Abstract
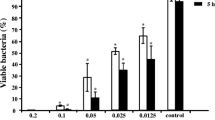
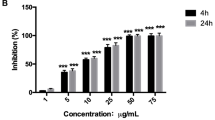
Ginkgo biloba has long been used in traditional Chinese medicine. In this study, ginkgoneolic acid, a kind of compound extracted from G. biloba, was investigated for its effects on growth, acid production, adherence, biofilm formation, and biofilm morphology of Streptococcus mutans. The results showed that ginkgoneolic acid inhibited not only the growth of S. mutans planktonic cells at minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 4 μg/mL and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of 8 μg/mL but also the acid production and adherence to saliva-coated hydroxyapatite of S. mutans at sub-MIC concentration. In addition, this agent was effective in inhibiting the biofilm formation of S. mutans (MBIC50 = 4 μg/mL), and it reduced 1-day-developed biofilm of S. mutans by 50 % or more at low concentration (MBRC50 = 32 μg/mL). Furthermore, the present study demonstrated that ginkgoneolic acid disrupted biofilm integrity effectively. These findings suggest that ginkgoneolic acid is a natural anticariogenic agent in that it exhibits antimicrobial activity against S. mutans and suppresses the specific virulence factors associated with its cariogenicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beighton D (2005) The complex oral microflora of high-risk individuals and groups and its role in the caries process. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 33:248–255
Brighenti FL, Luppens SBI, Delbem ACB, Deng DM, Hoogenkamp MA, Gaetti-Jardim E Jr, Dekker HL, Crielaard W, ten Cate JM (2008) Effect of Psidium cattleianum leaf extract on Streptococcus mutans viability, protein expression and acid Production. Caries Res 42:148–154
Carrilho MR, Carvalho RM, Sousa EN, Nicolau J, Breschi L, Mazzoni A, Tjäderhane L, Tay FR, Agee K, Pashley DH (2010) Substantivity of chlorhexidine to human dentin. Dent Mater 26:779–785
Choi JG, Jeong SI (2009) Antibacterial activity of hydroxyl alkenyl salicylic acids from sarcotesta of Ginkgo biloba against vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus. Fitoterapia 80:1820–1883
Clark WB, Bammann LL, Gibbons RJ (1978) Comparative estimates of bacterial affinities and adsorption sites on hydroxyapatite surfaces. Infect Immun 19:846–853
Cochran WL, Suh SJ, McFeters GA, Stewart PS (2000) Role of RpoS and AlgT in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm resistance to hydrogen peroxide and monochloramine. J Appl Microbiol 88:546–553
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318–1322
Desai M, Bühler T, Weller PH, Brown MR (1998) Increasing resistance of planktonic and biofilm cultures of Burkholderia cepacia to ciprofloxacin and ceftazidime during exponential growth. J Antimicrob Chemother 42:153–160
Donlan RM, Costerton JW (2002) Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin Microbiol Rev 15:167–193
Duarte S, Gregoire S, Singh AP, Vorsa N, Schaich K, Bowen WH, Koo H (2006) Inhibitory effects of cranberry polyphenols on formation and acidogenicity of Streptococcus mutans biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 257:50–56
Featherstone JDB (1999) Prevention and reversal of dental caries: role of low level fluoride. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 27:31–40
Featherstone JDB (2000) The science and practice of caries prevention. J Am Dent Assoc 131:887–899
Featherstone JDB (2009) Remineralization, the natural caries repair process—the need for new approaches. Adv Dent Res 21:4–7
Gibbons RJ (1989) Bacterial adhesion to oral tissues: a model for infectious diseases. J Dent Res 68:750–760
Guan X, Zhou Y, Liang X, Xiao J, He L, Li J (2012) Effects of compounds found in Nidus Vespae on the growth and cariogenic virulence factors of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Res 167:61–68
Hamada S, Koga T, Ooshima T (1984) Virulence factors of Streptococcus mutans and dental caries prevention. J Dent Res 63:407–411
Hayes C (2001) The effect of non-cariogenic sweeteners on the prevention of dental caries: a review of the evidence. J Dent Educ 65:1106–1109
Hoiby N, Ciofu O, Johansen HK, Song ZJ, Moser C, Jensen PO, Molin S, Givskov M, Tolker-Nielsen T, Bjarnsholt T (2011) The clinical impact of bacterial biofilms. Int J Oral Sci 3:55–65
Jeon JG, Rosalen PL, Falsetta ML, Koo H (2011) Natural products in caries research: current (limited) knowledge, challenges and future perspective. Caries Res 45:243–263
Kalkunte SS, Singh AP, Chaves FC, Gianfagna TJ, Pundir VS, Jaiswal AK, Vorsa N, Sharma S (2007) Antidepressant and antistress activity of GC-MS characterized lipophilic extracts of Ginkgo biloba leaves. Phytother Res 21:1061–1065
Katsura H, Tsukiyama R-I, Suzuki A, Kobayashi M (2001) In vitro antimicrobial activities of bakuchiol against oral microorganisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:3009–3013
Koo H, Rosalen PL, Cury JA, Park YK, Bowen WH (2002) Effects of compounds found in propolis on Streptococcus mutans growth and on glucosyltransferase activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:1302–1309
Kuchma SL, O’Toole GA (2000) Surface-induced and biofilm-induced changes in gene expression. Curr Opin Biotechnol 1:429–433
Leme AFP, Koo H, Bellato CM, Bedi G, Cury JA (2006) The role of sucrose in cariogenic dental biofilm formation—new insight. J Dent Res 85:878–887
Limsong J, Benjavongkulchai E, Kuvatanasuchati J (2004) Inhibitory effect of some herbal extracts on adherence of Streptococcus mutans. J Ethnopharmacol 92:281–289
Marsh PD (2010) Microbiology of dental plaque biofilms and their role in oral health and caries. Dent Clin N Am 54:441–454
Marthaler TM (2004) Changes in dental caries 1953–2003. Caries Res 38:173–181
Michalek SM, Katz J, Childers NK (2001) A vaccine against dental caries: an overview. BioDrugs 15:501–508
Nakahara K, Kawabata S, Ono H, Ogura K, Tanaka T, Ooshima T, Hamada S (1993) Inhibitory effect of oolong tea polyphenols on glycosyltransferases of mutans Streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:968–973
Nickel JC, Ruseska I, Wright JB, Costerton JW (1985) Tobramycin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 27:619–624
Prosser BL, Taylor D, Dix BA, Cleeland R (1987) Method of evaluating effects of antibiotics on bacterial biofilm. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 31:1502–1506
Rölla G (1989) Why is sucrose so cariogenic? The role of glucosyltransferase and polysaccharides. Eur J Oral Sci 97:115–119
Selwitz RH, Ismail AI, Pitts NB (2007) Dental caries. Lancet 369:51–59
Slot DE, Vaandrager NC, Van Loveren C, Van Palenstein Helderman WH, Van der Weijden GA (2011) The effect of chlorhexidine varnish on root caries: a systematic review. Caries Res 45:162–173
Stenudd C, Nordlund A, Ryberg M, Johansson I, KallestÅl C, Strömberg N (2001) The association of bacterial adhesion with dental caries. J Dent Res 80:2005–2010
ten Cate JM (2004) Fluorides in caries prevention and control: empiricism or science. Caries Res 38:254–257
Wu X, Yang L, Chen J, Yuan X, Xia G (2003) Preparation of ginkgolic acid monomers and their antifungal activity. Chem Ind For Prod 23:17–21
Xiao J, Zuo Y, Liu Y, Li J, Hao Y, Zhou X (2007) Effects of Nidus Vespae extract and chemical fractions on glucosyltransferases, adherence and biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans. Arch Oral Biol 52:869–875
Xu X, Zhou XD, Wu CD (2011a) Tea catechin epigallocatechin gallate inhibits Streptococcus mutans biofilm formation by suppressing gtf genes. Arch Oral Biol. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.10.021
Xu X, Zhou XD, Wu CD (2011b) The tea catechin epigallocatechin gallate suppresses cariogenic virulence factors of Streptococcus mutans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:1229–1236
Yang XM, Zhu W, Chen J, Qian ZY, Xie JM (2004) Study on anti-bacterium activity of ginkgolic acids and their momomers. Zhong Yao Cai 27:661–663
Yoo S, Murata RM, Duarte S (2011) Antimicrobial traits of tea- and cranberry-derived polyphenols against Streptococcus mutans. Caries Res 45:327–335
Zhou C, Li X, Du W, Feng Y, Kong X, Li Y, Xiao L, Zhang P (2010) Antitumor effects of ginkgolic acid in human cancer cell occur via cell cycle arrest and decrease the Bcl-2/Bax ratio to induce apoptosis. Chemotherapy 56:393–402
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases of Sichuan University for kindly providing the microorganisms and technical assistance, to Dr. Jing Xue for the critical assessment, and to the anonymous reviewers for their comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Wang, S., Wu, T. et al. Effects of ginkgoneolic acid on the growth, acidogenicity, adherence, and biofilm of Streptococcus mutans in vitro. Folia Microbiol 58, 147–153 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-012-0191-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-012-0191-9