Abstract
Objective
To investigate long-term prognosis of infants with esophageal atresia (EA) and/or tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF).
Methods
The data of patients with EA were investigated from their medical files. For the neurodevelopmental evaluation, they were requested to come for a return visit to authors' polyclinic. Intellectual development was assessed by Ankara Developmental Screening Inventory (ADSI) (for 0–6 age) and Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Revised (WISC-R) (for 6–16 age).
Results
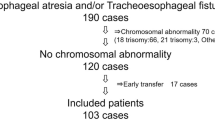
Of the 57 patients, 50 had EA+ distal TEF (87.7 %), six had isolated EA (10.5 %) and one had isolated TEF (1.8 %). Of the total patients, 18 cases (31 %) died and remaining 39 cases (69 %) survived. In the surviving cases, the most common long-term complication was dysphagia (n = 37, 94.8 %). Intellectual levels of the 24 patients assessed by ADSI were normal and of the remaining 15 cases evaluated by WISC-R ranged between 95 and 110 points.
Conclusions
The long-term complications and hospital visits are common in surviving cases of EA; however, they have normal cognitive functions and physical developmental characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harmon CM, Coran AG. Congenital anomalies of the esophagus. In: Grosfeld JL, O’Neill JA, Fonkalsrud EW, Coran AG, editors. Pediatric surgery. Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier; 2006. p. 1051–81.
Spitz L Esophageal atresia: lessons I have learned in a 40-year experience. J Pediatr Surg. 2006;41:1635–40.
Holder TM, Cloud DT, Lewis JE Jr, Pilling GP 4th. Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula. A survey of its members by the surgical section of the American academy of pediatrics. Pediatrics. 1964;34:542–9.
Demircan M, Aksoy T, Ceran C, Kafkasli A. Tracheal agenesis and esophageal atresia with proximal and distal bronchoesophageal fistulas. J Pediatr Surg. 2008;43:e1–3.
Felix JF, Tibboel D, de Klein A. Chromosomal anomalies in the etiology of oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula. Eur J Med Genet. 2007;50:163–75.
Starka Z, Patela N, Clarnette T, Moody A. Triad of tracheoesophageal fistula-esophageal atresia, pulmonary hypoplasia, and duodenal atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 2007;42:1146–8.
Sistonen SJ, Koivusalo A, Lindahl H, Pukkala E, Rintala RJ, Pakarinen MP. Cancer after repair of esophageal atresia: population-based long-term follow-up. J Pediatr Surg. 2008;43:602–5.
Little DC, Rescorla FJ, Grosfeld JL, West KW, Scherer LR, Engum SA. Long-term analysis of children with esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula. J Pediatr Surg. 2003;38:852–6.
Sezgin N Two different validity study of Ankara developmental screening inventory (ADSI): criterion- related validity and concurrent discrimination validity. Turk J Child Adolesc Ment Health. 2011;18:185–96.
Savasir I, Sahin N. Wechsler intelligence scale for children-revised (WISC-R) Turkish handbook. Ankara: Turkish Psychological Association Publications; 1995.
Celayir S, İlçe Z, Tekand GT, et al. The experience with esophagus atresia (1978–2000). Cerrahpaşa J Med. 2002;33:86–92.
Spitz L. Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal malformations. In: Ashcraff KW, Holcomb GW, Murphy JP, editors. Pediatric surgery. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2005. p. 352–70.
Mortell AE, Azizkhan RG. Esophageal atresia repair with thoracotomy: the Cincinnati contemporary experience. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2009;18:12–9.
Okamoto T, Takamizawa S, Arai H, et al. Esophageal atresia: prognostic classification revisited. Surgery. 2009;145:675–81.
Gupta DK, Sharma S. Esophageal atresia: the total care in a high-risk population. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2008;17:236–43.
Spitz L Gastric transposition in children. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2009;18:30–3.
Rintala RJ, Sistonen S, Pakarinen MP. Outcome of esophageal atresia beyond childhood. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2009;18:50–6.
Koivusalo A, Pakarinen MP, Rintala RJ. The cumulative incidence of significant gastrooesophageal reflux in patients with oesophageal atresia with a distal fistula-a systematic clinical, pH-metric, and endoscopic follow-up study. J Pediatr Surg. 2007;42:370–4.
Van der Zee DC, Klaas MA. Thoracoscopic treatment of esophageal atresia with distal fistula of tracheomalacia. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2007;16:224–30.
Bilirim A, Yurtçu M, Günel E, Abasıyanık A. 20 years' experience on esophageal atresia. Selçuk Tıp Derg. 2012;28:26–31.
Faugli A, Bjørnland K, Emblemc R, Novik TS, Diseth TH. Mental health and psychosocial functioning in adolescents with esophageal atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 2009;44:729–37.
Contributions
UB: Planing and writing of the paper; FE: Collection of the data; MS: Management and follow up of the patients; IE: Developmental evaluation of the cases; MA: Language redaction; AK: Supervisor of the study and will act as guarantor for this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bakal, U., Ersoz, F., Eker, I. et al. Long-Term Prognosis of Patients with Esophageal Atresia and/or Tracheoesophageal Fistula. Indian J Pediatr 83, 401–404 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-015-1930-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-015-1930-0