Abstract
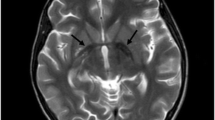
Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation comprises a heterogeneous group of disorders characterized clinically by progressive motor dysfunction. Accurate identification of de novo and rare inherited mutations is important for determining causative genes of undiagnosed neurological diseases. In the present study, we report a unique case with cerebellar ataxia symptoms and social communication difficulties in an intermarriage family. MRI showed a marked cerebellar atrophy and the “eye-of-the-tiger”-like sign in the medial globus pallidus. Potential genetic defects were screened by whole-exome sequencing (WES) for the patient and four additional family members. A previously undescribed de novo missense mutation (c.1634A>G, p.K545R) in the exon 12 of the PLA2G6 gene was identified. A second rare variant c.1077G>A at the end of exon 7 was also identified, which was inherited from the mother, and resulted in a frame-shift mutation (c.1074_1077del.GTCG) due to an alternative splicing. In conclusion, the identification of the “eye-of-the-tiger”-like sign in the globus pallidus of the patient expands the phenotypic spectrum of PLA2G6-associated disorders and reveals its value in differential diagnosis of PLA2G6-associated disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurian MA, Hayflick SJ (2013) Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN) and PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration (PLAN): review of two major neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA) phenotypes. Int Rev Neurobiol 110:49–71. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-410502-7.00003-X
Gregory A, Hayflick S (1993) Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation disorders overview. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH et al. (eds) GeneReviews(R). Seattle (WA),
Kurian MA, Morgan NV, MacPherson L, Foster K, Peake D, Gupta R, Philip SG, Hendriksz C, Morton JE, Kingston HM, Rosser EM, Wassmer E, Gissen P, Maher ER (2008) Phenotypic spectrum of neurodegeneration associated with mutations in the PLA2G6 gene (PLAN). Neurology 70(18):1623–1629. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000310986.48286.8e
Morgan NV, Westaway SK, Morton JE, Gregory A, Gissen P, Sonek S, Cangul H, Coryell J, Canham N, Nardocci N, Zorzi G, Pasha S, Rodriguez D, Desguerre I, Mubaidin A, Bertini E, Trembath RC, Simonati A, Schanen C, Johnson CA, Levinson B, Woods CG, Wilmot B, Kramer P, Gitschier J, Maher ER, Hayflick SJ (2006) PLA2G6, encoding a phospholipase A2, is mutated in neurodegenerative disorders with high brain iron. Nat Genet 38(7):752–754. doi:10.1038/ng1826
Paisan-Ruiz C, Bhatia KP, Li A, Hernandez D, Davis M, Wood NW, Hardy J, Houlden H, Singleton A, Schneider SA (2009) Characterization of PLA2G6 as a locus for dystonia-parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 65(1):19–23. doi:10.1002/ana.21415
Gregory A, Polster BJ, Hayflick SJ (2009) Clinical and genetic delineation of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. J Med Genet 46(2):73–80. doi:10.1136/jmg.2008.061929
Cai T, Yang L, Cai W, Guo S, Yu P, Li J, Hu X, Yan M, Shao Q, Jin Y, Sun ZS, Luo ZJ (2015) Dysplastic spondylolysis is caused by mutations in the diastrophic dysplasia sulfate transporter gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(26):8064–8069. doi:10.1073/pnas.1502454112
Yu P, Cui Y, Cai W, Wu H, Xiao X, Shao Q, Ma L, Guo S, Wu N, Jin ZB, Wang Y, Cai T, Sun ZS, Qu J (2015) Lysosomal storage disease in the brain: mutations of the beta-mannosidase gene identified in autosomal dominant nystagmus. Genet Med. doi:10.1038/gim.2015.10
Li J, Cai T, Jiang Y, Chen H, He X, Chen C, Li X, Shao Q, Ran X, Li Z, Xia K, Liu C, Sun ZS, Wu J (2015) Genes with de novo mutations are shared by four neuropsychiatric disorders discovered from NPdenovo database. Mol Psychiatry. doi:10.1038/mp.2015.58
Li J, Jiang Y, Wang T, Chen H, Xie Q, Shao Q, Ran X, Xia K, Sun ZS, Wu J (2015) mirTrios: an integrated pipeline for detection of de novo and rare inherited mutations from trios-based next-generation sequencing. J Med Genet 52(4):275–281. doi:10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102656
Wu Y, Jiang Y, Gao Z, Wang J, Yuan Y, Xiong H, Chang X, Bao X, Zhang Y, Xiao J, Wu X (2009) Clinical study and PLA2G6 mutation screening analysis in Chinese patients with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy. Eur J Neurol 16(2):240–245. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2008.02397.x
Lu CS, Lai SC, Wu RM, Weng YH, Huang CL, Chen RS, Chang HC, Wu-Chou YH, Yeh TH (2012) PLA2G6 mutations in PARK14-linked young-onset parkinsonism and sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 159B(2):183–191. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.32012
Mancuso DJ, Jenkins CM, Gross RW (2000) The genomic organization, complete mRNA sequence, cloning, and expression of a novel human intracellular membrane-associated calcium-independent phospholipase A(2). J Biol Chem 275(14):9937–9945
Tang J, Kriz RW, Wolfman N, Shaffer M, Seehra J, Jones SS (1997) A novel cytosolic calcium-independent phospholipase A2 contains eight ankyrin motifs. J Biol Chem 272(13):8567–8575
Larsson Forsell PK, Kennedy BP, Claesson HE (1999) The human calcium-independent phospholipase A2 gene multiple enzymes with distinct properties from a single gene. Eur J Biochem 262(2):575–585
Meyer E, Kurian MA, Hayflick SJ (2015) Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation: genetic diversity and pathophysiological mechanisms. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 16:257–279. doi:10.1146/annurev-genom-090314-025011
Illingworth MA, Meyer E, Chong WK, Manzur AY, Carr LJ, Younis R, Hardy C, McDonald F, Childs AM, Stewart B, Warren D, Kneen R, King MD, Hayflick SJ, Kurian MA (2014) PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration (PLAN): further expansion of the clinical, radiological and mutation spectrum associated with infantile and atypical childhood-onset disease. Mol Genet Metab 112(2):183–189. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2014.03.008
Shinzawa K, Sumi H, Ikawa M, Matsuoka Y, Okabe M, Sakoda S, Tsujimoto Y (2008) Neuroaxonal dystrophy caused by group VIA phospholipase A2 deficiency in mice: a model of human neurodegenerative disease. J Neurosci 28(9):2212–2220. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4354-07.2008
Paisan-Ruiz C, Li A, Schneider SA, Holton JL, Johnson R, Kidd D, Chataway J, Bhatia KP, Lees AJ, Hardy J, Revesz T, Houlden H (2012) Widespread Lewy body and tau accumulation in childhood and adult onset dystonia-parkinsonism cases with PLA2G6 mutations. Neurobiol Aging 33(4):814–823. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.05.009
Wada H, Yasuda T, Miura I, Watabe K, Sawa C, Kamijuku H, Kojo S, Taniguchi M, Nishino I, Wakana S, Yoshida H, Seino K (2009) Establishment of an improved mouse model for infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy that shows early disease onset and bears a point mutation in Pla2g6. Am J Pathol 175(6):2257–2263. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2009.090343
Zhang P, Gao Z, Jiang Y, Wang J, Zhang F, Wang S, Yang Y, Xiong H, Zhang Y, Bao X, Xiao J, Wu X, Wu Y (2013) Follow-up study of 25 Chinese children with PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration. Eur J Neurol 20(2):322–330. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2012.03856.x
Schipper HM (2012) Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation—clinical syndromes and neuroimaging. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822(3):350–360. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.06.016
McNeill A, Birchall D, Hayflick SJ, Gregory A, Schenk JF, Zimmerman EA, Shang H, Miyajima H, Chinnery PF (2008) T2* and FSE MRI distinguishes four subtypes of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Neurology 70(18):1614–1619. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000310985.40011.d6
Kruer MC, Hiken M, Gregory A, Malandrini A, Clark D, Hogarth P, Grafe M, Hayflick SJ, Woltjer RL (2011) Novel histopathologic findings in molecularly-confirmed pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. Brain 134(Pt 4):947–958. doi:10.1093/brain/awr042
Hogarth P (2015) Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation: diagnosis and management. J Mov Disord 8(1):1–13. doi:10.14802/jmd.14034
Shi CH, Tang BS, Wang L, Lv ZY, Wang J, Luo LZ, Shen L, Jiang H, Yan XX, Pan Q, Xia K, Guo JF (2011) PLA2G6 gene mutation in autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism in a Chinese cohort. Neurology 77(1):75–81. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318221acd3
Gui YX, Xu ZP, Wen L, Liu HM, Zhao JJ, Hu XY (2013) Four novel rare mutations of PLA2G6 in Chinese population with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19(1):21–26. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.07.016
Lv Z, Guo J, Sun Q, Li K, Yu R, Tian J, Yan X, Tang B (2012) Association between PLA2G6 gene polymorphisms and Parkinson’s disease in the Chinese Han population. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(5):641–644. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.02.015
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to the patient and her family members who participated in this study. Dr. Jinyu Wu supervised the process of the whole-exome sequencing of these subjects. This study was supported by the research funding from the Chinese Ministry of Health Project (No: 201302002 to XC), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81200074 to DJ), and Beijing Collaborative Innovative Research Center for Cardiovascular Diseases (PXM2014_014226_000002 to DJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Informed consent was obtained from the parents. This study was approved by the ethics committee of Wenzhou Medical University.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Sen Guo, Liu Yang and Huijie Liu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, S., Yang, L., Liu, H. et al. Identification of Novel Compound Mutations in PLA2G6-Associated Neurodegeneration Patient with Characteristic MRI Imaging. Mol Neurobiol 54, 4636–4643 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9991-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9991-2