Abstract
Background
To investigate the incidence, risk, and prognostic factors of acute kidney injury (AKI) in acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) patients.
Methods
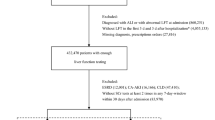
A total of 188 patients were prospectively included and divided into AKI and non-AKI groups. Patients were followed at 1, 3, 7, 14, 28, 60, and 90 days after the onset of AKI. Significant risk factors were screened by univariate and Cox multivariate survival analyses to confirm the independent risk factors for 30- or 90-day mortality and the 90-day renal function recovery rate.
Results
A total of 98 AKI cases (52.1%, [95% CI 44.9–59.3%]) occurred and the risk factors for AKI development in ACLF patients were age > 50 years (p = 0.009) and albumin (Alb) levels < 32 g/L (p = 0.007). The 30- and 90-day mortalities were significantly higher in the AKI than in the non-AKI group (79.6 vs 41.1%, 82.7 vs 56.7%, p < 0.05). AKI highest staging occurring within < 4 days of its onset and spontaneous peritonitis as well as MELD scores > 27 were independent risk factors for 30- and 90-day mortalities of ACLF AKI patients. AKI stage 3 and age > 52 years were independent risk factors for non-renal function recovery in ACLF patients with AKI.
Conclusions
ACLF patients had a high incidence of AKI, which correlated with 30- and 90-day mortalities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bydash JR, Ishani A. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: a work in progress. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2011;6:2555–2557
Angeli P, Rodriguez E, Piano S, Ariza X, Morando F, Sola E, et al. Acute kidney injury and acute-on-chronic liver failure classifications in prognosis assessment of patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gut 2015;64:1616–1622
Angeli P, Gines P, Wong F, Bernardi M, Boyer TD, Gerbes A, et al. Diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury in patients with cirrhosis: revised consensus recommendations of the International Club of Ascites. Gut 2015;64:531–537
Kidney Disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury working group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl 2012;2(1):1–138
Liver F, Artificial Liver Group CSoIDCMA, Severe Liver D, Artificial Liver Group CSoHCMA. Diagnostic and treatment guidelines for liver failure (2012 version). Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2013;21:177–183
Sarin SK, Kedarisetty CK, Abbas Z, Amarapurkar D, Bihari C, Chan AC, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure: consensus recommendations of the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) 2014. Hepatol Int 2014;8:453–471
Cholongitas E, Papatheodoridis GV, Vangeli M, Terreni N, Patch D, Burroughs AK. Systematic review: the model for end-stage liver disease—should it replace Child–Pugh’s classification for assessing prognosis in cirrhosis? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005;22:1079–1089
Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, Kremers W, Therneau TM, Kosberg CL, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology 2001;33:464–470
Palevsky PM, Zhang JH, O’Connor TZ, Chertow GM, Crowley ST, Choudhury D, et al. Intensity of renal support in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med 2008;359:7–20
Davenport A, Sheikh MF, Lamb E, Agarwal B, Jalan R. Acute kidney injury in acute-on-chronic liver failure: where does hepatorenal syndrome fit? Kidney Int 2017;92:1058–1070
Maiwall R, Sarin SK, Moreau R. Acute kidney injury in acute on chronic liver failure. Hepatol Int 2016;10:245–257
Bajaj JS. Defining acute-on-chronic liver failure: will East and West ever meet? Gastroenterology 2013;144:1337–1339
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, et al. Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 2007;11:R31
Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, Mehta RL, Palevsky P. Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative w. Acute renal failure—definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care 2004;8:R204–R212
Yuan W, Zhang YY, Zhang ZG, Zou Y, Lu HZ, Qian ZP. Risk factors and outcomes of acute kidney injury in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Am J Med Sci 2017;353:452–458
Hoste EA, Clermont G, Kersten A, Venkataraman R, Angus DC, De Bacquer D, et al. RIFLE criteria for acute kidney injury are associated with hospital mortality in critically ill patients: a cohort analysis. Crit Care 2006;10:R73
Uchino S, Bellomo R, Goldsmith D, Bates S, Ronco C. An assessment of the RIFLE criteria for acute renal failure in hospitalized patients. Crit Care Med 2006;34:1913–1917
Ricci Z, Cruz D, Ronco C. The RIFLE criteria and mortality in acute kidney injury: a systematic review. Kidney Int 2008;73:538–546
Joannidis M, Metnitz B, Bauer P, Schusterschitz N, Moreno R, Druml W, et al. Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients classified by AKIN versus RIFLE using the SAPS 3 database. Intensive Care Med 2009;35:1692–1702
Ali T, Khan I, Simpson W, Prescott G, Townend J, Smith W, et al. Incidence and outcomes in acute kidney injury: a comprehensive population-based study. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007;18:1292–1298
Peng Y, Qi X, Guo X. Child–Pugh versus MELD score for the assessment of prognosis in liver cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e2877
Duan BW, Lu SC, Wu JS, Guo QL, Zeng DB, Jiang T, et al. Model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score does not predict outcomes of hepatitis B-induced acute-on-chronic liver failure in transplant recipients. Transpl Proc 2014;46:3502–3506
Maiwall R, Kumar G, Bharadwaj A, Jamwal K, Bhadoria AS, Jain P, et al. AKI persistence at 48 h predicts mortality in patients with acute on chronic liver failure. Hepatol Int 2017;11:529–539
Zang H, Liu F, Liu H, You S, Zhu B, Wan Z, et al. Incidence, risk factors and outcomes of acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) of underlying cirrhosis. Hepatol Int 2016;10:807–818
Abdel-Kader K, Palevsky PM. Acute kidney injury in the elderly. Clin Geriatr Med. 2009;25:331–358
Wiedermann CJ, Wiedermann W, Joannidis M. Hypoalbuminemia and acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis of observational clinical studies. Intensive Care Med 2010;36:1657–1665
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (2013SY048); and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (14DZ2260200, the project of Shanghai Key Laboratory of Kidney and Blood Purification).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Nan Chen, Xiaohong Chen, Xiaoqiang Ding, and Jie Teng declare that they have no competing conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the ethical committee of the Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center (SHAPHC). The study was carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines and written informed consents were obtained from all participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, N., Chen, X., Ding, X. et al. Analysis of the high incidence of acute kidney injury associated with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Hepatol Int 12, 262–268 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-018-9866-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-018-9866-x