Abstract
Objective
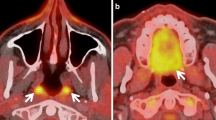
We investigated the prevalence and clinical significance of incidental focal 18F-FDG uptake in the frontal process of the maxilla, mimicking malignancy on PET/CT.
Methods
From a total of 32,834 patients who underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT, patients with focal uptake in the frontal process of the maxilla were selected by a database search. For those patients, medical records including relevant imaging studies were reviewed.
Results
Thirty-nine patients (0.12 %) demonstrated focal uptake on PET/CT. On CT of PET/CT, all lesions showed ground-glass attenuation with or without bony expansion, consistent with fibrous dysplasia. When comparing previous PET/CT, follow-up PET/CT, and CT, a significant difference in degree of 18F-FDG uptake was noted, with no associated change in the size of maxillary lesions. There were no patients who had symptoms or signs related to maxillary lesions during follow-up.
Conclusion
Focal 18F-FDG uptake in the frontal process of the maxilla is a rare, incidental, and persistent finding with variable uptake and can represent a benign condition.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi JY, Lee KS, Kim HJ, Shim YM, Kwon OJ, Park K, et al. Focal thyroid lesions incidentally identified by integrated 18F-FDG PET/CT: clinical significance and improved characterization. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:609–15.
Cho SK, Choi JY, Yoo J, Cheon M, Lee JY, Hyun SH, et al. Incidental focal 18F-FDG uptake in the prostate: clinical significance and differential diagnostic criteria. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;45:192–6.
Park SB, Choi JY, Lee EJ, Yoo J, Cheon M, Cho SK, et al. Diagnostic criteria on 18F-FDG PET/CT for differentiating benign from malignant focal hypermetabolic lesions of parotid gland. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;46:95–101.
Choi JY, Lee KS, Kwon OJ, Shim YM, Baek CH, Park K, et al. Improved detection of second primary cancer using integrated 18F fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography for initial tumor staging. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7654–9.
Yang BT, Wang YZ, Wang XY, Wang ZC, Xian JF, Li J. Fibrous dysplasia-like appearance of the frontal process of the maxilla on CT: prevalence in North China. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:471–3.
Xu H, Zhang M, Zhai G, Li B. The clinical significance of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in early detection of second primary malignancy in cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2010;136:1125–34.
Xu GZ, Guan DJ, He ZY. 18FDG-PET/CT for detecting distant metastases and second primary cancers in patients with head and neck cancer. A meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 2011;47:560–5.
Chong VF, Khoo JB, Fan YF. Fibrous dysplasia involving the base of the skull. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178:717–20.
Stegger L, Juergens KU, Kliesch S, Wormanns D, Weckesser M. Unexpected finding of elevated glucose uptake in fibrous dysplasia mimicking malignancy: contradicting metabolism and morphology in combined PET/CT. Eur Radiol. 2007;17:1784–6.
Kao CH, Sun SS, Shen YY, Chen YK. Misdiagnosis of multiple bone metastases due to increased FDG uptake in polyostotic fibrous dysplasia. Clin Nucl Med. 2007;32:409–10.
Shigesawa T, Sugawara Y, Shinohara I, Fukii T, Mochizuki T, Morishige I. Bone metastasis detected by FDG PET in a patient with breast cancer and fibrous dysplasia. Clin Nucl Med. 2005;30:571–3.
Toba M, Hayashida K, Imakita S, Fukuchi K, Kume N, Shimotsu Y, et al. Increased bone mineral turnover without increased glucose utilization in sclerotic and hyperplastic change in fibrous dysplasia. Ann Nucl Med. 1998;12:153–5.
Aoki J, Watanabe H, Shinozaki T, Takagishi K, Ishijima H, Oya N, et al. FDG PET of primary benign and malignant bone tumors: standardized uptake value in 52 lesions. Radiology. 2001;219:774–7.
Han J, Ryu JS, Shin MJ, Kang GH, Lee HK. Fibrous dysplasia with barely increased uptake on bone scan: a case report. Clin Nucl Med. 2000;25:785–8.
Machida K, Makita K, Nishikawa J, Ohtake T, Lio M. Scintigraphic manifestation of fibrous dysplasia. Clin Nucl Med. 1986;11:426–9.
Aras M, Ones T, Dane F, Nosheri O, Inanir S, Erdil TY, et al. False positive FDG PET/CT resulting from fibrous dysplasia of the bone in the work-up of a patient with bladder cancer: case report and review of the literature. Iran J Radiol. 2012;10:41–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.B., Choi, J.Y., Kim, HJ. et al. Incidental focal 18F-FDG uptake in the frontal process of the maxilla on PET/CT: prevalence and clinical significance. Ann Nucl Med 30, 619–623 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-016-1103-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-016-1103-x