Abstract
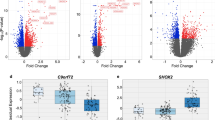
Cerebellar degeneration is a devastating manifestation of cerebellar-type multiple-system atrophy (MSA), a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disease, and the exact pathogenesis is unknown. Here, we examined the expression of micro-RNAs (miRNAs), which are short noncoding RNAs, in the cerebellum of MSA and the key target genes. miRNA microarray found 11 miRNAs with significantly different expression in MSA cerebellum compared to cerebellum from age-, sex-, and postmortem interval-matched controls. miR-202 was the most upregulated in the MSA samples. In silico analysis, followed by target gene luciferase assay, in vitro transfection, and Western blotting in human samples showed that miR-202 downregulates Oct1 (Pou2f1), a transcription factor expressed in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Transfection of Neuro-2a cells with miR-202 enhanced oxidative stress-induced cell death, and an antagomir to miR-202 inhibited this effect of miR-202. This study provides novel insight into the role of miRNA in cerebellar degeneration and suggests that miR-202 is a key miRNA mediating the pathogenesis of MSA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stefanova N, Bucke P, Duerr S, Wenning GK (2009) Multiple system atrophy: an update. Lancet Neurol 8:1172–1178
Ahmed Z, Asi YT, Sailer A, Lees AJ, Houlden H, Revesz T, Holton JL (2012) The neuropathology, pathophysiology and genetics of multiple system atrophy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 38:4–24
Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC (2009) Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:126–139
Esteller M (2011) Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet 12:861–874
Huang T, Liu Y, Huang M, Zhao X, Cheng L (2010) Wnt1-cre-mediated conditional loss of Dicer results in malformation of the midbrain and cerebellum and failure of neural crest and dopaminergic differentiation in mice. J Mol Cell Biol 2:152–163
Kuang Y, Liu Q, Shu X, Zhang C, Huang N, Li J, Jiang M, Li H (2012) Dicer1 and MiR-9 are required for proper Notch1 signaling and the Bergmann glial phenotype in the developing mouse cerebellum. Glia 60:1734–1746
Olsen L, Klausen M, Helboe L, Nielsen FC, Werge T (2009) MicroRNAs show mutually exclusive expression patterns in the brain of adult male rats. PLoS ONE 4:e7225
Zhang J, Zhang J, Zhou Y, Wu YJ, Ma L, Wang RJ, Huang SQ, Gao RR, Liu LH, Shao ZH, Shi HJ, Cheng LM, Yu L (2013) Novel cerebellum-enriched miR-592 may play a role in neural progenitor cell differentiation and neuronal maturation through regulating Lrrc4c and Nfasc in rat. Curr Mol Med 13:1432–1445
Lee Y, Samaco RC, Gatchel JR, Thaller C, Orr HT, Zoghbi HY (2008) miR-19, miR-101 and miR-130 co-regulate ATXN1 levels to potentially modulate SCA1 pathogenesis. Nat Neurosci 11:1137–1139
Persengiev S, Kondova I, Otting N, Koeppen AH, Bontrop RE (2011) Genome-wide analysis of miRNA expression reveals a potential role for miR-144 in brain aging and spinocerebellar ataxia pathogenesis. Neurobiol Aging 32(2316):e2317–2327
Rodriguez-Lebron E, Liu G, Keiser M, Behlke MA, Davidson BL (2013) Altered Purkinje cell miRNA expression and SCA1 pathogenesis. Neurobiol Dis 54:456–463
Abele M, Burk K, Schols L, Schwartz S, Besenthal I, Dichgans J, Zuhlke C, Riess O, Klockgether T (2002) The aetiology of sporadic adult-onset ataxia. Brain 125:961–968
Janssen HL, Reesink HW, Lawitz EJ, Zeuzem S, Rodriguez-Torres M, Patel K, van der Meer AJ, Patick AK, Chen A, Zhou Y, Persson R, King BD, Kauppinen S, Levin AA, Hodges MR (2013) Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N Engl J Med 368:1685–1694
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2005) Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 120:15–20
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M, Rajewsky N (2005) Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37:495–500
Kiriakidou M, Nelson PT, Kouranov A, Fitziev P, Bouyioukos C, Mourelatos Z, Hatzigeorgiou A (2004) A combined computational-experimental approach predicts human microRNA targets. Genes Dev 18:1165–1178
Heintz N (2004) Gene expression nervous system atlas (GENSAT). Nat Neurosci 7:483
Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, Kim JH, Huh JY, Yoon H, Park DK, Lim JY, Kim JM, Jeon D, Ryu H, Lee SK, Kim M, Roh JK (2012) miR-206 regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Alzheimer disease model. Ann Neurol 72:269–277
Kang J, Gemberling M, Nakamura M, Whitby FG, Handa H, Fairbrother WG, Tantin D (2009) A general mechanism for transcription regulation by Oct1 and Oct4 in response to genotoxic and oxidative stress. Genes Dev 23:208–222
Kang J, Shakya A, Tantin D (2009) Stem cells, stress, metabolism and cancer: a drama in two Octs. Trends Biochem Sci 34:491–499
Tantin D, Schild-Poulter C, Wang V, Hache RJ, Sharp PA (2005) The octamer binding transcription factor Oct-1 is a stress sensor. Cancer Res 65:10750–10758
Guevara-Garcia M, Gil-del Valle L, Velasquez-Perez L, Garcia-Rodriguez JC (2012) Oxidative stress as a cofactor in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2. Redox Rep 17:84–89
Hoffman AE, Liu R, Fu A, Zheng T, Slack F, Zhu Y (2013) Targetome profiling, pathway analysis and genetic association study implicate miR-202 in lymphomagenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 22:327–336
Yu J, Qiu X, Shen X, Shi W, Wu X, Gu G, Zhu B, Ju S (2013) miR-202 expression concentration and its clinical significance in the serum of multiple myeloma patients. Ann Clin Biochem. doi:10.1177/0004563213501155
Schrauder MG, Strick R, Schulz-Wendtland R, Strissel PL, Kahmann L, Loehberg CR, Lux MP, Jud SM, Hartmann A, Hein A, Bayer CM, Bani MR, Richter S, Adamietz BR, Wenkel E, Rauh C, Beckmann MW, Fasching PA (2012) Circulating micro-RNAs as potential blood-based markers for early stage breast cancer detection. PLoS ONE 7:e29770
Wainwright EN, Jorgensen JS, Kim Y, Truong V, Bagheri-Fam S, Davidson T, Svingen T, Fernandez-Valverde SL, McClelland KS, Taft RJ, Harley VR, Koopman P, Wilhelm D (2013) SOX9 regulates microRNA miR-202-5p/3p expression during mouse testis differentiation. Biol Reprod 89:34
Zongaro S, Hukema R, D'Antoni S, Davidovic L, Barbry P, Catania MV, Willemsen R, Mari B, Bardoni B (2013) The 3' UTR of FMR1 mRNA is a target of miR-101, miR-129-5p and miR-221: implications for the molecular pathology of FXTAS at the synapse. Hum Mol Genet 22:1971–1982
Magill ST, Cambronne XA, Luikart BW, Lioy DT, Leighton BH, Westbrook GL, Mandel G, Goodman RH (2010) microRNA-132 regulates dendritic growth and arborization of newborn neurons in the adult hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:20382–20387
Chen L, Zhang J, Feng Y, Li R, Sun X, Du W, Piao X, Wang H, Yang D, Sun Y, Li X, Jiang T, Kang C, Li Y, Jiang C (2012) MiR-410 regulates MET to influence the proliferation and invasion of glioma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:1711–1717
Ozawa T, Paviour D, Quinn NP, Josephs KA, Sangha H, Kilford L, Healy DG, Wood NW, Lees AJ, Holton JL, Revesz T (2004) The spectrum of pathological involvement of the striatonigral and olivopontocerebellar systems in multiple system atrophy: clinicopathological correlations. Brain 127:2657–71
Fernagut PO, Tison F (2012) Animal models of multiple system atrophy. Neuroscience 211:77–82
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korean Health Technology R&D Project (A121660), Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Soon-Tae Lee and Kon Chu contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, ST., Chu, K., Jung, KH. et al. Altered Expression of miR-202 in Cerebellum of Multiple-System Atrophy. Mol Neurobiol 51, 180–186 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8788-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8788-4