Abstract
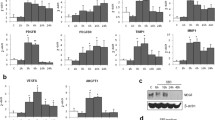
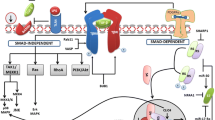
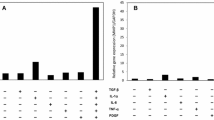
Regardless to the exact nature of damage, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and other non-parenchymal liver cells transform to activated myofibroblasts, synthesizing the accumulating extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, and transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) plays a crucial role in this process. Later it was discovered that decorin, member of the small leucin rich proteoglycan family is able to inhibit this action of TGF-β1. The aim of our present study was to clarify whether HSCs and activated myofibroblasts of portal region exert identical or different response to TGF-β1 exposure, and the inhibitory action of decorin against the growth factor is a generalized phenomenon on myofibroblast of different origin? To this end we measured mRNA expression and production of major collagen components (collagen type I, III and IV) of the liver after stimulation and co-stimulation with TGF-β1 and decorin in primary cell cultures of HSCs and myofibroblasts (MFs). Production of matrix proteins, decorin and members of the TGF-β1 signaling pathways were assessed on Western blots. Messenger RNA expression of collagens and TIEG was quantified by real-time RT-PCR. HSCs and MFs responded differently to TGF-β1 exposure. In contrast to HSCs in which TGF-β1 stimulated the synthesis of collagen type I, type III, and type IV, only the increase of collagen type IV was detected in portal MFs. However, in a combined treatment, decorin seemed to interfere with TGF-β1 and its stimulatory effect was abolished. The different mode of TGF-β1 action is mirrored by the different activation of signaling pathways in activated HSCs and portal fibroblasts. In HSCs the activation of pSMAD2 whereas in myofibroblasts the activation of MAPK pathway was detected. The inhibitory effect of decorin was neither related to the Smad-dependent nor to the Smad-independent signaling pathways.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blomhoff R, Wake K (1991) Perisinusoidal stellate cells of the liver: important roles in retinol metabolism and fibrosis. FASEB J: Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 5(3):271–277
Ramadori G (1991) The stellate cell (Ito-cell, fat-storing cell, lipocyte, perisinusoidal cell) of the liver. New insights into pathophysiology of an intriguing cell. Virchows Archiv B, Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol 61(3):147–158
Neubauer K, Saile B, Ramadori G (2001) Liver fibrosis and altered matrix synthesis. Can J Gastroenterol = J Can de Gastroenterol 15(3):187–193
Friedman SL (1990) Cellular sources of collagen and regulation of collagen production in liver. Semin Liver Dis 10(1):20–29. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1040454
Bhunchet E, Wake K (1992) Role of mesenchymal cell populations in porcine serum-induced rat liver fibrosis. Hepatology 16(6):1452–1473
Bataller R, Brenner DA (2005) Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 115(2):209–218. doi:10.1172/JCI24282
Arthur MJ (2000) Fibrogenesis II. Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 279(2):G245–G249
Nakatsukasa H, Nagy P, Evarts RP, Hsia CC, Marsden E, Thorgeirsson SS (1990) Cellular distribution of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and procollagen types I, III, and IV transcripts in carbon tetrachloride-induced rat liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest 85(6):1833–1843. doi:10.1172/JCI114643
Castilla A, Prieto J, Fausto N (1991) Transforming growth factors beta 1 and alpha in chronic liver disease. Effects of interferon alfa therapy. N Engl J Med 324(14):933–940. doi:10.1056/NEJM199104043241401
Border WA, Noble NA (1994) Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Engl J Med 331(19):1286–1292. doi:10.1056/NEJM199411103311907
Saile B, Matthes N, Knittel T, Ramadori G (1999) Transforming growth factor beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit both apoptosis and proliferation of activated rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 30(1):196–202. doi:10.1002/hep.510300144
Saile B, Matthes N, El Armouche H, Neubauer K, Ramadori G (2001) The bcl, NFkappaB and p53/p21WAF1 systems are involved in spontaneous apoptosis and in the anti-apoptotic effect of TGF-beta or TNF-alpha on activated hepatic stellate cells. Eur J Cell Biol 80(8):554–561
Guyot C, Lepreux S, Combe C, Doudnikoff E, Bioulac-Sage P, Balabaud C, Desmouliere A (2006) Hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis: the (myo)fibroblastic cell subpopulations involved. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38(2):135–151. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.08.021
Forbes SJ, Russo FP, Rey V, Burra P, Rugge M, Wright NA, Alison MR (2004) A significant proportion of myofibroblasts are of bone marrow origin in human liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 126(4):955–963
Russo FP, Alison MR, Bigger BW, Amofah E, Florou A, Amin F, Bou-Gharios G, Jeffery R, Iredale JP, Forbes SJ (2006) The bone marrow functionally contributes to liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 130(6):1807–1821. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.01.036
Eyden B (2008) The myofibroblast: phenotypic characterization as a prerequisite to understanding its functions in translational medicine. J Cell Mol Med 12(1):22–37. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00213.x
Yamaguchi Y, Mann DM, Ruoslahti E (1990) Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-beta by the proteoglycan decorin. Nature 346(6281):281–284. doi:10.1038/346281a0
Border WA, Noble NA, Yamamoto T, Harper JR, Yamaguchi Y, Pierschbacher MD, Ruoslahti E (1992) Natural inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta protects against scarring in experimental kidney disease. Nature 360(6402):361–364. doi:10.1038/360361a0
Dudas J, Kovalszky I, Gallai M, Nagy JO, Schaff Z, Knittel T, Mehde M, Neubauer K, Szalay F, Ramadori G (2001) Expression of decorin, transforming growth factor-beta 1, tissue inhibitor metalloproteinase 1 and 2, and type IV collagenases in chronic hepatitis. Am J Clin Pathol 115(5):725–735. doi:10.1309/J8CD-E9C8-X4NG-GTVG
Jarmay K, Gallai M, Karacsony G, Ozsvar Z, Schaff Z, Lonovics J, Kovalszky I (2000) Decorin and actin expression and distribution in patients with chronic hepatitis C following interferon-alfa-2b treatment. J Hepatol 32(6):993–1002
Takeuchi Y, Kodama Y, Matsumoto T (1994) Bone matrix decorin binds transforming growth factor-beta and enhances its bioactivity. J Biol Chem 269(51):32634–32638
Bi Y, Stuelten CH, Kilts T, Wadhwa S, Iozzo RV, Robey PG, Chen XD, Young MF (2005) Extracellular matrix proteoglycans control the fate of bone marrow stromal cells. J Biol Chem 280(34):30481–30489. doi:10.1074/jbc.M500573200
Cui X, Shimizu I, Lu G, Itonaga M, Inoue H, Shono M, Tamaki K, Fukuno H, Ueno H, Ito S (2003) Inhibitory effect of a soluble transforming growth factor beta type II receptor on the activation of rat hepatic stellate cells in primary culture. J Hepatol 39(5):731–737
Shi YF, Zhang Q, Cheung PY, Shi L, Fong CC, Zhang Y, Tzang CH, Chan BP, Fong WF, Chun J, Kung HF, Yang M (2006) Effects of rhDecorin on TGF-beta1 induced human hepatic stellate cells LX-2 activation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760(11):1587–1595. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2006.09.012
Baghy K, Iozzo RV, Kovalszky I (2012) Decorin-TGFbeta axis in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. J Histochem Cytochem 60(4):262–268. doi:10.1369/0022155412438104
Baghy K, Dezso K, Laszlo V, Fullar A, Peterfia B, Paku S, Nagy P, Schaff Z, Iozzo RV, Kovalszky I (2011) Ablation of the decorin gene enhances experimental hepatic fibrosis and impairs hepatic healing in mice. Lab Investig 91(3):439–451. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2010.172
de Leeuw AM, McCarthy SP, Geerts A, Knook DL (1984) Purified rat liver fat-storing cells in culture divide and contain collagen. Hepatology 4(3):392–403
Knittel T, Kobold D, Saile B, Grundmann A, Neubauer K, Piscaglia F, Ramadori G (1999) Rat liver myofibroblasts and hepatic stellate cells: different cell populations of the fibroblast lineage with fibrogenic potential. Gastroenterology 117(5):1205–1221
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Sahin MB, Schwartz RE, Buckley SM, Heremans Y, Chase L, Hu WS, Verfaillie CM (2008) Isolation and characterization of a novel population of progenitor cells from unmanipulated rat liver. Liver Transplant: Off Publ Am Assoc Study Liver Dis Int Liver Transplant Soc 14(3):333–345. doi:10.1002/lt.21380
Sanderson N, Factor V, Nagy P, Kopp J, Kondaiah P, Wakefield L, Roberts AB, Sporn MB, Thorgeirsson SS (1995) Hepatic expression of mature transforming growth factor beta 1 in transgenic mice results in multiple tissue lesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(7):2572–2576
Dudas J, Mansuroglu T, Batusic D, Saile B, Ramadori G (2007) Thy-1 is an in vivo and in vitro marker of liver myofibroblasts. Cell Tissue Res 329(3):503–514. doi:10.1007/s00441-007-0437-z
Dezso K, Jelnes P, Laszlo V, Baghy K, Bodor C, Paku S, Tygstrup N, Bisgaard HC, Nagy P (2007) Thy-1 is expressed in hepatic myofibroblasts and not oval cells in stem cell-mediated liver regeneration. Am J Pathol 171(5):1529–1537. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2007.070273
Weiss TS, Lichtenauer M, Kirchner S, Stock P, Aurich H, Christ B, Brockhoff G, Kunz-Schughart LA, Jauch KW, Schlitt HJ, Thasler WE (2008) Hepatic progenitor cells from adult human livers for cell transplantation. Gut 57(8):1129–1138. doi:10.1136/gut.2007.143321
Ueberham E, Low R, Ueberham U, Schonig K, Bujard H, Gebhardt R (2003) Conditional tetracycline-regulated expression of TGF-beta1 in liver of transgenic mice leads to reversible intermediary fibrosis. Hepatology 37(5):1067–1078. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50196
Schonherr E, Sunderkotter C, Iozzo RV, Schaefer L (2005) Decorin, a novel player in the insulin-like growth factor system. J Biol Chem 280(16):15767–15772. doi:10.1074/jbc.M500451200
Goldoni S, Iozzo RV (2008) Tumor microenvironment: modulation by decorin and related molecules harboring leucine-rich tandem motifs. Int J Cancer Journal Int du Cancer 123(11):2473–2479. doi:10.1002/ijc.23930
Goldoni S, Humphries A, Nystrom A, Sattar S, Owens RT, McQuillan DJ, Ireton K, Iozzo RV (2009) Decorin is a novel antagonistic ligand of the met receptor. J Cell Biol 185(4):743–754. doi:10.1083/jcb.200901129
Baghy K, Horvath Z, Regos E, Kiss K, Schaff Z, Iozzo RV, Kovalszky I (2013) Decorin interferes with platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling in experimental hepatocarcinogenesis. FEBS J 280(10):2150–2164. doi:10.1111/febs.12215
Yu MC, Chen CH, Liang X, Wang L, Gandhi CR, Fung JJ, Lu L, Qian S (2004) Inhibition of T-cell responses by hepatic stellate cells via B7-H1-mediated T-cell apoptosis in mice. Hepatology 40(6):1312–1321. doi:10.1002/hep.20488
Chen CH, Kuo LM, Chang Y, Wu W, Goldbach C, Ross MA, Stolz DB, Chen L, Fung JJ, Lu L, Qian S (2006) In vivo immune modulatory activity of hepatic stellate cells in mice. Hepatology 44(5):1171–1181. doi:10.1002/hep.21379
Merline R, Moreth K, Beckmann J, Nastase MV, Zeng-Brouwers J, Tralhao JG, Lemarchand P, Pfeilschifter J, Schaefer RM, Iozzo RV, Schaefer L (2011) Signaling by the matrix proteoglycan decorin controls inflammation and cancer through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21. Sci Signal 4(199):ra75. doi:10.1126/scisignal.2001868
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Scientific Found (OTKA) 67925 and 100904, OM-8/2004 grants, by the Székelyhidi Miklós. Award of the Hungarian Liver Research Foundation, by the European Community Action Schemes for the Mobility of University Students (ERASMUS), and the DAAD/MÖB 2007/25 fellowship, NTP-FÖ-P-15-0903.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fullár, A., Firneisz, G., Regős, E. et al. Response of Hepatic Stellate Cells to TGFB1 Differs from the Response of Myofibroblasts. Decorin Protects against the Action of Growth Factor. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 23, 287–294 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-016-0095-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-016-0095-0