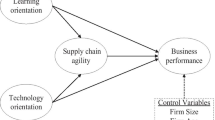
Abstract
To improve business performance in rapidly changing environments, supply chain agility can be a crucial requisite to address responsiveness issues, especially in environments with high levels of customization. This paper examines the effect of supply chain agility on customer service, differentiation, and business performance. A survey research methodology was employed using a sample of 156 manufacturing firms that provide high levels of customization. In particular, structural equation modeling (SEM) was employed to evaluate the proposed model. The results suggest that supply chain agility influences customer service and differentiation positively. However, it does not affect business performance directly; instead, better business performance can be achieved and mediated through improved customer service and differentiation. In particular, differentiation through customer service is the most effective way to improve business performance, and supply chain agility can help to achieve high-level customer service. The paper advises managers on details of how to fulfil their business performance ambitions better through suggested key agile supply chain management activities.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Shankar R, Tiwari MK (2006) Modeling the metrics of lean, agile and leagile supply chain: an ANP-based approach. Eur J Oper Res 173(1):211–225
Aitken JMC, Towill D (2002) Understanding, implementing and exploiting agility and leanness. Int J Logist 5(1):59–74
Armstrong JS, Overton TS (1977) Estimating nonresponse bias in mail surveys. J Mark Res 14(3):396–402
Baker P (2008) The design and operation of distribution centres within agile supply chains. Int J Prod Econ 111(1):27–41
Beamon BM (1998) Supply chain design and analysis: models and methods. Int J Prod Econ 55(3):281–294
Beamon BM (1999) Measuring supply chain performance. Int J Oper Prod Manag 19(3/4):275–292
Bernardes ES, Hanna MD (2009) A theoretical review of flexibility, agility and responsiveness in the operations management literature toward a conceptual definition of customer responsiveness. Int J Oper Prod Manag 29(2):30–53
Chan FTS, Qi HJ (2003) An innovative performance measurement method for supply chain management. Supply Chain Manag 8(3/4):209–223
Chiang CY, Hillmer C, Suresh N (2016) An empirical investigation of the impact of strategic sourcing and flexibility on firm’s supply chain agility. Int J Oper Prod Manag 32(1):49–78
Fisher ML (1997) What is the right supply chain for your product? Harv Bus Rev 75(2):105–116
Fisher ML, Ittner CD (1999) The impact of product variety on automobile assembly operations: empirical evidence and simulation analysis. Manag Sci 45(6):771–786
Fornell C, Larcker DF (1981) Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J Mark Res 18(1):39–50
Gligor DM, Holcomb MC (2012) Understanding the role of logistics capabilities in achieving supply chain agility: a systematic literature review. Supply Chain Manag 17(4):438–453
Goldman SL, Nagel RN, Preiss K (1995) Agile competitors and virtual organizations: strategies for enriching the customer. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Hair FJ, Black WC, Babin BJ, Anderson RE (2010) Multivariate data analysis: a global perspective. Pearson Education, New Jersey
Hallgren M, Olhager J (2009) Lean and agile manufacturing: external and internal drivers and performance outcomes. Int J Oper Prod Manag 29(10):976–999
Hiroshi K, David B (1999) Agility, adaptability and leanness: a comparison of concepts and a study of practice. Int J Prod Econ 60(3):43–51
Hu SJ, Ko J, Weyand L, ElMaraghy HA, Lien TK, Koren Y, Bley H, Chryssolouris G, Nasr N, Shpitalni M (2011) Assembly system design and operations for product variety. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 60(2):715–733
Hughes P, Morgan RE (2008) Fitting strategic resources with product-market strategy: performance implications. J Bus Res 61(4):323–331
Jeong JS, Hong P (2007) Customer orientation and performance outcomes in supply chain management. J Enterp Inf Manag 20(5):578–594
Kim SW (2006) Effects of supply chain management practices, integration and competition capability on performance. J Supply Chain Manag 11(3):241–248
Kline RB (2011) Principles and practice of structural equation modelling. Guilford Press, New York
Kotha S, Orne D (1989) Generic manufacturing strategies: a conceptual synthesis. Strateg Manag J 10(3):211–231
Lampel J, Mintzberg H (1996) Customizing customization. Sloan Manage Rev 38(1):21–30
Liu H, Ke W, Wei K, Hua Z (2013) The impact of IT capabilities on firm performance: the mediating role of absorptive capacity and supply chain agility. Decis Support Syst 54:1452–1462
Mason JR, Naylor B, Towill DR (2000) Lean, agile or leagile? Matching your supply chain to the marketplace. Int J Prod Res 38(17):4061–4070
Mentzer JT, DeWitt W, Keebler JS, Min S, Nix NW, Smith CD, Zacharia ZG (2001) Defining supply chain management. J Bus Logist 22(2):1–26
Meyr H (2004) Supply chain planning in the German automotive industry. OR Spectr 26(4):447–470
Miles RE, Snow CC (1978) Organizational strategy, structure, and process. McGraw-Hill, New York
Milfont TL, Fischer R (2010) Testing measurement invariance across groups: applications in cross-cultural research. Int J Psychol Res 3(1):111–121
Narasimhan R, Soo Wook K (2002) Effect of supply chain integration on the relationship between diversification and performance: evidence from Japanese and Korean firms. J Oper Manag 20(3):303–323
Ngai EWT, Chau DCK, Chan TLA (2011) Information technology, operational, and management competencies for supply chain agility: findings from case studies. J Strateg Inf Syst 20(3):232–249
Otto A, Kotzab H (2003) Does supply chain management really pay? Six perspectives to measure the performance of managing a supply chain. Eur J Oper Res 144(2):306–320
Panayides PM (2007) The impact of organizational learning on relationship orientation, logistics service effectiveness and performance. Ind Mark Manag 36(1):68–80
Porter ME (1980) Competitive strategy: techniques for analyzing industries and competitors. Free Press, New York
Ramdas K, Spekman R (2000) Chain or shackles: understanding what drives supply-chain performance. Interfaces 30(4):3–21
Rosenzweig ED, Roth AV, Dean JW (2003) The influence of an integration strategy on competitive capabilities and business performance: an exploratory study of consumer products manufacturers. J Oper Manag 21(4):437–456
Sánchez AM, Pérez MP (2005) Supply chain flexibility and firm performance: a conceptual model and empirical study in the automotive industry. Int J Oper Prod Manag 25(7):681–700
Segars AH, Grover V (1993) Re-examining perceived ease of use and usefulness: a confirmatory factor analysis. MIS Q 17(4):517–525
Sezen B (2008) Relative effects of design, integration and information sharing on supply chain performance. Supply Chain Manag 13(3):233–240
Sharifi H, Zhang Z (1999) A methodology for achieving agility in manufacturing organisations: an introduction. Int J Prod Econ 62(2):7–22
Stavrulaki E, Davis M (2010) Aligning products with supply chain processes and strategy. Int J Logist Manag 21(1):127–151
Swafford PM, Ghosh S, Murthy N (2006) The antecedents of supply chain agility of a firm: scale development and model testing. J Oper Manag 24(2):170–188
Swafford PM, Ghosh S, Murthy N (2008) Achieving supply chain agility through IT integration and flexibility. Int J Prod Econ 116(2):288–297
Treville SD, Shapiro RD, Hameri AP (2004) From supply chain to demand chain: the role of lead time reduction in improving demand chain performance. J Oper Manag 21(6):613–627
Tse YK, Zhang M, Akhtar P, MacBryde F (2016) Embracing supply chain agility: an investigation in the electronics industry. J Supply Chain Manag 21(1):140–156
Van Hoek RI, Harrison A, Christopher M (2001) Measuring agile capabilities in the supply chain. Int J Oper Prod Manag 21(2):126–147
Vickery SK, Calantone R, Dröge C (1999) Supply chain flexibility: an empirical study. J Supply Chain Manag 35(3):16–24
Vickery SK, Jayaram J, Droge C, Calantone R (2003) The effects of an integrative supply chain strategy on customer service and financial performance: an analysis of direct versus indirect relationships. J Oper Manag 21(5):523–539
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Um, J. The impact of supply chain agility on business performance in a high level customization environment. Oper Manag Res 10, 10–19 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-016-0120-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-016-0120-1