Abstract
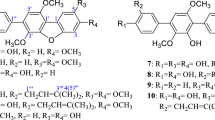
In our search for bioactive metabolites from a marine sponge-associated bacterium Psychrobacter sp., a new bile acid derivative (1), which was assumed to be an artifact, were isolated along with six known (2–7) compounds by bioactivity-guided fractionation. Elucidation of the structure of the new compound was done using a combination of NMR (1H, 13C, HMBC, HSQC, and COSY) and MS spectroscopy. Compound 1 exhibited moderate suppressive effects on both NO and IL-6 production at a concentration of 200 μM (87.3 μg/mL) without significant cytotoxicity against cells. Compounds 2–5 and 7 showed selective inhibitory activity against several human pathogenic bacterial strains at the low concentration of 30 μg/well. In a cytotoxicity evaluation, only compound 7 showed mild cytotoxicity against five human solid tumor cell lines (A-549, SK-OV-3, SK-MEL-2, XF-498, and HCT-15) with ED50 values in the range of 11–14 μg/mL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bettarello, L., Bortolini, O., Fantin, G., and Guerrini, A., Mixed oxo-hydroxy bile acids as actual or potential impurities in ursodeoxycholic acid preparation: a 1H and 13C NMR study. Il Farmaco, 55, 51–55 (2000).
Bowman, J. P., Cavanagh, J., Austin, J. J., and Sanderson, K., Novel Psychrobacter species from Antarctic ornithogenic soils. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 46, 841–848 (1996).
Danzinger, R. G., Hofmann, A. F., Schoenfield, L. J., and Thistle, J. L., Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by chenodeoxycholic acid. N. Engl. J. Med. 286, 1–8 (1972).
Fantin, G., Fogagnolo, M., Medici, A., Pedrini, P., and Cova, U., Spontaneous ketalization of 3-keto-5b-cholanic acids in methanol. Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 3235–3236 (1992).
Fantin, G., Fogagnolo, M., Medici, A., Pedrini, P., and Cova, U., Synthesis of 7- and 12-hydroxy- and 7,12-dihydroxy-3-keto-5fl-cholan-24-oic acids by reduction of 3,7-, 3,12- and 3,7,12-oxo derivatives. Steroids, 58, 524–526 (1993).
Fiorucci, S., Rizzo, G., Donini, A., Distrutti, E., and Santucci, L., Targeting farnesoid X receptor for liver and metabolic disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 13, 298–309 (2007).
Hofmann, A. F. and Hagey, L. R., Bile acids: chemistry, pathochemistry, biology, pathobiology, and therapeutics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 65, 2461–2483 (2008).
Howard, D. E. and Fromm, H., Nonsurgical management of gallstone disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 28, 133–144 (1999).
Kim, D., Lee, J. S., Kim, J., Kang, S. J., Yoon, J. H., Kim, W. G., and Lee, C. H., Biosynthesis of bile acids in a variety of marine bacterial taxa. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 17, 403–407 (2007).
Lehrer, R. I., Rosenman, M., Harwig, S. S. S. L., Jackson, R., and Eisenhauer, P., Ultrasensitive assays for endogenous antimicrobial activity. J. Immunol. Methods, 137, 167–173 (1991).
Li, H., Lee, B. C., Kim, T. S., Bae, K. S., Hong, J., Choi, S. H., Bao, B., and Jung, J. H., Bioactive cyclic dipeptides from a marine sponge-associated bacterium, Psychrobacter sp. Biomol. Ther., 16, 356–363 (2008).
Li, Z., Hu, Y., Liu, Y., Huang, Y., He, L., and Miao, X., 16S rRNA clone library-based bacterial phylogenetic diversity associated with three South China Sea sponges. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 23, 1265–1272 (2007).
Maneerat, S., Nitoda, T., Kanzaki, H., and Kawai, F., Bile acids are new products of a marine bacterium, Myroides sp. strain SM1. Appl. Michrobiol. Biotechnol., 67, 679–683 (2005).
Park, S. C., Kim, C. J., Uramoto, M., Yun, H. I., Yoon, K. H., and Oh, T. K., Antibacterial substance produced by Streptococcus faecium under anaerobic culture. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem., 59, 1966–1967 (1995).
Piel, J., Metabolites from symbiotic bacteria. Nat. Prod. Rep., 21, 519–538 (2004).
Ryu, S. Y., Oak, M. H., Yoon, S. K., Cho, D. I., Yoo, G. S., Kim, T. S., and Kim, K. M., Anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory triterpenes from the herb of Prunella vulgaris. Planta Med., 66, 358–360 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors equally contributed to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Shinde, P.B., Lee, H.J. et al. Bile acid derivatives from a sponge-associated bacterium Psychrobacter sp.. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 857–862 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1607-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1607-1