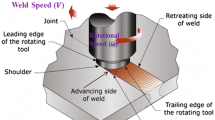
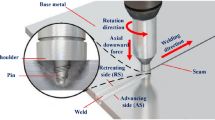
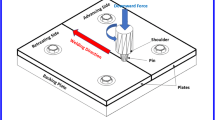
Abstract
Friction stir welding is a solid-state welding method commonly used for aluminum alloy or lightweight metal. It has the advantages of low welding strain, high welding quality, and low residual welding stress while requiring no protection gas. Welding strain analysis of friction stir welding using finite element analysis has been the subject of many studies that focused on the substance fluid using threedimensional computational fluid dynamics; however, this approach is inefficient for large structures and requires much time for analysis. To address this drawback, this study proposes a faster method for analyzing extruded aluminum material that exploits the advantages of the inherent strain-based equivalent load.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. A. Colegrove and H. R. Shercliff, 3-dimensional CFD modeling of flow round a threaded friction stir welding tool profile, J.Mats.Proc.Tech., 169 (2005).
H. Schmidt, J. Hattel and J. Wert, An analytical model for the heat generation in friction stir welding, Modeling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering, 12 (2004).
Z. Feng and X. L. Wang, Modeling of residual stresses and property distributions in friction stir welds of aluminum alloy 6061-T6, Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 12(4) (2007) 348–356.
D.-Q. Wang, C. R. Hubbard and S. Spooner, Residual stress determination for a ferritic steel weld plate, ORNL, Tm1999/141.
Y. J. Chao and X. Qi, Thermal and thermo-mechanical modeling of friction stir welding of aluminum alloy 6061-T6, J. of Materials Processing & Manufacturing Science, 7 (1998).
O. Frigaard, O. Grong and O. T. Midling, A process model for friction stir welding of age hardening aluminum alloys, Metallurgical and materials transactions A, 32A (2001).
G. J. Bendzsak, T. H. North and C. B. Smith, An experimentally validated 3D model for friction stir welding, Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on ‘Friction Stir Welding’ TWI Ltd., Gothenburg, Sweden (2000).
Y. J. Chao, X. Qi and W. Tang, Heat transfer in friction stir wlding-experimental and numerical studies, Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 125 (2003).
W. H. Jiang and R. Kovacevic, Feasibility study of friction stir welding of 6061-T6 aluminium alloy with AISI 1018 steel, Proc.Instn Mech.Engrs Bol.218 Part B: J.Engineerign Manufacture (2004).
P. J. Ditzel, Microstructure / property relationships in aluminum friction stir welds, MSc thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA (1997).
C. D. Jang, S. I. Seo and D. E. Ko, A study on the prediction of deformations of plates due to line heating using a simplified thermal elasto-plastic analysis, J. of Ship Production, 13(1) (1997).
T. H. Kim, The study on the prediction of plate deformation by triangle heating using inherent strain method, MSc. thesis, Seoul National University (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Youngseong Lee
Hyung Suk Mun, Ph.D. received a doctor degree in Department of Naval Architecture at Seoul National University, Seoul Korea in 2008 and he completed a master of science degree in Department of Mechanical Engineering at The George Washington University, Washington D.C U.S.A, in 1994. He is a passionate researcher of welding analysis and heat stress. He published many research paper on prediction of welding deformation as well as involved in national research projects which were related structural analysis, finite element analysis for critical joints, rolling contact fatigue analysis, dynamic analysis and design of steering system, elasto-plastic finite element analysis, development manufacturing system and maintenance system based on RAMS.
Sung Il Seo, Ph.D., ia s chief resear cher of Korea Railroad Research Institute. Dr. Seo was born at Seoul, Korea in 1962. He graduated from Department of Naval Architecture, Seoul National University in 1984 and received a doctor degree fromthe same university in 1994. He entered Hanjin Heavy Industries Co. in 1986 and was engaged in structural design of ship and development of aluminum rolling stocks. He transferred to KRRI in 2002. He was engaged in development of Korea High Speed Train. He has been in charge of the development project for Korea Tilting Train. He published many research papers on high speed train, structural design and welding deformations in international journals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mun, HS., Seo, SI. Welding strain analysis of friction stir-welded aluminum alloy structures using inherent strain-based equivalent loads. J Mech Sci Technol 27, 2775–2782 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-013-0724-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-013-0724-4