Abstract
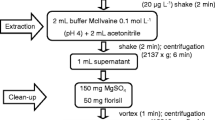
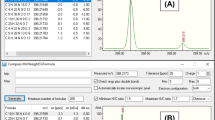
The aim of the present study was to develop a rapid and simple method for the detection and quantification of antibiotic and antibacterial residues in honey using liquid chromatography with electronspray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Two different extraction methods were used. The first method uses water and 1% formic acid in acetonitrile for the determination of sulfonamides while the second uses phosphate buffer, 10% trichloroacetic acid, and acetonitrile as the extracting solvent for the determination of tetracyclines, amphenicols, fluoroquinolones, penicillin g, trimethoprim, and tiamulin. The multi-residue method was validated in a thyme honey matrix. Thirty-six different antibiotics and residues from four different families (sulfonamides, tetracyclines, amphenicols, fluoroquinolones) and some individual antibiotics (penicillin g, trimethoprim, and tiamulin) were tested in 20 honey samples originating from Cyprus and Greece. The decision limits (CCα) were from 0.1 to 9.2 μg kg−1; the detection capabilities (CCβ) were from 0.3 to 27.6 μg kg−1 while recoveries were from to be between 65.0 and 116.1%. The method was successfully applied to commercial samples from different types of honey from Greece and Cyprus. Among them, oxolonic acid, sulfathiazole, and sulfadimethoxine were found in three honey samples. Finally, proficiency testing was applied to the proposed method while analysis of certified samples showed good method performance characteristics.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Commision Decision of 12 august 2002 implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results, Off. J. Eur. Commun. 2002/657/EC, 2002.
CRLs view on state of the art analytical methods for national residue control plans, CRL Guidance Paper (7 December 2007).
Debayle D, Dessalces G, Grenier-Loustalot MF (2008) Multi-residue analysis of traces of pesticides and antibiotics in honey by HPLC-MS-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1011–1020
Economou A, Petraki O, Tsipi D, Botitsi E (2012) Development of a liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of sulfonamides, trimethoprim and dapsone in honey and validation according to Commission Decision 2002/657/EC for banned compounds. Talanta 97:32–41
Galarini R, Saluti G, Giusepponi D, Rossi R, Moretti S (2015) Multiclass determination of 27 antibiotics in honey. Food Control 48:12–24
Hammed Y-A, Mohamed R, Gremaud E, Le Breton M-H, Guy PA (2008) Multi-screening approach to monitor and quantify 42 antibiotic residues in honey by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1177:58–76
Huerta-Fontela M, Galceran MT, Ventura F (2010) Fast liquid chromatography-quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry for the analysis of pharmaceuticals and hormones in water resources. J Chromatogr A 1217:4212–4222
Jin Y, Zhang J, Zhao W, Zhang W, Lin W, Zhou J, Li Y (2017) Development and validation of a multiclass method for the quantification of veterinary drug residues in honey and royal jelly by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 221:1298–1307
Kennedy DG, McCracken RJ, Cannavan A, Hewitt SA (1998) Use of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in the analysis of residues of antibiotics in meat and milk. J Chromatogr A 812:77–98
Kivrak I, Kivrak S, Harmandar M (2016) Development of a rapid method for the determination of antibiotic residues in honey using UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Food Sci Technol, Campinas 36(1):90–96
Li J, Chen L, Wang X, Jin H, Ding L, Zhang K, Zhang H (2008) Determination of tetracyclines residues in honey by on-line solid-phase extraction high-performance liquid chromatography. Talanta 75:1245–1252
Louppis AP, Anastasia V, Badeka PK, Paleologos EK, Kontominas MG (2010) Determination of okadaic acid, dinophysistoxin-1 and related esters in Greek mussels using HPLC with fluorometric detection, LC-MS/MS and mouse bioassay. Toxicon 55:724–733
Moretti S, Dusi G, Giusepponi D, Pellicciotti S, Rossi R, Saluti G, Cruciani G, Galarini R (2016) Screening and confirmatory method for multiclass determination of 62 antibiotics in meat. J Chromoatogr A 1429:175–188
Orso D, Floriano L, Ribeiro L, Bandeira N, Prestes O, Zanella R (2015) Simultaneous determination of multiclass pesticides and antibiotics in honey samples based on ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 9:1638–1653
Regulation (EC) No 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin.
Sajid M, Na N, Safdar M, Lu X, Ma L, He L, Jin O (2013) Rapid trace level determination of sulfonamide residues in honey with online extraction using short C-18 column by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr A 1314:173–179
Shao B, Chen D, Zhang J, Wu Y, Sun C (2009) Determination of 76 pharmaceutical drugs by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry in slaughterhouse wastewater. J Chromatogr A 1216:8312–8318
Shendy AH, Al-Ghobashy M, Alla SG, Lotfy HM (2016) Development and validation of a modified QuEChERS protocol coupled to LC–MS/MS for simultaneous determination of multi-class antibiotic residues in honey. Food Chem 190:982–989
Stefan B (2006) Apidology. Contaminants of bee products 37:1–18
Su R, Li X, Liu W, Wang X, Yang H (2016) Headspace microextraction of sulfonamides from honey by hollow fibers coupled with ultrasonic nebulization. J Agr Food Chem 64:1627–1634
World Health Organization, Antibiotic resistance, factsheet, October (2016) http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/antibiotic-resistance/en/
Zaneta B, Slebioda M, Namiesnik J (2011) Determination of antibiotic residues in honey. Trends Analyt Chem 30:7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Louppis, A.P., Kontominas, M.G. & Papastephanou, C. Determination of Antibiotic Residues in Honey by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Electronspray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 10, 3385–3397 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0899-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0899-x