Abstract
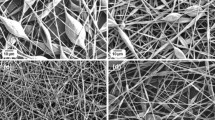
Well-aligned PMIA nanofiber mats were fabricated by electrospinning and then hot-stretching along the fiber axis was used to improve the mechanical properties of nanofibers in this paper. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) were used to characterize the morphology and properties of nanofibers. The results showed that the nanofibers became thinner and better alignment than the as-spun nanofibers after hotstretching, and the average diameter of the nanofibers decreased with the increasing of the tensile force. In the same time, hotstretching improved the crystallinity and T g of the as-spun PMIA nanofibers. The tensile strength and modulus of the hotstretched nanofiber mats peaked at ca.50 % and ca.196 % respectively at the tensile force of 12 N compared with the as-spun nanofiber mats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Frenot and I. S. Chronakis, Curr. Opin. Colloid. In., 8, 64 (2003).
Z. M. Huang, Y. Z. Zhang, M. Kotaki, and S. Ramakrishna, Compos. Sci. Technol., 63, 2223 (2003).
D. Li and Y. Xia, Adv. Mater., 16, 1151 (2004).
D. H. Reneker, A. L. Yarin, E. Zussman, and H. Xu, Adv. Appl. Mech., 41, 43 (2007).
S. Agarwal, J. H. Wendorff, and A. Greiner, Polymer, 49, 5603 (2008).
A. Baji, Y. W. Mai, S. C. Wong, M. Abtahi, and P. Chen, Compos. Sci. Technol., 70, 703 (2010).
D. Yu, J. Yang, L. Li, P. Lu, and L. Zhu, Fiber. Polym., 13, 450 (2012).
T. J. Shin, S. Y. Park, H. J. Kim, H. J. Lee, and J. H. Youk, Biotechnol. Lett., 32, 877 (2010).
Y. Liu, J. Li, and Z. Pan, J. Polym. Res., 18, 2055 (2011).
N. Bhardwaj and S. C. Kundu, Biotechnol. Adv., 28, 325 (2010).
L. Q. Liu, D. Tasis, M. Prato, and H. D. Wagner, Adv. Mater., 19, 1228 (2007).
W. Sun, Q. Cai, P. Li, X. Deng, Y. Wei, M. M. Xu, and X. Yang, Dental. Materials., 26, 873 (2010).
R. Jalili, M. Morshed, and S. A. H. Ravandi, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 101, 4350 (2006).
X. H. Zong, S. F. Ran, D. F. Fang, B. S. Hsiao, and B. Chu, Polymer, 44, 4959 (2003).
S. Asano, A. Ohmory, A. Akiyama, M. Osawa, K. Shizuka, and M. Kouno, U. S. Patent, 4758649 (1988).
N. N. Machalaba and K. E. Perepelkin, J. Ind. Text., 31, 189 (2002).
Y. J. Wu, J. C. Seferis, and V. Lorentz, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 86, 1149 (2002).
L. Yao, C. Lee, and J. Kim, Fiber. Polym., 11, 1032 (2010).
L. Yao and J. Kim, Adv. Mater. Res., 175-176, 318 (2011).
X. Wang, K. Zhang, M. Zhu, H. Yu, Z. Zhou, Y. Chen, and B. S. Hsiao, Polymer, 49, 2755 (2008).
C. Lai, G. Zhong, Z. Yue, L. Zhang, A. Vakili, Y. Wang, L. Zhu, J. Liu, and H. Fong, Polymer, 5, 519 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, B., Tian, L., Li, J. et al. Effect of hot-stretching on morphology and mechanical properties of electrospun PMIA nanofibers. Fibers Polym 14, 405–408 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-013-0405-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-013-0405-z