Abstract
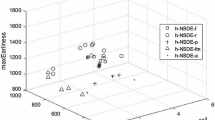
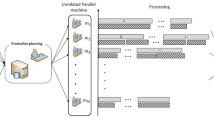
This paper addresses a fuzzy mixed-integer non-linear programming (FMINLP) model by considering machine-dependent and job-sequence-dependent set-up times that minimize the total completion time, the number of tardy jobs, the total flow time and the machine load variation in the context of unrelated parallel machine scheduling (UPMS) problem. The above-mentioned multi-objectives were considered based on non-zero ready times, machine- and sequence-dependent set-up times and secondary resource constraints for jobs. The proposed approach considers unrelated parallel machines with inherent uncertainty in processing times and due dates. Since the problem is shown to be NP-hard in nature, it is a challenging task to find the optimal/near-optimal solutions for conflicting objectives simultaneously in a reasonable time. Therefore, we introduced a new multi-objective-based evolutionary artificial immune non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (AI-NSGA-II) to resolve the above-mentioned complex problem. The performance of the proposed multi-objective AI-NSGA-II algorithm has been compared to that of multi-objective particle swarm optimization (MOPSO) and conventional non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm (CNSGA-II), and it is found that the proposed multi-objective-based hybrid meta-heuristic produces high-quality solutions. Finally, the results obtained from benchmark instances and randomly generated instances as test problems evince the robust performance of the proposed multi-objective algorithm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ying K C and Liao C J 2004 An ant colony system for permutation flow-shop sequencing. Comput. Oper. Res. 31(5): 791–801
Allahverdi A, Ng C T, Cheng T E and Kovalyov M Y 2008 A survey of scheduling problems with setup times or costs. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 187(3): 985–1032
Frendewey J O and Sumichrast R T 1988 Scheduling parallel processors with setup cost and resource limitations. Decision Sci. 19(1): 138–146
Blidgue U, Kirac F, Kurtulan M and Pekgun P 2004 A tabu search algorithm for parallel machine total tardiness problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 31(3): 397–414
Lin S W, Lu C C and Ying K C 2011 Minimization of total tardiness on unrelated parallel machines with sequence- and machine-dependent setup times under due date constraints. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 53(1–4): 353–361
Lin Y K, Pfund M E and Fowler J W 2011 Heuristics for minimizing regular performance measures in unrelated parallel machine scheduling problems. Comput. Oper. Res. 38(6): 901–916
Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Taheri F, Bazzazi M, Izadi M and Sassani F 2009 Design of a genetic algorithm for bi-objective unrelated parallel machines scheduling with sequence-dependent setup times and precedence constraints. Comput. Oper. Res. 36(12): 3224–3230
Cheng T C E and Sin C C S 1990 A state of the art review of parallel-machine scheduling research. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 47(3): 271–292
Santos F Charrua, Francisco Brojo and Pedro M Vilarinho 2012 Lot sizing and scheduling in parallel uniform machines—a case study. INTECH Open Access Publisher. doi:10.5772/50975
Kamath S 2011 Unrelated parallel machine scheduling—perspectives and progress. OPSEARCH 48(4): 318–334
Wang X and Cheng T C E 2015 A heuristic for scheduling jobs on two identical parallel machines with a machine availability constraint. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 161: 74–82
Li K, Shi Y, Yang S L and Cheng B Y 2011 Parallel machine scheduling problem to minimize the makespan with resource dependent processing times. Appl. Soft Comput. 11(8): 5551–5557
Cao D, Chen M and Wan G 2005 Parallel machine selection and job scheduling to minimize machine cost and job tardiness. Comput. Oper. Res. 32(8): 1995–2012
Gairing M, Monien B and Woclaw A 2007 A faster combinatorial approximation algorithm for scheduling unrelated parallel machines. Theor. Comput. Sci. 380(1): 87–99
Rocha P, Ravetti M, Mateus G and Pardalos P 2008 Exact algorithms for a scheduling problem with unrelated parallel machines and sequence and machine-dependent setup times. Comput. Oper. Res. 35: 1250–1264
Fanjul-Peyro L and Ruiz R 2010 Iterated greedy local search methods for unrelated parallel machine scheduling. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 207: 55–69
Mehravaran Y and Logendran R B 2011 Supply chain scheduling on unrelated-parallel machines. J. Chin. Inst. Ind. Eng. 28(2): 91–101
Yilmaz Eroglu D, Ozmutlu H C and Ozmutlu S 2014 Genetic algorithm with local search for the unrelated parallel machine scheduling problem with sequence-dependent set-up times. Int. J. Prod. Res. 52(19): 5841–585
Yin N, Kang L, Sun T C, Yue C and Wang X R 2014 Unrelated parallel machines scheduling with deteriorating jobs and resource dependent processing times. Appl. Math. Model. 38(19): 4747–4755
Wang I L, Wang Y C and Chen C W 2013 Scheduling unrelated parallel machines in semiconductor manufacturing by problem reduction and local search heuristics. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 25(3): 343–366
Gokhale R, and Mathirajan M 2012 Scheduling identical parallel machines with machine eligibility restrictions to minimize total weighted flowtime in automobile gear manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 60(9–12): 1099–1110
Chang P C and Chen S H 2011 Integrating dominance properties with genetic algorithms for parallel machine scheduling problems with setup times. Appl. Soft Comput. 11(1): 1263–1274
Vairaktarakis G L and Cai X 2003 The value of processing flexibility in multipurpose machines. IIE Trans. 35(8): 763–774
Chen J F and Wu T H 2006 Total tardiness minimization on unrelated parallel machine scheduling with auxiliary equipment constraints. Omega 34(1): 81–89
Chen J F 2005 Unrelated parallel machine scheduling with secondary resource constraints. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 26(3):285–292
Ying K C, Lee Z J, Lu C C and Lin S W 2012 Metaheuristics for scheduling a no-wait flowshop manufacturing cell with sequence-dependent family setups. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 58(5–8): 671–682
Hu X, Bao J S and Jin Y 2010 Minimising makespan on parallel machines with precedence constraints and machine eligibility restrictions. Int. J. Prod. Res. 48(6): 1639–1651.
Lamothe J, Marmier F, Dupuy M, Gaborit P and Dupont L 2011 Scheduling rules to minimize total tardiness in a parallel machine problem with setup and calendar constraints. Comput. Oper. Res. 39(6): 1236–1244
Rambod M and Rezaeian J 2014 Robust meta-heuristics implementation for unrelated parallel machines scheduling problem with rework processes and machine eligibility restrictions. Comput. Ind. Eng. 77: 15–28
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S and Meyarivan T 2002 A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6: 182–197
Goldberg D E 1989 Genetic algorithms in search optimization and machine learning. New York: Addison-Wesley
Srinivas N and Deb K 1994 Multi-objective optimization using nondominated sorting in genetic algorithms. Evol. Comput. 2: 221–248
Chen P C and Hwang Y K 1992 SANDROS: A motion planner with performance proportional to task difficulty. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation, IEEE 1992, pp. 2346–2353
Cheng R and Gen M 1998 Loop layout design problem in flexible manufacturing systems using genetic algorithms. Comput. Ind. Eng. 34(1): 53–61
Torabi S A, Sahebjamnia N, Mansouri S A and Bajestani M A 2013 A particle swarm optimization for a fuzzy multi-objective unrelated parallel machines scheduling problem. Appl. Soft. Comput. 13(12): 4750–4762
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8(3): 338–353
Kennedy J F, Kennedy J, Eberhart R C and Shi Y 2001 Swarm intelligence. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco
Reeves C R 1995 A genetic algorithm for flowshop sequencing. Comput. Oper. Res. 22(1): 5–13
Huo Y, Leung J Y T and Zhao H 2007 Bi-criteria scheduling problems: number of tardy jobs and maximum weighted tardiness. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 177(1): 116–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MANUPATI, V.K., RAJYALAKSHMI, G., CHAN, F.T.S. et al. A hybrid multi-objective evolutionary algorithm approach for handling sequence- and machine-dependent set-up times in unrelated parallel machine scheduling problem. Sādhanā 42, 391–403 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-017-0611-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-017-0611-2