunnarsdottir, A. Adeyemo, Y. Chen, G. Chen, I. Reynisdottir, R. Benediktsson, A. Hinney, T. Hansen, G. Andersen, K. Borch-Johnsen, T. Jorgensen, H. Schafer, M. Faruque, A. Doumatey, J. Zhou, R.L. Wilensky, M.P. Reilly, D.J. Rader, Y. Bagger, C. Christiansen, G. Sigurdsson, J. Hebebrand, O. Pedersen, U. Thorsteinsdottir, J.R. Gulcher, A. Kong, C. Rotimi, and K. Stefansson. 2007. Refining the impact of TCF7L2 gene variants on type 2 diabetes and adaptive evolution. Nature Genetics 39: 218–225.
Herzig, S., F. Long, U.S. Jhala, S. Hedrick, R. Quinn, A. Bauer, D. Rudolph, G. Schutz, C. Yoon, P. Puigserver, B. Spiegelman, and M. Montminy. 2001. CREB regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis through the coactivator PGC-1. Nature 413: 179–183.
Huber, O., R. Korn, J. Mclaughlin, M. Ohsugi, B.G. Herrmann, and R. Kemler. 1996. Nuclear localization of beta-catenin by interaction with transcription factor LEF-1. Mechanisms of Development 59: 3–10.
Iourgenko, V., W. Zhang, C. Mickanin, I. Daly, C. Jiang, J.M. Hexham, A.P. Orth, L. Miraglia, J. Meltzer, D. Garza, G.W. Chirn, E. Mcwhinnie, D. Cohen, J. Skelton, R. Terry, Y. Yu, D. Bodian, F.P. Buxton, J. Zhu, C. Song, and M.A. Labow. 2003. Identification of a family of cAMP response element-binding protein coactivators by genome-scale functional analysis in mammalian cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 100: 12147–12152.
Iyer, A.K., and E.R. Mccabe. 2004. Molecular mechanisms of DAX1 action. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism 83: 60–73.
Kim, D.H., G. Perdomo, T. Zhang, S. Slusher, S. Lee, B.E. Phillips, Y. Fan, N. Giannoukakis, R. Gramignoli, S. Strom, S. Ringquist, and H.H. Dong. 2011. FoxO6 integrates insulin signaling with gluconeogenesis in the liver. Diabetes 60: 2763–2774.
Kim, D.K., D. Ryu, M. Koh, M.W. Lee, D. Lim, M.J. Kim, Y.H. Kim, W.J. Cho, C.H. Lee, S.B. Park, S.H. Koo, and H.S. Choi. 2012. Orphan nuclear receptor estrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) is key regulator of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 287: 21628–21639.
Kim, Y.D., K.G. Park, Y.S. Lee, Y.Y. Park, D.K. Kim, B. Nedumaran, W.G. Jang, W.J. Cho, J. Ha, I.K. Lee, C.H. Lee, and H.S. Choi. 2008. Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis through AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent regulation of the orphan nuclear receptor SHP. Diabetes 57: 306–314.
Koo, S.H., L. Flechner, L. Qi, X. Zhang, R.A. Screaton, S. Jeffries, S. Hedrick, W. Xu, F. Boussouar, P. Brindle, H. Takemori, and M. Montminy. 2005. The CREB coactivator TORC2 is a key regulator of fasting glucose metabolism. Nature 437: 1109–1111.
Koo, S.H., H. Satoh, S. Herzig, C.H. Lee, S. Hedrick, R. Kulkarni, R.M. Evans, J. Olefsky, and M. Montminy. 2004. PGC-1 promotes insulin resistance in liver through PPAR-alpha-dependent induction of TRB-3. Nature Medicine 10: 530–534.
Krones-Herzig, A., A. Mesaros, D. Metzger, A. Ziegler, U. Lemke, J.C. Bruning, and S. Herzig. 2006. Signal-dependent control of gluconeogenic key enzyme genes through coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1. Journal of Biological Chemistry 281: 3025–3029.
Kwok, R.P., J.R. Lundblad, J.C. Chrivia, J.P. Richards, H.P. Bachinger, R.G. Brennan, S.G. Roberts, M.R. Green, and R.H. Goodman. 1994. Nuclear protein CBP is a coactivator for the transcription factor CREB. Nature 370: 223–226.
Lee, J.H., P. Giannikopoulos, S.A. Duncan, J. Wang, C.T. Johansen, J.D. Brown, J. Plutzky, R.A. Hegele, L.H. Glimcher, and A.H. Lee. 2011. The transcription factor cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein H regulates triglyceride metabolism. Nature Medicine 17: 812–815.
Lee, J.M., W.Y. Seo, K.H. Song, D. Chanda, Y.D. Kim, D.K. Kim, M.W. Lee, D. Ryu, Y.H. Kim, J.R. Noh, C.H. Lee, J.Y. Chiang, S.H. Koo, and H.S. Choi. 2010a. AMPK-dependent repression of hepatic gluconeogenesis via disruption of CREB.CRTC2 complex by orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner. Journal of Biological Chemistry 285: 32182–32191.
Lee, M.W., D. Chanda, J. Yang, H. Oh, S.S. Kim, Y.S. Yoon, S. Hong, K.G. Park, I.K. Lee, C.S. Choi, R.W. Hanson, H.S. Choi, and S.H. Koo. 2010b. Regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis by an ER-bound transcription factor CREBH. Cell Metabolism 11: 331–339.
Lee, Y.S., D. Chanda, J. Sim, Y.Y. Park, and H.S. Choi. 2007. Structure and function of the atypical orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner. International Review of Cytology 261: 117–158.
Lehman, D.M., K.J. Hunt, R.J. Leach, J. Hamlington, R. Arya, H.E. Abboud, R. Duggirala, J. Blangero, H.H. Goring, and M.P. Stern. 2007. Haplotypes of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene and its upstream region are associated with type 2 diabetes and age of onset in Mexican Americans. Diabetes 56: 389–393.
Lehtinen, M.K., Z. Yuan, P.R. Boag, Y. Yang, J. Villen, E.B. Becker, S. Dibacco, N. De La Iglesia, S. Gygi, T.K. Blackwell, and A. Bonni. 2006. A conserved MST-FOXO signaling pathway mediates oxidative-stress responses and extends life span. Cell 125: 987–1001.
Lin, J., C. Handschin, and B.M. Spiegelman. 2005. Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metabolism 1: 361–370.
Lin, J., P.H. Wu, P.T. Tarr, K.S. Lindenberg, J. St-Pierre, C.Y. Zhang, V.K. Mootha, S. Jager, C.R. Vianna, R.M. Reznick, L. Cui, M. Manieri, M.X. Donovan, Z. Wu, M.P. Cooper, M.C. Fan, L.M. Rohas, A.M. Zavacki, S. Cinti, G.I. Shulman, B.B. Lowell, D. Krainc, and B.M. Spiegelman. 2004. Defects in adaptive energy metabolism with CNS-linked hyperactivity in PGC-1alpha null mice. Cell 119: 121–135.
Liu, Y., R. Dentin, D. Chen, S. Hedrick, K. Ravnskjaer, S. Schenk, J. Milne, D.J. Meyers, P. Cole, J. Yates III, J. Olefsky, L. Guarente, and M. Montminy. 2008. A fasting inducible switch modulates gluconeogenesis via activator/coactivator exchange. Nature 456: 269–273.
Mangelsdorf, D.J., C. Thummel, M. Beato, P. Herrlich, G. Schutz, K. Umesono, B. Blumberg, P. Kastner, M. Mark, P. Chambon, and R.M. Evans. 1995. The nuclear receptor superfamily: The second decade. Cell 83: 835–839.
Matsumoto, M., A. Pocai, L. Rossetti, R.A. Depinho, and D. Accili. 2007. Impaired regulation of hepatic glucose production in mice lacking the forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 in liver. Cell Metabolism 6: 208–216.
Molenaar, M., M. Van De Wetering, M. Oosterwegel, J. Peterson-Maduro, S. Godsave, V. Korinek, J. Roose, O. Destree, and H. Clevers. 1996. XTcf-3 transcription factor mediates beta-catenin-induced axis formation in Xenopus embryos. Cell 86: 391–399.
Moore, M.C., C.C. Connolly, and A.D. Cherrington. 1998. Autoregulation of hepatic glucose production. European Journal of Endocrinology 138: 240–248.
Motta, M.C., N. Divecha, M. Lemieux, C. Kamel, D. Chen, W. Gu, Y. Bultsma, M. Mcburney, and L. Guarente. 2004. Mammalian SIRT1 represses forkhead transcription factors. Cell 116: 551–563.
Nakae, J., B.C. Park, and D. Accili. 1999. Insulin stimulates phosphorylation of the forkhead transcription factor FKHR on serine 253 through a Wortmannin-sensitive pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274: 15982–15985.
Nedumaran, B., S. Hong, Y.B. Xie, Y.H. Kim, W.Y. Seo, M.W. Lee, C.H. Lee, S.H. Koo, and H.S. Choi. 2009. DAX-1 acts as a novel corepressor of orphan nuclear receptor HNF4alpha and negatively regulates gluconeogenic enzyme gene expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry 284: 27511–27523.
Nordlie, R.C., J.D. Foster, and A.J. Lange. 1999. Regulation of glucose production by the liver. Annual Review of Nutrition 19: 379–406.
Norton, L., M. Fourcaudot, M.A. Abdul-Ghani, D. Winnier, F.F. Mehta, C.P. Jenkinson, and R.A. Defronzo. 2011. Chromatin occupancy of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) and its role in hepatic glucose metabolism. Diabetologia 54: 3132–3142.
Ogryzko, V.V., R.L. Schiltz, V. Russanova, B.H. Howard, and Y. Nakatani. 1996. The transcriptional coactivators p300 and CBP are histone acetyltransferases. Cell 87: 953–959.
Oh, K.J., J. Park, S.S. Kim, H. Oh, C.S. Choi, and S.H. Koo. 2012. TCF7L2 modulates glucose homeostasis by regulating CREB- and FoxO1-dependent transcriptional pathway in the liver. PLoS Genetics 8: e1002986.
Panagopoulos, I., E. Moller, A. Dahlen, M. Isaksson, N. Mandahl, A. Vlamis-Gardikas, and F. Mertens. 2007. Characterization of the native CREB3L2 transcription factor and the FUS/CREB3L2 chimera. Genes, Chromosomes and Cancer 46: 181–191.
Pilkis, S.J., and T.H. Claus. 1991. Hepatic gluconeogenesis/glycolysis: regulation and structure/function relationships of substrate cycle enzymes. Annual Review of Nutrition 11: 465–515.
Pilkis, S.J., M.R. El-Maghrabi, and T.H. Claus. 1988. Hormonal regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. Annual Review of Biochemistry 57: 755–783.
Postic, C., R. Dentin, P.D. Denechaud, and J. Girard. 2007. ChREBP, a transcriptional regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism. Annual Review of Nutrition 27: 179–192.
Puigserver, P., G. Adelmant, Z. Wu, M. Fan, J. Xu, B. O’malley, and B.M. Spiegelman. 1999. Activation of PPARgamma coactivator-1 through transcription factor docking. Science 286: 1368–1371.
Puigserver, P., J. Rhee, J. Donovan, C.J. Walkey, J.C. Yoon, F. Oriente, Y. Kitamura, J. Altomonte, H. Dong, D. Accili, and B.M. Spiegelman. 2003. Insulin-regulated hepatic gluconeogenesis through FOXO1-PGC-1alpha interaction. Nature 423: 550–555.
Puigserver, P., Z. Wu, C.W. Park, R. Graves, M. Wright, and B.M. Spiegelman. 1998. A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell 92: 829–839.
Rubinfeld, B., P. Robbins, M. El-Gamil, I. Albert, E. Porfiri, and P. Polakis. 1997. Stabilization of beta-catenin by genetic defects in melanoma cell lines. Science 275: 1790–1792.
Ryu, D., K.J. Oh, H.Y. Jo, S. Hedrick, Y.N. Kim, Y.J. Hwang, T.S. Park, J.S. Han, C.S. Choi, M. Montminy, and S.H. Koo. 2009. TORC2 regulates hepatic insulin signaling via a mammalian phosphatidic acid phosphatase, LIPIN1. Cell Metabolism 9: 240–251.
Saberi, M., D. Bjelica, S. Schenk, T. Imamura, G. Bandyopadhyay, P. Li, C. Vargeese, W. Wang, K. Bowman, Y. Zhang, B. Polisky, and J.M. Olefsky. 2009. Novel liver-specific TORC2 siRNA corrects hyperglycemia in rodent models of type 2 diabetes. American Journal of Physiology, Endocrinology and Metabolism 297(5): E1137–E1146.
Saltiel, A.R., and C.R. Kahn. 2001. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 414: 799–806.
Seol, W., H.S. Choi, and D.D. Moore. 1996. An orphan nuclear hormone receptor that lacks a DNA binding domain and heterodimerizes with other receptors. Science 272: 1336–1339.
Shu, L., N.S. Sauter, F.T. Schulthess, A.V. Matveyenko, J. Oberholzer, and K. Maedler. 2008. Transcription factor 7-like 2 regulates beta-cell survival and function in human pancreatic islets. Diabetes 57: 645–653.
Stirling, J., and P. O’hare. 2006. CREB4, a transmembrane bZip transcription factor and potential new substrate for regulation and cleavage by S1P. Molecular Biology of the Cell 17: 413–426.
Takahashi, Y., H. Daitoku, K. Hirota, H. Tamiya, A. Yokoyama, K. Kako, Y. Nagashima, A. Nakamura, T. Shimada, S. Watanabe, K. Yamagata, K. Yasuda, N. Ishii, and A. Fukamizu. 2011. Asymmetric arginine dimethylation determines life span in C. elegans by regulating forkhead transcription factor DAF-16. Cell Metabolism 13: 505–516.
Tanaka, Y., I. Naruse, T. Maekawa, H. Masuya, T. Shiroishi, and S. Ishii. 1997. Abnormal skeletal patterning in embryos lacking a single Cbp allele: A partial similarity with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 94: 10215–10220.
Towle, H.C., E.N. Kaytor, and H.M. Shih. 1997. Regulation of the expression of lipogenic enzyme genes by carbohydrate. Annual Review of Nutrition 17: 405–433.
Uyeda, K., and J.J. Repa. 2006. Carbohydrate response element binding protein, ChREBP, a transcription factor coupling hepatic glucose utilization and lipid synthesis. Cell Metabolism 4: 107–110.
Van Der Horst, A., L.G. Tertoolen, L.M. De Vries-Smits, R.A. Frye, R.H. Medema, and B.M. Burgering. 2004. FOXO4 is acetylated upon peroxide stress and deacetylated by the longevity protein hSir2(SIRT1). Journal of Biological Chemistry 279: 28873–28879.
Van Schaftingen, E., and I. Gerin. 2002. The glucose-6-phosphatase system. The Biochemical Journal 362: 513–532.
Vecchi, C., G. Montosi, K. Zhang, I. Lamberti, S.A. Duncan, R.J. Kaufman, and A. Pietrangelo. 2009. ER stress controls iron metabolism through induction of hepcidin. Science 325: 877–880.
Wadzinski, B.E., W.H. Wheat, S. Jaspers, L.F. Peruski Jr, R.L. Lickteig, G.L. Johnson, and D.J. Klemm. 1993. Nuclear protein phosphatase 2A dephosphorylates protein kinase A-phosphorylated CREB and regulates CREB transcriptional stimulation. Molecular and Cellular Biology 13: 2822–2834.
Wallberg, A.E., S. Yamamura, S. Malik, B.M. Spiegelman, and R.G. Roeder. 2003. Coordination of p300-mediated chromatin remodeling and TRAP/mediator function through coactivator PGC-1alpha. Molecular Cell 12: 1137–1149.
Wang, Y., H. Inoue, K. Ravnskjaer, K. Viste, N. Miller, Y. Liu, S. Hedrick, L. Vera, and M. Montminy. 2010. Targeted disruption of the CREB coactivator Crtc2 increases insulin sensitivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107: 3087–3092.
Wang, Y., G. Li, J. Goode, J.C. Paz, K. Ouyang, R. Screaton, W.H. Fischer, J. Chen, I. Tabas, and M. Montminy. 2012. Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis in fasting and diabetes. Nature 485: 128–132.
Xu, Z., Y. Wang, and H. Liu. 2012. Protein arginine methylation in hepatic glucose metabolism regulation: Histone, or non-histone? That is the question. Hepatology. doi:10.1002/hep.25943.
Yamagata, K., H. Daitoku, Y. Takahashi, K. Namiki, K. Hisatake, K. Kako, H. Mukai, Y. Kasuya, and A. Fukamizu. 2008. Arginine methylation of FOXO transcription factors inhibits their phosphorylation by Akt. Molecular Cell 32: 221–231.
Yamauchi, T., Y. Oike, J. Kamon, H. Waki, K. Komeda, A. Tsuchida, Y. Date, M.X. Li, H. Miki, Y. Akanuma, R. Nagai, S. Kimura, T. Saheki, M. Nakazato, T. Naitoh, K. Yamamura, and T. Kadowaki. 2002. Increased insulin sensitivity despite lipodystrophy in Crebbp heterozygous mice. Nature Genetics 30: 221–226.
Yao, T.P., S.P. Oh, M. Fuchs, N.D. Zhou, L.E. Ch’ng, D. Newsome, R.T. Bronson, E. Li, D.M. Livingston, and R. Eckner. 1998. Gene dosage-dependent embryonic development and proliferation defects in mice lacking the transcriptional integrator p300. Cell 93: 361–372.
Yi, F., P.L. Brubaker, and T. Jin. 2005. TCF-4 mediates cell type-specific regulation of proglucagon gene expression by beta-catenin and glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. Journal of Biological Chemistry 280: 1457–1464.
Yoon, J.C., P. Puigserver, G. Chen, J. Donovan, Z. Wu, J. Rhee, G. Adelmant, J. Stafford, C.R. Kahn, D.K. Granner, C.B. Newgard, and B.M. Spiegelman. 2001. Control of hepatic gluconeogenesis through the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. Nature 413: 131–138.
Yoon, Y.S., M.W. Lee, D. Ryu, J.H. Kim, H. Ma, W.Y. Seo, Y.N. Kim, S.S. Kim, C.H. Lee, T. Hunter, C.S. Choi, M.R. Montminy, and S.H. Koo. 2010. Suppressor of MEK null (SMEK)/protein phosphatase 4 catalytic subunit (PP4C) is a key regulator of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107: 17704–17709.
Zhang, K., X. Shen, J. Wu, K. Sakaki, T. Saunders, D.T. Rutkowski, S.H. Back, and R.J. Kaufman. 2006. Endoplasmic reticulum stress activates cleavage of CREBH to induce a systemic inflammatory response. Cell 124: 587–599.
Zinker, B., A. Mika, P. Nguyen, D. Wilcox, L. Ohman, T.W. Von Geldern, T. Opgenorth, and P. Jacobson. 2007. Liver-selective glucocorticoid receptor antagonism decreases glucose production and increases glucose disposal, ameliorating insulin resistance. Metabolism 56: 380–387.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Korea (2011-0016454, 2011-0019448).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, KJ., Han, HS., Kim, MJ. et al. Transcriptional regulators of hepatic gluconeogenesis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 36, 189–200 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0018-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0018-5