Abstract
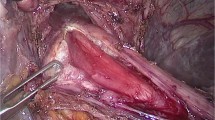
The results of cardiomyotomy in patients of achalasic megaesophagus with axis deviation are not satisfactory. Usually, an esophagectomy is advocated. We describe the technical details and outcomes of laparoscopic esophagogastroplasty for end-stage achalasia. The patient had end-stage achalasia, characterized by tortuous megaesophagus with axis deviation. The surgery was performed in supine position using four abdominal ports. The steps included mobilization of the gastroesophageal junction and lower intrathoracic esophagus, straightening the pulled intrathoracic esophagus into the abdomen, and a side-side esophagogastroplasty using purple Endo GIA Articulating Tri-Staple load, two firings. Duration of surgery was 52 min. The patient was ambulated on the first postoperative day. Oral feeding was initiated by the third postoperative day. The patients had significant improvements of dysphagia. At 3 months of follow-up, the patient is euphagic without significant symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. Laparoscopic esophagogastroplasty is an effective option for relieving dysphagia in megaesophagus due to achalasia with axis deviation. It is a reasonable alternative before subjecting to a major and potentially morbid esophagectomy. It creates a large gastroesophageal (GE) junction, which, with the help of gravity, helps food transit. By dividing the muscles of the GE junction completely, it also achieves a complete cardiomyotomy. Less operative time and blood loss, quicker recovery, and better cosmesis make it an attractive option. While potential reflux is a possibility, the reported case has not shown significant GERD symptoms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heller E (1913) Extramukose cardiaplastik beim chonischen cardiospasmus mit dilatation des oesophagus. Mitt Grenzgeb Med Chir 27:141–149
Stefanidis D, Richardson W, Farrell TM, Kohn GP, Augenstein V, Fanelli RD (2012) Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) guidelines for the surgical treatment of esophageal achalasia. Surg Endosc 26(2):296–311
Rezende JM, Lauar KM, Oliveira AR (1960) Aspectos clínicos e radiológicos da aperistalse do esôfago. Rev Bras Gastroenterol 12:247
Devaney EJ, Lannettoni MD, Orringer MB, Marshall B (2001) Esophagectomy for achalasia: patient selection and clinical experience. Ann Thorac Surg 72(3):854–858
Agarwal AK, Javed A (2013) Laparoscopic esophagogastroplasty: a minimally invasive alternative to esophagectomy in the surgical management of megaesophagus with axis deviation. Surg Endosc 27(6):2238–2242
Source(s) of Support
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was presented during the AMASICON 2013.
Key Message
Laparoscopic esophagogastroplasty is an effective option for relieving dysphagia in megaesophagus due to achalasia with axis deviation
All the authors contributed to the manuscript from conception to final submission.
Surgical Technique
Laparoscopic esophagogastroplasty in management of megaesophagus with axis deviation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panda, N., Bansal, N.K., Narsimhan, M. et al. Laparoscopic Esophagogastroplasty in Management of Megaesophagus with Axis Deviation. Indian J Surg 77 (Suppl 3), 1453–1455 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-014-1193-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12262-014-1193-4