Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the coagulation parameters at the time of diagnosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) patients.
Methods
A total of 65 newly diagnosed ALL patients upto 18 y of age along with 30 age and sex matched controls were included in the study. Coagulation tests including Prothrombin Time (PT), Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT), Fibrinogen (FBG) assay, D-dimer (D-DI) assay, Coagulation inhibitor levels and tests for fibrinolysis were performed.
Results
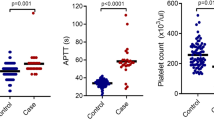
At baseline, APTT of the patients was significantly prolonged (p 0.033), but PT and fibrinogen were comparable in the two groups. Protein C (PC) and Protein S (PS) were both significantly reduced in the cases, while antithrombin was comparable to control values (p < 0.001, p < 0.001 & p = 0.828 respectively). Tissue plasminogen activator levels (tPA) were significantly lower in the cases (p < 0.001) but Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) values were comparable. D-DI levels were significantly high (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
The onset of leukemia is associated with hemostatic derangement favouring hypercoagulability. The coagulopathy is due to thrombin activation (as evidenced by raised d-dimer). The decreased fibrinolysis (due to reduced tPA and raised PAI-1) and low levels of PC and PS contribute to the hypercoagulable state at the time of diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young YL, Miller RW. Incidence of malignant tumors in U.S. children. J Pediatr. 1975;86:254–8.
Swerdlow SH, Camp E, Harris NL, et al. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2008. p. 168.
Athale UH, Chan AK. Thrombosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: part I. Epidemiology of thrombosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Thromb Res. 2003;111:125–31.
Caruso V, Iacoviello L, Di Castelnuovo A, et al. Thrombotic complications in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis of 17 prospective studies comprising 1752 pediatric patients. Blood. 2006;108:2216–22.
Ku GH, White RH, Chew HK, Harvey DJ, Zhou H, Wun T. Venous thromboembolism in patients with acute leukemia: incidence, risk factors, and effect on survival. Blood. 2009;113:3911–7.
Celkan T. Thrombosis in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Austral-Asian J Cancer. 2008;7:203–19.
Priest JR, Ramsay NK, Bennett AJ, Krivit W, Edson JR. The effect of l-asparaginase on antithrombin, plasminogen, and plasma coagulation during therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Pediatr. 1982;100:990–5.
Ribeiro RC, Pui CH. The clinical and biological correlates of coagulopathy in children with acute leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1986;4:1212–8.
Homans AC, Rybak ME, Baglini RL, Tiarks C, Steiner ME, Forman EN. Effect of l-asparaginase administration on coagulation and platelet function in children with leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 1987;5:811–7.
Giordano P, Molinari AC, Del Vecchio GC, et al. Prospective study of hemostatic alterations in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2010;85:325–30.
Abshire TC, Gold SH, Odom LF, Carson SD, Hathaway WF. The coagulopathy of childhood leukemia. Thrombin activation or primary fibrinolysis? Cancer. 1990;66:716–21.
Mitchell L, Hoogendoorn H, Giles AR, Vegh P, Andrew M. Increased endogenous thrombin generation in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: risk of thrombotic complications in l-asparaginase induced antithrombin deficiency. Blood. 1994;83:386–91.
Oner AG, Gurgey A, Kirazli S, Okur H, Tunc B. Changes of hemostatic factors in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia receiving combined chemotherapy including high dose methylprednisolone and l-asparaginase. Leuk Lymphoma. 1999;33:361–4.
Mitchell LG, Halton JM, Vegh PA, et al. Effect of disease and chemotherapy on haemostasis in children with acute lymphoid leukemia. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1994;16:120–6.
Dixit A, Kannan M, Mahapatra M, Choudhry VP, Saxena R. Roles of protein C, protein S, and antithrombin III in acute leukemia. Am J Hematol. 2006;81:171–4.
Mall V, Thomas KB, Sauter S, Niemeyer CM, Sutor AH. Effect of glucocorticoids, E.Coli and Erwinia l-asparaginase on haemostatic proteins in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Klin Padiatr. 1999;211:205–10.
Legnani C, Palareti G, Pession A, et al. Intravascular coagulation phenomena associated with prevalent fall in fibrinogen and plasminogen during l-asparaginase treatment in leukemia children. Haemostasis. 1988;18:179–86.
Semeraro N, Montemurro P, Giordano P, et al. Unbalanced coagulation-fibrinolysis potential during l-asparaginase therapy in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Thromb Haemost. 1990;64:38–40.
Andrew M, Vegh P, Johnston M, Bowker J, Ofosu F, Mitchell L. Maturation of the hemostatic system during childhood. Blood. 1992;80:1998–2005.
Kwaan HC. Double hazard of thrombophilia and bleeding in leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2007;1:151–7.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Bhavuk Garg for help in statistical analysis and Dr. Arushi Sehgal for help with data compilation and statistical analysis.
Contributions
SS: Conducted the study, performed the tests and statistics, analysed the data and wrote the article. SS: Supervised the study, edited the article and will act as guarantor for the paper; JC and AN: Supervised the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sehgal, S., Sharma, S., Chandra, J. et al. Coagulation Profile at Diagnosis in Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Indian J Pediatr 83, 1082–1086 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-016-2114-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-016-2114-2