Abstract
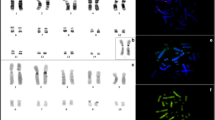
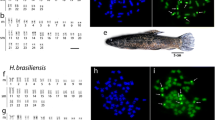
The karyotype of the neotropical primate genus Cebus (Platyrrhini: Cebidae), considered the most ancestral one, shows the greatest amount of heterochromatin described among Platyrrhini genera. Banding techniques and restriction enzyme digestion have previously revealed great variability of quantity and composition of heterochromatin in this genus. In this context, we use fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) to analyse this genomic region and discuss its possible role in the diversification of Cebus. We used a heterochromatin probe for chromosome 11 of Cebus libidinosus (11qHe+ CLI probe), obtained by chromosome microdissection. Twenty-six specimens belonging to the families Atelidae, Cebidae, Callitrichidae and Pithecidae (Platyrrhini) were studied. Fourteen out of 26 specimens were Cebus (Cebidae) individuals of C. libidinosus, C. xanthosternos, C. apella, C. nigritus, C. albifrons, C. kaapori and C. olivaceus. In Cebus specimens, we found 6 to 22 positive signals located in interstitial and telomeric positions along the different species. No hybridization signal was observed among the remaining Ceboidea species, thus reinforcing the idea of a Cebus-specific heterochromatin composed of a complex system of repetitive sequences.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral P. J. S., Finotelo L. F. M., de Oliveira E. H. C., Pissinatti A., Nagamachi C. Y. and Pieczarka J. C. 2008 Phylogenetic studies of the genus Cebus (Cebidae-Primates) using chromosome painting and G-banding. BMC Evol. Biol. 8, 169 (doi:10.1186/1471-2148-8-169).
Buckton K. and Evans H., 1973 Method for the analysis of human chromosome aberrations. WHO Publications, Geneva, Switzerland.
Capanna E. 1995 Mus musculus: un modelo de especiación cromosómica. Marmosiana 1, 7–22.
Capanna E., Civitelli M. V. and Cristaldim M. 1977 Chromosomal rearrangement, reproductive isolation and speciation in mammals. The case of Mus musculus. Boll. Zool. 44, 213–246.
Dutrillaux B., Couturier J., Viegas-Péquignot E., Chauvier G. and Trebbau P. 1978 Présence d’une hétérochromatine abondante dans le caryotype de deux Cebus: C. capucinus et C. nigrivittatus. Ann. Génét. 21, 142–148.
Egòzcue J. 1971 Técnicas en Citogénetica. Espaxs, Madrid, España.
Fanning T. G., Seuánez H. N and Forman L. 1993 Satellite DNA sequences in the New World primate Cebus apella (Platyrrhini, Primates). Chromosoma 102, 306–311.
Ferrucci L., Romano E., Derme V., Nicolai F., Gorostiaga M., Zunino G. and Mudry M. D. 1995 Restriction enzymes induced band in Cebus apella: A method for detect intraspecific variability of satellite DNA sequences. XII International Chromosome Conference. Chromosome Res. 3, 74.
Garagna S., Broccoli D., Redi C. A., Searle J. B., Cooke H. J. and Capanna E. 1995 Robertsonian metacentrics of the house mouse loses telomeric sequences but retain some minor satellite DNA in the pericentromeric area. Chromosoma 103, 685–692.
García M., Freitas L., Miró R. and Egòzcue J. 1976 Banding patterns of the chromosomes of Cebus albifrons. Comparative studies with Cebus apella. Folia Primatol. 25, 313–319.
García Haro F., Ruiz-Herrera A., Egòzcue J., Ponsà M. and García M. 2002 Chromosomal homologies between Cebus and Ateles (Primates) based on ZOO-FISH and G-banding comparisons. Am. J. Primatol. 57, 177–188.
García F., García M., Mora L., Alarcón L., Egòzcue J. and Ponsà M. 2003 Qualitative analysis of constitutive heterochromatin and primate evolution. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 80, 107–124.
Groves C. 2005 Order primates. In Mammal species of the world, 3rd edition (ed. D. Wilson and D. M. Reeder), pp. 111–184. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, USA.
Koiffmann C. P. and Saldanha P. H. 1974 Cytogenetics of Brazilian monkeys. J. Hum. Evol. 3, 275–282.
Ma N. S. F. and Jones T. C. 1975 Added heterochromatin segments in chromosomes of squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus). Folia Primatol. 24, 282–292.
Martinez R. A., Torres E., Nieves M., Szapkievich V., Rodriguez S., Schinini A. et al. 2004 Genetic variability in two captive colonies of Cebus apella paraguayanus (Primates: Platyrrhini) from eastern Paraguay. Caryologia 57, 332–336.
Massarini A., Barros M. A., Ortells M. O. and Reig O. A. 1991 Chromosomal polymorphism and small karyotypic differentiation in a group of Ctenomys species from Central Argentina (Rodentia: Octodontidae). Genetica 83, 131–144.
Matayoshi T., Seuánez H. N., Nasazzi N., Nagle C., Armada J. L., Freitas L. and Alves G. 1987 Heterochromatic variation in Cebus apella (Cebidae: Platyrrhini) of different geographic regions. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 44, 158–162.
Meltzer P. S., Guan X. Y. and Trent J. 1992 Rapid generation of region specific probes by chromosome microdissection and their application. Nat. Genet. 1, 24–28.
Mudry de Pargament M. D., Labal de Vinuesa M. L. and Brieux de Salum S. 1985 Quantitative estimation of heteromorphism in C bands of Cebus apella. J. Hum. Evol. 14, 693–698.
Mudry de Pargament M. D. and Labal de Vinuesa M. L. 1988 Variabilidad en bandas C de dos poblaciones de Cebus apella. Mendeliana 8, 79–86.
Mudry M. D. 1990 Cytogenetic variability within and across populations of Cebus apella in Argentina. Folia Primatol. 54, 206–216.
Mudry M. D., Ponsà M., Borrel A., Egòzcue J. and García M. 1994 Prometaphase chromosomes of the Howler Monkey (Alouatta caraya): G, C, NOR, and restriction enzyme (REs) banding. Am. J. Primatol. 33, 121–132.
Mühlmann-Díaz M. C., Christian A. T. and Bedford J. S. 1995 Chromosome microdissection. In Radiation research congress. Lectures of the 10th International Conference, volume 2 (ed. U. Hagen, D. Harder, H. Jung and C. Streffer), pp. 468–471. Würzburg, Germany.
Nieves M., Ascunce M. S., Rahn M. and Mudry M. D. 2005a Phylogenetic relationships among some Ateles species employing chromosomic and molecular characters. Primates 46, 155–164.
Nieves M., Mühlmann M. and Mudry M. D. 2005b Heterochromatin and chromosome evolution: a FISH probe of Cebus apella paraguayanus (Primate: Platyrrhini) developed by chromosome microdissection. Genet. Mol. Res. 4, 675–683.
Nieves M. 2007 Heterocromatina y evolución cromosómica en primates neotropicales, Ph.D. thesis, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Argentina.
Nieves M., Mendez G., Ortiz A., Mühlmann M. and Mudry M. D. 2008 Karyological diagnosis of Cebus (Primates, Platyrrhini) in captivity: Detection of hybrids and management program applications. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 108, 66–78.
Nieves M., Mühlmann M. and Mudry M. D. 2010 Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) analysis of Cebus paraguayanus and C. nigritus (Primates, Platyrrhini). Citogenet. Genome Res. 128, 214–220.
Pieczarka J. C., Nagamachi C. Y., Muniz J. A., Barros L. M. and Mattevi M. S. 2001 Restriction enzyme and fluorochrome banding analysis of the constitutive heterochromatin of Saguinus species (Callitrichidae, Primates). Cytobios 105, 13–26.
Ponsà M., García M., Borrell A., García F., Egòzcue J., Gorostiaga M. A. et al. 1995 Heterochromatin and cytogenetic polymorphisms in Cebus apella (Cebidae, Platyrrhini). Am. J. Primatol. 37, 325–331.
Reig O. A. and Kiblinsky P. 1969 Chromosome multiformity in the genus Ctenomys (Rodentia: Octodontidae). Chromosoma 28, 211–244.
Richard F., Lombard M. and Dutrillaux B. 1996 Zoo-FISH suggests a complete homology between human and capuchin monkey (Platyrrhini) euchromatin. Genomics 36, 417–423.
Rossi M. S., Redi C. A., Viale G., Massarinia A. I. and Capanna E. 1995 Chromosomal distribution of the major satellite DNA of South American rodents of the genus Ctenomys. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 69, 179–184.
Scherthan H., Cremer T., Arnason U., Weier H. U., Lima-de-Faria A. and Frönicke L. 1994 Comparative chromosome painting discloses homologous segments in distantly related mammals. Nat. Genet. 6, 342–347.
Schweizer D. 1976 Reverse fluorescent banding with chromomicin and DAPI. Chromosoma 58, 307.
Seabright M. 1971 A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet 298, 971–972.
Seuánez H. N., Armada J. L. A., Freitas L., Rocha e Silva R., Pissinatti A. and Coimbra-Filho A. F. 1986 Intraspecific chromosome variation in Cebus apella (Cebidae: Platyrrhini). The chromosomes of the yellow breasted capuchin Cebus apella xanthosternos Wield, 1920. Am. J. Primatol. 10, 237–247.
Sumner A. T. 1972 A simple technique for demostrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 75, 304.
Taguchi T., Akimaru K., Hirai H., Hirai Y., Mwenda J. M. and Yuri K. 2003 A probe generated by chromosome microdissection, useful for analyzing Y chromosome evolution in Old World monkeys. Chromosome Res. 11, 147–152.
Torres de Caballero O. M., Ramírez C. and Yunis E. 1976 Genus Cebus Q- and G-Band karyotypes and natural hybrids. Folia Primatol. 26, 310–321.
Wichman H. A., Payne C. T., Ryder O. A., Hamilton M. J., Maltbie M. and Baker R. J. 1991 Genomic distribution of heterochromatic sequences in Equids: implications to rapid chromosomal evolution. J. Hered. 82, 369–377.
Yang F., Carter N. P., Shi L. and Ferguson-Smith M. A. 1995 A comparative study of karyotypes of muntjacs by chromosome painting. Chromosoma 103, 642–652.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Nieves M., De Oliveira E. H. C., Amaral P. J. S., Nagamachi C. Y., Pieczarka J. C., Mühlmann M. C. and Mudry M. D. 2011 Analysis of the heterochromatin of Cebus (Primates, Platyrrhini) by micro-FISH and banding pattern comparisons. J. Genet. 90, 111–117]
María C. Mühlmann (Deceased).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
NIEVES, M., DE OLIVEIRA, E.H.C., AMARAL, P.J.S. et al. Analysis of the heterochromatin of Cebus (Primates, Platyrrhini) by micro-FISH and banding pattern comparisons. J Genet 90, 111–117 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-011-0047-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-011-0047-0