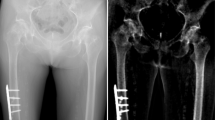
Abstract
Currently, it is difficult to carry out refraction-contrast radiography by using a conventional X-ray generator. Thus, we developed an embossed radiography system utilizing dual-energy subtraction for decreasing the absorption contrast in unnecessary regions, and the contrast resolution of a target region was increased by use of image-shifting subtraction and a linear-contrast system in a flat panel detector (FPD). The X-ray generator had a 100-μm-focus tube. Energy subtraction was performed at tube voltages of 45 and 65 kV, a tube current of 0.50 mA, and an X-ray exposure time of 5.0 s. A 1.0-mm-thick aluminum filter was used for absorbing low-photon-energy bremsstrahlung X-rays. Embossed radiography was achieved with cohesion imaging by use of the FPD with pixel sizes of 48 × 48 μm, and the shifting dimension of an object in the horizontal direction ranged from 100 to 200 μm. At a shifting distance of 100 μm, the spatial resolutions in the horizontal and vertical directions measured with a lead test chart were both 83 μm. In embossed radiography of non-living animals, we obtained high-contrast embossed images of fine bones, gadolinium oxide particles in the kidney, and coronary arteries approximately 100 μm in diameter.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson AC, Zeman HD, Brown GS, Morrison J, Reiser P, Padmanabahn V, et al. First operation of the medical research facility at the NSLS for coronary angiography. Rev Sci Instrum. 1992;63:625–8.
Mori H, Hyodo K, Tanaka E, Mohammed MU, Yamakawa A, Shinozaki Y, et al. Small-vessel radiography in situ with monochromatic synchrotoron radiation. Radiology. 1996;201:173–7.
Hyodo K, Ando M, Oku Y, Yamamoto S, Takeda T, Itai Y, et al. Development of a two-dimensional imaging system for clinical applications of intravenous coronary angiography using intense synchrotron radiation produced by a multipole wiggler. J Synchrotron Radiat. 1998;5:1123–6.
Momose A, Takeda T, Itai Y, Hirano K. Phase-contrast X-ray computed tomography for observing biological soft tissues. Nat Med. 1996;2:473–5.
Ando M, Maksimenko A, Sugiyama H, Pattanasiriwisawa W, Hyodo K, Uyama C. Simple X-ray dark- and bright-field imaging using achromatic Laue optics. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2002;41:L1016–8.
Ando M, Sugiyama H, Ichihara S, Endo T, Bando H, Yamasaki K, et al. Sharper image of breast cancer cells and stroma in dense breast using thinner angular filter under X-ray dark-field imaging. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2006;45:L740–3.
Iida S, Kawado S, Maehara T, Chikaura Y, Suzuki Y, Kajiwara K, et al. Plane-wave X-ray topography of grown-in microdefects in silicon crystals. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2005;38:A23–7.
Chen Y, Dhanaraj G, Dudley M, Sanchez EK, MacMillan MF. Sense determination of micropipes via grazing-incidence synchrotron white beam X-ray topography in 4H silicon carbide. Appl Phys Lett. 2007;91:071917.
Sato E, Sagae M, Tanaka E, Hayasi Y, Germer R, Mori H, et al. Quasi-monochromatic flash X-ray generator utilizing a disk-cathode molybdenum tube. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2004;43:7324–8.
Sato E, Tanaka E, Mori H, Kawai T, Sato S, Takayama K. Clean monochromatic X-ray irradiation from weakly ionized linear copper plasma. Opt Eng. 2005;44:049002–16.
Sato E, Hayasi Y, Germer R, Tanaka E, Mori H, Kawai T, et al. X-ray spectra from weakly ionized linear copper plasma. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2006;45:5301–6.
Sato E, Tanaka E, Mori H, Kawai T, Inoue T, Ogawa A, et al. Characteristic X-ray generator utilizing angle dependence of bremsstrahlung X-ray distribution. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2006;45:2845–9.
Sato E, Tanaka E, Mori H, Kawai T, Ichimaru T, Sato S, et al. Demonstration of enhanced K-edge angiography using a cerium target X-ray generator. Med Phys. 2004;31:3017–21.
Sato E, Tanaka E, Mori H, Kawai T, Inoue T, Ogawa A, et al. Variations in cerium X-ray spectra and enhanced K-edge angiography. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2005;44:8204–9.
Wilkins SW, Gureyev TE, Gao D, Pogany A, Stevenson AW. Phase-contrast imaging using polychromatic hard X-rays. Nature. 1996;384:335–8.
Bornefalk H, Lewin J, Danielsson M, Lundqvist M. Single-shot dual-energy subtraction mammography with electronic spectrum splitting: feasibility. Euro J Radiol. 2006;60:275–8.
Kido S, Kuriyama K, Hosomi N, Inoue E, Kuroda C, Horai T. Low-cost soft-copy display accuracy in the detection of pulmonary nodules by single-exposure dual-energy subtraction: comparison with hard-copy viewing. J Digit Imag. 2000;13:33–7.
Osawa A, Sato E, Matsukiyo H, Enomoto T, Watanabe M, Nagao J, et al. Novel embossed radiography system utilizing energy subtraction. Proc SPIE. 2008;7080:708003–16.
Ishisaka A, Ohara H, Honda C. A new method of analyzing edge effect in phase contrast imaging with incoherent X-rays. Opt Rev. 2000;7:566–72.
Enomoto T, Sato E, Sumiyama Y, Aizawa K, Watanabe M, Tanaka E, et al. Enhanced magnification angiography using 20-μm-focus tungsten tube. Jpn J Appl Phys. 2006;45:8005–9.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our thanks to the reviewers for giving very helpful advice concerning our paper. This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research and Advanced Medical Scientific Research from MECSST, Health and Labor Sciences Research Grants, Grants from the Keiryo Research Foundation, Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private Schools of Japan, the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), and the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Osawa, A., Watanabe, M., Sato, E. et al. Embossed radiography utilizing energy subtraction. Radiol Phys Technol 2, 77–86 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-008-0048-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-008-0048-8