Abstract
Background
Obesity is associated with poor asthma outcomes; weight loss improves such outcomes. Inaccurate recognition of obesity may impede weight control.
Purpose
We examined perception of weight by early adolescents with uncontrolled asthma and their caregivers, and tested the relationship between medical visit frequency and accuracy of perceived weight status.
Methods
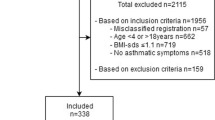
A total of 373 adolescents and their caregivers reported the adolescent’s height/weight and weight perception; caregivers reported healthcare utilization. We measured height/weight. Logistic regression modeled accuracy of weight perception.
Results
A total of 43.7 % of the overweight/obese adolescents and caregivers accurately perceived weight status. BMI percentile [odds ratio (OR) = 1.19, confidence interval (CI) = 1.10–1.28] and total medical visits (OR = 1.18, CI = 1.05–1.33) were associated with higher accuracy in caregivers. Total medical visits (OR = 0.84, CI = 0.74–0.96) was associated with lower accuracy in adolescents.
Conclusions
Accurate perception of weight status was poor for overweight adolescents with uncontrolled asthma and their caregivers. Frequent medical visits were associated with improved caregivers’ but not adolescents’ perceptions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, Lamb MM, Flegal KM. Prevalence of high body mass index in US children and adolescents, 2007–2008. JAMA. 2010;303:242–249.
Wang YC, Gortmaker SL, Taveras EM. Trends and racial/ethnic disparities in severe obesity among US children and adolescents, 1976–2006. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011;6:12–20.
Calzada PJ, Anderson-Worts P. The obesity epidemic: Are minority individuals equally affected? Prim Care. 2009;36:307–317.
Luder E, Melnik TA, DiMaio M. Association of being overweight with greater asthma symptoms in inner city Black and Hispanic children. J Pediatr. 1998;132:699–703.
Gennuso J, Epstein LH, Paluch RA, Cerny F. The relationship between asthma and obesity in urban minority children and adolescents. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1998;152:1197–1200.
Abramson NW, Wamboldt FS, Mansell AL, Carter R, Federico MJ, Wamboldt MZ. Frequency and correlates of overweight status in adolescent asthma. J Asthma. 2008;45:135–139.
Matricardi PM, Gruber C, Wahn U, et al. The asthma-obesity link in childhood: Open questions, complex evidence, a few answers only. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007;37:476–484.
Story RE. Asthma and obesity in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2007;19:680–684.
Belamarich PF, Luder E, Kattan M, et al. Do obese inner-city children with asthma have more symptoms than nonobese children with asthma? Pediatrics. 2000;106:1436–1441.
Quinto KB, Zuraw BL, Poon K-YT, Chen W, Schatz M, Christiansen SC. The association of obesity and asthma severity and control in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:964–969.
Chu YT, Chen WY, Wang TN, Tseng HI, Wu JR, Ko YC. Extreme BMI predicts higher asthma prevalence and is associated with lung function impairment in school-aged children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2009;44:472–479.
Sin DD, Sutherland ER. Obesity and the lung: 4. obesity and asthma. Thorax. 2008;63:1018–1023.
Jay M, Wijetunga NA, Stepney C, Dorsey K, Chua DM, Bruzzese JM. The relationship between asthma and obesity in urban, Hispanic and Black early adolescents. Pediatr Allergy Immu Pulm. 2012;25:1–9.
Ford ES. The epidemiology of obesity and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005;115:897–909.
Rosenstock IM. Why people use health services. Milbank Mem Fund Q. 1966;44:94–127.
Rosenstock IM, Strecher VJ, Becker MH. Social learning theory and the health belief model. Health Educ Behav. 1988;15:175–183.
Cummings KM, Jette AM, Rosenstock IM. Construct validation of the Health Belief Model. Health Educ Monogr. 1978;6:394–405.
Epstein LH, Paluch RA, Roemmich JN, Beecher MD. Family-based obesity treatment, then and now: Twenty-five years of pediatric obesity treatment. Health Psychol. 2007;26:381–391.
Edwards NM, Pettingell S, Borowsky IW. Where perception meets reality: Self-perception of weight in overweight adolescents. Pediatrics. 2010;125:e452–e458.
Lenhart CM, Daly BP, Eichen DM. Is accuracy of weight perception associated with health risk behaviors in a a diverse sample of obese adolescents? J Sch Nurs. 2011;27(6):416–423.
Jáuregui-Lobera I, Bolaños-Ríos P, Santiago-Fernández MJ, Garrido-Casals O, Sánchez E. Perception of weight and psychological variables in a sample of Spanish adolescents. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2011;4:245–251.
Brener ND, Eaton DK, Lowry R, McManus T. The association between weight perception and BMI among high school students. Obes Res. 2004;12:1866–1874.
Skinner AC, Weinberger M, Mulvaney S, Schlundt D, Rothman RL. Accuracy of perceptions of overweight and relation to self-care behaviors among adolescents with type 2 diabetes and their parents. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:227–229.
Goodman E, Hinden BR, Khandelwal S. Accuracy of teen and parental reports of obesity and body mass index. Pediatrics. 2000;106:52–58.
Chaimovitz R, Issenman T, Moffat T, Persad R. Body perception: Do parents, their children, and their children’s physicians perceive body image differently? J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008;47:76–80.
Carnell S, Edwards C, Croker H, Boniface D, Wardle J. Parental perceptions of overweight in 3–5 y olds. Int J Obes. 2005;29:353–355.
Maximova K, McGrath JJ, Barnett T, O'Loughlin J, Paradis G, Lambert M. Do you see what I see? Weight status misperception and exposure to obesity among children and adolescents. Int J Obes. 2008;32:1008–1015.
Parry LL, Netuveli G, Parry J, Saxena S. A systematic review of parental perception of overweight status in children. J Ambul Care Manage. 2008;31:253–268.
Etelson D, Brand DA, Patrick PA, Shirali A. Childhood obesity: Do parents recognize this health risk? Obesity (Silver Spring). 2003;11:1362–1368.
Weinstein ND. Unrealistic optimism about future life events. J Per Soc Psychol. 1980;39:806–820.
Weinstein ND. Unrealistic optimism about susceptibility to health problems: Conclusions from a community-wide sample. J Behav Med. 1987;10:481–500.
Weinstein ND. Effects of personal experience on self-protective behavior. Psychol Bull. 1989;105:31–50.
Gregory CO, Blanck HM, Gillespie C, Maynard LM, Serdula MK. Health perceptions and demographic characteristics associated with underassessment of body weight. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2008;16:979–986.
Kuchler F, Variyam JN. Mistakes were made: Misperception as a barrier to reducing overweight. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003;27:856–861.
Adams K, Sargent RG, Thompson SH, Richter D, Corwin SJ, Rogan TJ. A study of body weight concerns and weight control practices of 4th and 7th grade adolescents. Ethn Health. 2000;5:79–94.
Kronenfeld LW, Reba-Harrelson L, Von Holle A, Reyes ML, Bulik CM. Ethnic and racial differences in body size perception and satisfaction. Body Image. 2010;7:131–136.
Young-Hyman D, Herman LJ, Scott DL, Schlundt DG. Care giver perception of children's obesity-related health risk: A study of African American families. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2000;8:241–248.
Neumark-Sztainer D, Story M, Faibisch L. Perceived stigmatization among overweight African-American and Caucasian adolescent girls. J Adolesc Health. 1998;23:264–270.
Brown HS, Evans AE, Mirchandani GG, Kelder SH, Hoelscher DM. Observable weight distributions and children's individual weight assessment. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2009;18:202–205.
Jay M, Gillespie C, Ark T, et al. Do internists, pediatricians, and psychiatrists feel competent in obesity care? Using a needs assessment to drive curriculum design. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23:1066–1070.
Forman-Hoffman V. High prevalence of abnormal eating and weight control practices among U.S. high-school students. Eat Behav. 2004;5:325–336.
Hernandez RG, Cheng TL, Serwint JR. Parents’ healthy weight perceptions and preferences regarding obesity counseling in preschoolers: Pediatricians matter. Clin Pediatr. 2010;49:790–798.
Bruzzese J-M, Unikel LH, Gallagher R, Evans D, Colland VT. Feasibility and impact of a school-based intervention for families of urban adolescents with asthma: Results from a randomized pilot trial. Fam Process. 2008;47:95–113.
N.H.L.B.I.: Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma NIH Publication No. 97–4051. NIH: Bethesda, 1997.
Division of Nutrition Physical Activity and Obesity: A SAS Program for the CDC Growth Charts. Retrieved June 15 2007, from http://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpao/growthcharts/resources/sas.htm
Boutelle K, Fulkerson JA, Neumark-Sztainer D, Story M. Mothers' perceptions of their adolescents' weight status: Are they accurate? Obes Res. 2004;12:1754–1757.
Miller JE. Predictors of asthma in young children: Does reporting source affect our conclusions? Am J Epidemiol. 2001;154:245–250.
Evans R 3rd, Gergen PJ, Mitchell H, et al. A randomized clinical trial to reduce asthma morbidity among inner-city children: Results of the National Cooperative Inner-City Asthma Study. J Pediatr. 1999;135:332–338.
Kattan M, Kumar R, Bloomberg GR, et al. Asthma control, adiposity, and adipokines among inner-city adolescents. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:584–592.
Cohen J. Weighted kappa: Nominal scale agreement provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol Bull. 1968;70:213–220.
Fleiss JL, Levin BA, Paik MC. Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions. 3rd ed. Hoboken: Wiley; 2003.
Neumark-Sztainer D, Croll J, Story M, Hannan P, French S, Perry C. Ethnic/racial differences in weight-related concerns and behaviors among adolescent girls and boys: Findings from Project EAT. J Psychosom Res. 2002;53:963–974.
Magzamen S, Mortimer KM, Davis A, Tager IB. School-based asthma surveillance: A comparison of student and parental report. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2005;16:669–678.
Yawn BP, Wollan P, Kurland M, Bertram S. Comparison of parent and student responses to asthma surveys: Students grades 3–12 and their parents from a suburban private school setting. J Sch Health. 2006;76:241–245.
Lara M, Duan N, Sherbourne C, et al. Differences between child and parent reports of symptoms among Latino children with asthma. Pediatrics. 1998;102:E68.
Kelly AM, Powell CV, Williams A. Parent visual analogue scale ratings of children's pain do not reliably reflect pain reported by child. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2002;18:159–162.
Palermo TM, Zebracki K, Cox S, Newman AJ, Singer NG. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Parent–child discrepancy on reports of pain and disability. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:1840–1846.
Cohen LL, Vowles KE, Eccleston C. Adolescent chronic pain-related functioning: Concordance and discordance of mother-proxy and self-report ratings. Eur J Pain. 2010;14:882–886.
Nakamura EF, Cui L, Lateef T, Nelson KB, Merikangas KR. Parent–child agreement in the reporting of headaches in a national sample of adolescents. J Child Neurol. 2012;27:61–67.
Panepinto J, Hoffmann R, Pajewski N. The effect of parental mental health on proxy reports of health-related quality of life in children with sickle cell disease. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2010;55:714–721.
Elkind D. Egocentrism in adolescence. Child Dev. 1967;38:1025–1034.
Lara M, Akinbami L, Flores G, Morgenstern H. Heterogeneity of childhood asthma among Hispanic children: Puerto Rican children bear a disproportionate burden. Pediatrics. 2006;117:43–53.
Moorman JE, Rudd RA, Johnson CA, et al. National surveillance for asthma—United States, 1980–2004. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007;56(1–14):18–54.
Esteban CA, Klein RB, McQuaid EL, et al. Conundrums in childhood asthma severity, control, and health care use: Puerto Rico versus Rhode Island. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124(238–244):e231–235. 244.
Waldman HB, Perlman SP. Health insurance for Hispanic and other children: Access to care. J Dent Child (Chic). 2005;72:36–38.
Stingone JA, Claudio L. Disparities in the use of urgent health care services among asthmatic children. Ann Allerg Asthma Im. 2006;97:244–250.
Cohen RT, Canino GJ, Bird HR, Shen S, Rosner BA, Celedon JC. Area of residence, birthplace, and asthma in Puerto Rican children. Chest. 2007;131:1331–1338.
Lara M, Gamboa C, Kahramanian MI, Morales LS, Bautista DEH. Acculturation and Latino health in the United States: A review of the literature and its sociopolitical context. Annu Rev Public Health. 2005;26:367–397.
Ayala GX, Baquero B, Klinger S. A systematic review of the relationship between acculturation and diet among Latinos in the United States: Implications for future research. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108:1330–1344.
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no actual or potential conflict of interest, either personal or financial, to disclose.
Funding Source
This research was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute at the National Institutes of Health (R01HL079953; PI = J-M.B.)
Clinical Trial Registry Information
Family Approach to Managing Asthma in Early Teens; NCT00241852
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Jay, M., Stepney, C., Wijetunga, N.A. et al. Accuracy of Weight Perception Among Urban Early Adolescents with Uncontrolled Asthma and Their Caregivers. ann. behav. med. 45, 239–248 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-012-9452-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12160-012-9452-8