Abstract
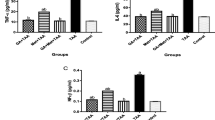
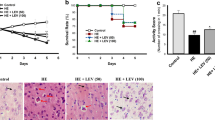
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neuropsychiatric syndrome resulting from acute liver failure. Previously, we demonstrated hepatoprotective effects of genistein in d-galactosamine (d-GalN)-induced fulminant hepatic failure (FHF). In this study, we evaluated behavioural and neuroprotective effects of genistein in rat model of HE. HE was induced by intraperitonial administration of d-GalN (250 mg/kg BW) twice a week for 30 days Genistein was given as co-treatment through oral gavage daily at dose of 5 mg/kg BW. d-GalN administration significantly resulted in acute liver failure which was further associated with hyperammonemia, neurological dysfunction, as evident from behavioural and functional impairment and reduced learning ability in Morris water maze. Genistein significantly alleviated behavioural and functional impairment and restored learning ability in Morris water maze. Considerable histopathological changes, including portal inflammation, sinusoidal dilation, necrotic lesions and swelled astrocytes with pale nuclei, were seen in the liver and brain sections of d-GalN-challenged rats while genistein co-treated rats revealed normal cellular and morphological architecture as no pathological features were seen. Furthermore, pro-inflammatory markers (interleukin (IL)-10, IL-4, IL-1β and TNF-α) and membrane expression of subunits α1 of GABAA receptor and GluR2 of AMPA marked significant increase, while subunits GluR1 of AMPA receptors showed reduced expression in d-GalN-challenged rats leading to neuroinflammation and dysregulated neurotransmission. Genistein significantly normalized altered expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and membrane receptor of GABA and GluR. Our study suggests strong therapeutic potential of genistein in animal model of HE. Genistein can be used a strong anti-oxidant to attenuate neurotoxic effects of xenobiotics.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HE:
-
Hepatic encephalopathy
- FHF:
-
Fulminant hepatic failure
- GABA:
-
Gama amino butyric acid
- GluR:
-
Glutamate receptor
- AMPA:
-
α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen activated protein kinase
- CPCSEA:
-
Committee for the purpose of control and supervision of experiments on animals
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulphoxide
- ALT:
-
Alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- OTM:
-
Olive tail moment
- HEPES:
-
4-(2-Hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethanesulfonic acid
- IGEPAL:
-
Octylphenoxypolyethoxyethanol
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene difluoride
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- TBST:
-
Tris-buffered saline Tween
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
References
Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K, Tarter R, Weissenborn K, Blei AT (2002) Hepatic encephalopathy—definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of Gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 35:716–721. doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.31250
Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A, Wendon J (2010) Acute liver failure. Lancet 376:190–201. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(10)60274-7
Hazell AS, Butterworth RF (1999) Hepatic encephalopathy: an update of pathophysiologic mechanisms. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine (New York, NY) 222:99–112
Cauli O et al (2009) Glutamatergic and gabaergic neurotransmission and neuronal circuits in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 24:69–80. doi:10.1007/s11011-008-9115-4
Raghavan M, Marik PE (2006) Therapy of intracranial hypertension in patients with fulminant hepatic failure. Neurocrit Care 4:179–189. doi:10.1385/ncc:4:2:179
Rose C (2002) Increased extracellular brain glutamate in acute liver failure: decreased uptake or increased release? Metab Brain Dis 17:251–261
Butterworth RF (2002) Pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy: a new look at ammonia. Metab Brain Dis 17:221–227
Shawcross D, Jalan R (2005) The pathophysiologic basis of hepatic encephalopathy: central role for ammonia and inflammation. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS 62:2295–2304. doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5089-0
Moore AH, Wu M, Shaftel SS, Graham KA, O’Banion MK (2009) Sustained expression of interleukin-1beta in mouse hippocampus impairs spatial memory. Neuroscience 164:1484–1495. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.08.073
Wang DS et al (2012) Memory deficits induced by inflammation are regulated by alpha5-subunit-containing GABAA receptors. Cell Rep 2:488–496. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2012.08.022
Zaki AE, Ede RJ, Davis M, Williams R (1984) Experimental studies of blood brain barrier permeability in acute hepatic failure. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 4:359–363
Ganai AA, Khan AA, Malik ZA, Farooqi H (2015) Genistein modulates the expression of NF-κB and MAPK (p-38 and ERK1/2), thereby attenuating d-Galactosamine induced fulminant hepatic failure in Wistar rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 283:139–146. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2015.01.012
Filipe P et al (2005) Contrasting action of flavonoids on phototoxic effects induced in human skin fibroblasts by UVA alone or UVA plus cyamemazine, a phototoxic neuroleptic. Photochemical & photobiological sciences : Official journal of the European Photochemistry Association and the European Society for Photobiology 4:420–428. doi:10.1039/b416811a
Kim JS et al (2012) Genistein mitigates radiation-induced testicular injury. Phytotherapy research : PTR 26:1119–1125. doi:10.1002/ptr.3689
Kruk I, Aboul-Enein HY, Michalska T, Lichszteld K, Kladna A (2005) Scavenging of reactive oxygen species by the plant phenols genistein and oleuropein. Luminescence : the journal of biological and chemical luminescence 20:81–89. doi:10.1002/bio.808
Soucy NV, Parkinson HD, Sochaski MA, Borghoff SJ (2006) Kinetics of genistein and its conjugated metabolites in pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats following single and repeated genistein administration. Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 90:230–240. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfj077
Kulling SE, Honig DM, Simat TJ, Metzler M (2000) Oxidative in vitro metabolism of the soy phytoestrogens daidzein and genistein. J Agric Food Chem 48:4963–4972
Rimbach G et al (2003) Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of isoflavone metabolites. Xenobiotica; the fate of foreign compounds in biological systems 33:913–925. doi:10.1080/0049825031000150444
Fang YC, Chen BH, Huang RF, Lu YF (2004) Effect of genistein supplementation on tissue genistein and lipid peroxidation of serum, liver and low-density lipoprotein in hamsters. J Nutr Biochem 15:142–148. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2003.06.001
Monfort P, Erceg S, Piedrafita B, Llansola M, Felipo V (2007) Chronic liver failure in rats impairs glutamatergic synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in hippocampus and learning ability. Eur J Neurosci 25:2103–2111. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05444.x
Rogers DC, Fisher EM, Brown SD, Peters J, Hunter AJ, Martin JE (1997) Behavioral and functional analysis of mouse phenotype: SHIRPA, a proposed protocol for comprehensive phenotype assessment. Mammalian genome : official journal of the International Mammalian Genome Society 8:711–713
Kind PR, King EJ (1954) Estimation of plasma phosphatase by determination of hydrolysed phenol with amino-antipyrine. J Clin Pathol 7:322–326
Ratnakumari L, Murthy CR (1990) Effect of methionine sulfoximine on pyruvate dehydrogenase, citric acid cycle enzymes and aminotransferases in the subcellular fractions isolated from rat cerebral cortex. Neurosci Lett 108:328–334
Reitman S, Frankel S (1957) A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminases. Am J Clin Pathol 28:56–63
Yang FR, Fang BW, Lou JS (2010) Effects of Haobie Yangyin Ruanjian decoction on hepatic fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. World journal of gastroenterology : WJG 16:1458–1464
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL (1988) A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res 175:184–191
Lackner P et al (2006) Behavioural and histopathological alterations in mice with cerebral malaria. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 32:177–188. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2006.00706.x
Romano-Silva MA et al (1993) Rat cortical synaptosomes have more than one mechanism for Ca2+ entry linked to rapid glutamate release: studies using the Phoneutria nigriventer toxin PhTX2 and potassium depolarization. Biochem J 296:313–319
Dunkley PR, Heath JW, Harrison SM, Jarvie PE, Glenfield PJ, Rostas JA (1988) A rapid Percoll gradient procedure for isolation of synaptosomes directly from an S1 fraction: homogeneity and morphology of subcellular fractions. Brain Res 441:59–71
Nicholls DG, Sihra TS, Sanchez-Prieto J (1987) Calcium-dependent and -independent release of glutamate from synaptosomes monitored by continuous fluorometry. J Neurochem 49:50–57
Matsuzaki Y, Koyama M, Hitomi T, Kawanaka M, Sakai T (2004) Indole-3-carbinol activates the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p15(INK4b) gene. FEBS Lett 576:137–140. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.09.002
Ozturk E et al (2008) Propofol and erythropoietin antioxidant properties in rat brain injured tissue. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:81–86. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.07.016
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM, Blake D (1985) Metal ions and oxygen radical reactions in human inflammatory joint disease. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 311:659–671
Mustafa HN, El Awdan SA, Hegazy GA (2013) Protective role of antioxidants on thioacetamide-induced acute hepatic encephalopathy: biochemical and ultrastructural study. Tissue & cell 45:350–362. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2013.06.001
Hein AM et al (2010) Sustained hippocampal IL-1beta overexpression impairs contextual and spatial memory in transgenic mice. Brain Behav Immun 24:243–253. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2009.10.002
Mendez M et al (2008) Spatial memory alterations in three models of hepatic encephalopathy. Behav Brain Res 188:32–40. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2007.10.019
Ortiz M, Cordoba J, Jacas C, Flavia M, Esteban R, Guardia J (2006) Neuropsychological abnormalities in cirrhosis include learning impairment. J Hepatol 44:104–110. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2005.06.013
Serantes R et al (2006) Interleukin-1beta enhances GABAA receptor cell-surface expression by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway: relevance to sepsis-associated encephalopathy. J Biol Chem 281:14632–14643. doi:10.1074/jbc.M512489200
Lai AY, Swayze RD, El-Husseini A, Song C (2006) Interleukin-1 beta modulates AMPA receptor expression and phosphorylation in hippocampal neurons. J Neuroimmunol 175:97–106. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.03.001
Albrecht J, Hilgier W, Zielinska M, Januszewski S, Hesselink M, Quack G (2000) Extracellular concentrations of taurine, glutamate, and aspartate in the cerebral cortex of rats at the asymptomatic stage of thioacetamide-induced hepatic failure: modulation by ketamine anesthesia. Neurochem Res 25:1497–1502
McArdle P, Penning DH, Dexter F, Reynolds JD (1996) Flumazenil does not affect the increase in rat hippocampal extracellular glutamate concentration produced during thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 11:329–342. doi:10.1007/BF02029494
Moroni F, Lombardi G, Moneti G, Cortesini C (1983) The release and neosynthesis of glutamic acid are increased in experimental models of hepatic encephalopathy. J Neurochem 40:850–854
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the University Grants Commission under Dr. D. S. Kothari Postdoctoral Fellowship Scheme. The support provided by the animal house facility Jamia Hamdard is highly acknowledged.
Author Contribution
Ajaz Ahmad Ganai: performed experiments and wrote the manuscript
Mohammad Husain: checked the manuscript
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All experimental procedures were in full compliance with CPCSEA guidelines.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganai, A.A., Husain, M. Genistein Alleviates Neuroinflammation and Restores Cognitive Function in Rat Model of Hepatic Encephalopathy: Underlying Mechanisms. Mol Neurobiol 55, 1762–1772 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0454-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0454-1