Abstract
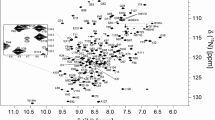
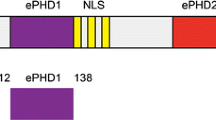
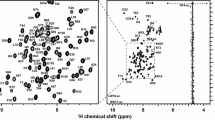
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) can be divided into subgroups based on their RNA-binding characteristics. One subgroup in mammalian cells are the Poly(C)-binding proteins (PCBPs) comprised of hnRNP K/J and hnRNP E1-4 [the latter also known as PCBP 1–4 or α-complex proteins (α-CP) 1–4]. Each subgroup member has three K homology (KH) nucleic acid-binding domains. Individual KH domains bind short single-stranded (ss), poly-pyrimidine-rich nucleic acid sequences with rather weak affinity. In this study, we report the 1H, 13C and 15N backbone resonance assignments of the first and second KH domains of hnRNP E1, which plays a pivotal role in posttranscriptional and translational regulation of RNA targets. Our NMR assignments lay the foundation for a detailed investigation of the dynamic cooperation of the tandem KH1 and KH2 domains to bind nucleic acids.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du Z, Fenn S, Tjhen R, James TL (2008) Structure of a construct of a human poly(C)-binding protein containing the first and second KH domains reveals insights into its regulatory mechanisms. J Biol Chem 283(42):28757–28766
Grishin NV (2001) KH domain: one motif, two folds. Nucleic Acids Res 29(3):638–643
Hussey GS, Chaudhury A, Dawson AE, Lindner DJ, Knudsen CR, Wilce MC, Merrick WC, Howe PH (2011) Identification of an mRNP complex regulating tumorigenesis at the translational elongation step. Mol Cell 41(4):419–431
Leffers H, Dejgaard K, Celis JE (1995) Characterisation of two major cellular poly (rC)-binding human proteins, each containing three K-homologous (KH) domains. Eur J Biochem 230(2):447–453
Makeyev AV, Liebhaber SA (2002) The poly(C)-binding proteins: a multiplicity of functions and a search for mechanisms. RNA 8(3):265–278
Matunis MJ, Michael WM, Dreyfuss G (1992) Characterization and primary structure of the poly(C)-binding heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex K protein. Mol Cell Biol 12(1):164–171
Shen Y, Delaglio F, Cornilescu G, Bax A (2009) TALOS+: a hybrid method for predicting protein backbone torsion angles from NMR chemical shifts. J Biomol NMR 44(4):213–223
Tomonaga T, Levens D (1996) Activating transcription from single stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(12):5830–5835
Vranken WF, Boucher W, Stevens TJ, Fogh RH, Pajon A, Llinas M, Ulrich EL, Markley JL, Ionides J, Laue ED (2005) The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: development of a software pipeline. Proteins 59(4):687–696
Yoga YM, Traore DA, Sidiqi M, Szeto C, Pendini NR, Barker A, Leedman PJ, Wilce JA, Wilce MC (2012) Contribution of the first K-homology domain of poly(C)-binding protein 1 to its affinity and specificity for C-rich oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res 40(11):5101–5114
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the South Carolina Clinical & Translational Research (SCTR) Institute (UL1TR000062). We thank Dr. Daniella Ishimaru (MUSC) for KH1–KH2 NMR sample preparation and acknowledge Dr. Philip H. Howe (MUSC) for the generous gift of the parent GST-hnRNP E1 construct and the support of the Hollings Marine Laboratory NMR facility for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Hennig, M. 1H, 15N and 13C backbone resonance assignments of the N-terminal, tandem KH domains of human hnRNP E1. Biomol NMR Assign 9, 431–434 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-015-9624-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-015-9624-0