Abstract
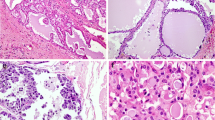
The recently described mammary analogue secretory carcinoma (MASC) is a low-grade salivary gland malignancy that harbors the recurrent cytogenetic abnormality t(12;15) (p13;q25) ETV6-NTRK3. Confirmation of this is currently considered the gold standard for diagnosis. Some have postulated that morphology together with supporting immunohistochemistry is sufficient to diagnose MASC. In this study we retrospectively review a series of 19 MASCs diagnosed based on histology in conjunction with immunohistochemistry; subsequently we performed in situ hybridization using an ETV6 break-apart probe. Immunohistochemistry for S100 protein and mammaglobin as well as fluorescence in situ hybridization using the Vysis ETV6 Dual Color Break-Apart FISH Probe Kit were performed on all cases. The 19 cases were from 12 females and 7 males with ages ranging from 16 to 76 years (mean = 45 years). Sixteen cases were from the parotid gland, 1 case was from a periparotid lymph node and 2 cases were from the submandibular gland. All 19 cases demonstrated moderate to strong expression of S100 protein. Eighteen cases demonstrated strong, diffuse expression of mammaglobin, while one case had only rare tumor cells that strongly expressed mammaglobin. Eighteen of 19 cases (95 %) demonstrated the ETV6 rearrangement by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Given that morphology together with immunohistochemistry is highly correlated with the ETV6 gene rearrangement, we conclude that molecular confirmation is not required to diagnose MASC.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Skalova A, Vanecek T, Sima R, Laco J, Weinreb I, Perez-Ordonez B, Starek I, Geierova M, Simpson RH, Passador-Santos F, Ryska A, Leivo I, Kinkor Z, Michal M. Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary glands, containing the ETV6-NTRK3 fusion gene: a hitherto undescribed salivary gland tumor entity. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010;34:599–608.
Tognon C, Knezevich SR, Huntsman D, Roskelley CD, Melnyk N, Mathers JA, Becker L, Carneiro F, MacPherson N, Horsman D, Poremba C, Sorensen PH. Expression of the ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion as a primary event in human secretory breast carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:367–76.
Knezevich SR, McFadden DE, Tao W, Lim JF, Sorensen PH. A novel ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion in congenital fibrosarcoma. Nat Genet. 1998;18:184–7.
Rubin BP, Chen CJ, Morgan TW, Xiao S, Grier HE, Kozakewich HP, Perez-Atayde AR, Fletcher JA. Congenital mesoblastic nephroma t(12;15) is associated with ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion: cytogenetic and molecular relationship to congenital (infantile) fibrosarcoma. Am J Pathol. 1998;153:1451–8.
Eguchi M, Eguchi-Ishimae M, Tojo A, Morishita K, Suzuki K, Sato Y, Kudoh S, Tanaka K, Setoyama M, Nagamura F, Asano S, Kamada N. Fusion of ETV6 to neurotrophin-3 receptor TRKC in acute myeloid leukemia with t(12;15)(p13;q25). Blood. 1999;93:1355–63.
Kralik JM, Kranewitter W, Boesmueller H, Marschon R, Tschurtschenthaler G, Rumpold H, Wiesinger K, Erdel M, Petzer AL, Webersinke G. Characterization of a newly identified ETV6-NTRK3 fusion transcript in acute myeloid leukemia. Diagn Pathol. 2011;6:19.
Lannon CL, Sorensen PH. ETV6-NTRK3: a chimeric protein tyrosine kinase with transformation activity in multiple cell lineages. Semin Cancer Biol. 2005;15:215–23.
Nordkvist A, Mark J, Gustafsson H, Bang G, Stenman G. Non-random chromosome rearrangements in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the salivary glands. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1994;10:115–21.
Mitani Y, Li J, Rao P, Zhao YJ, Bell D, Lippman SM, Weber RS, Caulin C, El-Naggar AK. Comprehensive analysis of the MYB-NFIB gene fusion in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma: incidence, variability, and clinicopathologic significance. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:4722–31.
Brill LB, Kanner WA, Fehr A, Andrén Y, Moskaluk CA, Löning T, Stenman G, Frierson HF Jr. Analysis of MYB expression and MYB-NFIB gene fusions in adenoid cystic carcinoma and other salivary neoplasms. Mod Pathol. 2011;24:1169–76.
Martins C, Cavaco B, Tonon G, Kaye FJ, Soares J, Fonseca I. A study of MECT1-MAML2 in mucoepidermoid carcinoma and Warthin’s tumor of salivary glands. J Mol Diagn. 2004;6:205–10.
Behboudi A, Enlund F, Winnes M, Andrén Y, Nordkvist A, Leivo I, Flaberg E, Szekely L, Mäkitie A, Grenman R, Mark J, Stenman G. Molecular classification of mucoepidermoid carcinomas-prognostic significance of the MECT1-MAML2 fusion oncogene. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2006;45:470–81.
Kas K, Voz ML, Röijer E, Aström AK, Meyen E, Stenman G, Van de Ven WJ. Promoter swapping between the genes for a novel zinc finger protein and beta-catenin in pleiomorphic adenomas with t(3;8)(p21;q12) translocations. Nat Genet. 1997;15:170–4.
Kas K, Voz ML, Hensen K, Meyen E, Van de Ven WJ. Transcriptional activation capacity of the novel PLAG family of zinc finger proteins. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:23026–32.
Astrom AK, Voz ML, Kas K, Röijer E, Wedell B, Mandahl N, Van de Ven W, Mark J, Stenman G. Conserved mechanism of PLAG1 activation in salivary gland tumors with and without chromosome 8q12 abnormalities: identification of SII as a new fusion partner gene. Cancer Res. 1999;59:918–23.
Persson F, Andren Y, Winnes M, Wedell B, Nordkvist A, Gudnadottir G, Dahlenfors R, Sjögren H, Mark J, Stenman G. High-resolution genomic profiling of adenomas and carcinomas of the salivary glands reveals amplification, rearrangement, and fusion of HMGA2. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009;48:69–82.
Matsuyama A, Hisaoka M, Nagao Y, Hashimoto H. Aberrant PLAG1 expression in pleomorphic adenomas of the salivary gland: a molecular genetic and immunohistochemical study. Virchows Arch. 2011;458:583–92.
Antonescu CR, Katabi N, Zhang L, Sung YS, Seethala RR, Jordan RC, Perez-Ordoñez B, Have C, Asa SL, Leong IT, Bradley G, Klieb H, Weinreb I. EWSR1-ATF1 fusion is a novel and consistent finding in hyalinizing clear-cell carcinoma of salivary gland. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2011;50:559–70.
Shah AA, LeGallo RD, van Zante A, Frierson HF Jr, Mills SE, Berean KW, Mentrikoski MJ, Stelow EB. EWSR1 genetic rearrangements in salivary gland tumors: a specific and very common feature of hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013;37:571–8.
Chenevert J, Duvvuri U, Chiosea S, Dacic S, Cieply K, Kim J, Shiwarski D, Seethala RR. DOG1: a novel marker of salivary acinar and intercalated duct differentiation. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:919–29.
Chiosea SI, Griffith C, Assaad A, Seethala RR. The profile of acinic cell carcinoma after recognition of mammary analog secretory carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:343–50.
Connor A, Perez-Ordonez B, Shago M, Skalova A, Weinreb I. Mammary analog secretory carcinoma of salivary gland origin with the ETV6 gene rearrangement by FISH: expanded morphologic and immunohistochemical spectrum of a recently described entity. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36(1):27–34.
Patel KR, Solomon IH, El-Mofty SK, Lewis JS Jr, Chernock RD. Mammaglobin and S-100 immunoreactivity in salivary gland carcinomas other than mammary analogue secretory carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2013;44:2501–8.
Bishop JA, Yonescu R, Batista D, Eisele DW, Westra WH. Most nonparotid “acinic cell carcinomas” represent mammary analog secretory carcinomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013;37:1053–7.
Laco J, Svajdler M Jr, Andrejs J, Hrubala D, Hacova M, Vanacek T, Skalova A, Ryska A. Mammary analog secretory carcinoma of salivary glands: a report of 2 cases with expression of basal/myoepithelial markers (calponin, CD10 and p63 protein). Pathol Res Pract. 2013;209:167–72.
Bishop JA, Yonescu R, Batista D, Begum S, Eisele DW, Westra WH. Utility of mammaglobin immunohistochemistry as a proxy marker for the ETV6-NTRK3 translocation in the diagnosis of salivary mammary analogue secretory carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2013;44:1982–8.
Sasaki E, Tsunoda N, Hatanaka Y, Mori N, Iwata H, Yatabe Y. Breast-specific expression of MGB1/mammaglobin: an examination of 480 tumors from various organs and clinicopathological analysis of MGB1-positive breast cancers. Mod Pathol. 2007;20:208–14.
Brandwein-Gensler M, Hille J, Wang BY, Urken M, Gordon R, Wang LJ, Simpson JR, Simpson RH, Gnepp DR. Low-grade salivary duct carcinoma: description of 16 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:1040–4.
Chiosea SI, Griffith C, Assaad A, Seethala RR. Clinicopathological characterization of mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary glands. Histopathology. 2012;61:387–94.
Skalova A, Vanecek T, Majewska H, Laco J, Grossmann P, Simpson RH, Hauer L, Andrle P, Hosticka L, Branzovsky J, Michal M. Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma of salivary glands with high-grade transformation: report of 3 cases with the ETV6-NTRK3 gene fusion and analysis of TP53, β-catenin, EGFR, and CCND1 genes. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014;38:23–33.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Harriet Scruggs for allowing us to use her laboratory expertise in fluorescence in situ hybridization.
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, A.A., Wenig, B.M., LeGallo, R.D. et al. Morphology in Conjunction with Immunohistochemistry is Sufficient for the Diagnosis of Mammary Analogue Secretory Carcinoma. Head and Neck Pathol 9, 85–95 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-014-0557-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12105-014-0557-1