Abstract
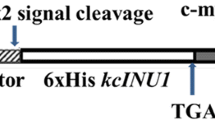
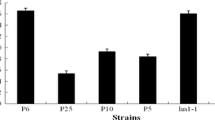
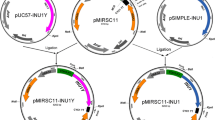
The INU1 gene encoding an exo-inulinase from the marine-derived yeast Candida membranifaciens subsp. flavinogenie W14-3 was cloned and characterized. It had an open reading frame of 1,536 bp long encoding an inulinase. The coding region of it was not interrupted by any intron. The cloned gene encoded 512 amino acid residues of a protein with a putative signal peptide of 23 amino acids and a calculated molecular mass of 57.8 kDa. The protein sequence deduced from the inulinase gene contained the inulinase consensus sequences (WMNDPNGL), (RDP), ECP FS and Q. The protein also had six conserved putative N-glycosylation sites. The deduced inulinase from the yeast strain W14-3 was found to be closely related to that from Candida kutaonensis sp. nov. KRF1, Kluyveromyces marxianus, and Cryptococcus aureus G7a. The inulinase gene with its signal peptide encoding sequence was subcloned into the pMIRSC11 expression vector and expressed in Saccharomyces sp. W0. The recombinant yeast strain W14-3-INU-112 obtained could produce 16.8 U/ml of inulinase activity and 12.5 % (v/v) ethanol from 250 g/l of inulin within 168 h. The monosaccharides were detected after the hydrolysis of inulin with the crude inulinase (the yeast culture). All the results indicated that the cloned gene and the recombinant yeast strain W14-3-INU-112 had potential applications in biotechnology.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chi, Z. M., Chi, Z., Zhang, T., et al. (2009). Inulinase-expressing microorganisms and applications of inulinases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 82, 211–220.
Chi, Z. M., Zhang, T., Cao, T. S., et al. (2011). Biotechnological potential of inulin for bioprocesses. Bioresources Technology, 102, 4295–4303.
Cao, T. S., Wang, G. Y., Chi, Z., et al. (2013). Cloning, characterization and heterelogous expression of the INU1 gene from Cryptococcus aureus HYA. Gene, 516, 255–262.
Liu, G. L., Chi, Z., & Chi, Z. M. (2013). Molecular characterization and expression of microbial inulinase genes. Critical Reviews in Microbiology, 39(2), 152–165.
Yuan, B., Hu, N., Sun, J., et al. (2012). Purification and characterization of a novel extracellular inulinase from a new yeast species Candida kutaonensis sp. nov. KRF1T. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 96, 1517–1526.
Zhang, T., Gong, F., Chi, Z., et al. (2008). Cloning and characterization of the inulinase gene from a marine yeast Pichia guilliermondii and its expression in Pichia pastoris. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, 95, 13–22.
Gancedo, J. M. (1998). Yeast carbon catabolite repression. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 62, 334–361.
MacPherson, S., Larochelle, M., & Turcotte, B. (2006). A fungal family of transcriptional regulators: the zinc cluster proteins. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 70, 583–604.
Wang, L., Chi, Z. M., Wang, X. H., et al. (2008). Isolation and characterization of Candida membranifaciens subsp. flavinogenie W14-3, a novel riboflavin-producing marine yeast. Microbiological Research, 163, 255–266.
Chi, Z., Wang, L., Ju, L., et al. (2008). Optimisation of riboflavin production by the marine yeast Candida membranifaciens subsp. flavinogenie W14-3 using response surface methodology. Annual Microbiology, 58, 677–681.
Wang, J. M., Zhang, T., Chi, Z., et al. (2011). 18S rDNA integration of the exo-inulinase gene into chromosomes of the high ethanol producing yeast Saccharomyces sp. W0 for direct conversion of inulin to bioethanol. Biomass and Bioenergy, 35, 3032–3039.
Chi, Z. M., & Arneberg, N. (1999). Relationship between lipid composition, frequency of ethanol-induced respiratory deficient mutants, and ethanol tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 86, 1047–1052.
Zhang, T., Chi, Z., Chi, Z. M., et al. (2010). Expression of the inulinase gene from the marine-derived Pichia guilliermondii in Saccharomyces sp. W0 and ethanol production from inulin. Microbial Biotechnology, 3, 576–582.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., & Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (Vol. 2, pp. 367–370). Beijing: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. Chinese translating ed.
Chi, Z. M., Ma, C., Wang, P., et al. (2007). Optimization of medium and cultivation conditions for alkaline protease production by the marine yeast Aureobasidium pullulans. Bioresources Technology, 98, 534–538.
Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., Plewniak, F., et al. (1997). The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Research, 24, 4876–4882.
Arnold, K., Bordoli, L., Kopp, J., et al. (2006). The SWISS-MODEL Workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modeling. Bioinformatics, 22, 195–201.
Gong, F., Sheng, J., Chi, Z. M., et al. (2007). Inulinase production by a marine yeast Pichia guilliermondii and inulin hydrolysis by the crude inulinase. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34, 179–185.
Spiro, R. G. (1966). Analysis of sugars found in glycoproteins. Methods in Enzymology, 8, 3–26.
Chi, Z. M., Liu, J., & Zhang, W. (2001). Trehalose accumulation from soluble starch by Saccharomycopsis fibuligera sdu. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 38, 240–246.
Zhang, T., Gong, F., Peng, Y., et al. (2009). Optimization for high-level expression of the Pichia guilliermondii recombinant inulinase in Pichia pastoris and characterization of the recombinant inulinase. Process Biochemistry, 44, 1335–1339.
Laloux, O., Cassart, J. P., Delcour, J., et al. (1991). Cloning and sequencing of the inulinase gene of Kluyveromyces marxianus var. marxianus ATCC 12424. FEBS Letters, 289, 64–68.
Wen, T., Liu, F., Huo, K., et al. (2003). Cloning and analysis of the inulinase gene from Kluyveromyces cicerisporus CBS4857. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 19, 423–426.
Li, Y., Liu, G. L., & Chi, Z. M. (2013). Ethanol production from inulin and unsterilized meal of Jerusalem artichoke tubers by Saccharomyces sp. W0 expressing the endo-inulinase gene from Arthrobacter sp. Bioresources Technology, 147, 254–259.
Sheng, J., Chi, Z. M., Gong, F., & Li, J. (2008). Purification and characterization of extracellular inulinase from a marine yeast Cryptococcus aureus G7a and inulin hydrolysis by the purified inulinase. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 144, 111–121.
Wang, S. A., & Li, F. L. (2013). Invertase SUC2 is the key hydrolase for inulin degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79, 403–406.
Yuan, B., Wang, S. A., & Li, F. L. (2013). Improved ethanol fermentation by heterologous endoinulinase and inherent invertase from inulin by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresource technology, 139, 402–405.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (863) (Grant no. 2012AA021205).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, LL., Tan, MJ., Liu, GL. et al. Cloning and Characterization of an Inulinase Gene From the Marine Yeast Candida membranifaciens subsp. flavinogenie W14-3 and Its Expression in Saccharomyces sp. W0 for Ethanol Production. Mol Biotechnol 57, 337–347 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-014-9827-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-014-9827-0