Abstract
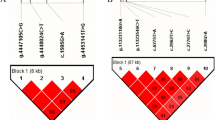
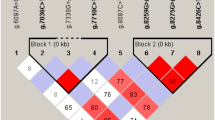
The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is an evolutionarily conserved sensor of cellular and systemic energy balance. PRKAB1, the gene that encodes the β1 regulatory subunit of AMPK, has been shown to be highly involved in the glycogen metabolism. To date, several mutations affecting function of human PRKAB1 have been identified but few studies have shown a complete description of the variability of bovine PRKAB1. In the present study, we report the investigation of PRKAB1 genetic polymorphism in a sample of 811 Chinese indigenous bovine individuals. The screening of the coding regions with their intron–exon boundaries and the proximal flanking regions was performed using a PCR–SSCP strategy. Following sequence analysis revealed 29 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of bovine PRKAB1 gene. Four were in the 5′-UTR; eight were in the coding region, among which one was nonsense mutant,one was missense mutant, six were synonymous mutation; and seventeen were in the introns. We also investigated haplotype frequencies and linkage disequilibrium (LD) coefficients for these SNPs in three Chinese indigenous cattle breeds. Three LD blocks were found in Nanyang cattle and four common haplotypes were identified based on five SNPs, with the most common haplotypes (GGTCC) occurring at a frequency of 82.7%. In Qinchuan cattle, one major block and two of the four possible haplotypes were found, one main haplotypes (CG) accounted for 93.8% of all possible marker combinations. In Jiaxian cattle, two LD blocks were found and four common haplotypes were identified based on four SNPs, the most common haplotypes (CCGT) accounted for 77.4% of the total. Variations detected here might have an impact on PRKAB1 activity and function and underpin the development of gene markers for bovine energy balance and in the glycogen metabolism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corton, J. M., Gillespie, J. G., & Hardie, D. G. (1994). Role of the AMP-activated protein kinase in the cellular stress response. Current Biology, 4(4), 315–324.
Hardie, D. G., Carling, D., & Carlson, M. (1998). The AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinase subfamily: metabolic sensors of the eukaryotic cell? Annual Reviews of Biochemistry, 67, 821–855.
Mitchelhill, K. I., Stapleton, D., Gao, G., House, C., Michell, B., Katsis, F., et al. (1994). Mammalian AMP-activated protein kinase shares structural and functional homology with the catalytic domain of yeast Snf1 protein kinase. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269(4), 2361–2364.
Stapleton, D., Mitchelhill, K. I., Gao, G., Widmer, J., Michell, B. J., Teh, T., et al. (1996). Mammalian AMP-activated protein kinase subfamily. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271(2), 611–614.
Iseli, T. J., Oakhill, J. S., Bailey, M. F., Wee, S., Walter, M., van Denderen, B. J., et al. (2008). AMP-activated protein kinase subunit interactions: beta1:gamma1 association requires beta1 Thr-263 and Tyr-267. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283(8), 4799–4807.
Mahtani, M. M., Widen, E., Lehto, M., Thomas, J., McCarthy, M., Brayer, J., et al. (1996). Mapping of a gene for type 2 diabetes associated with an insulin secretion defect by a genome scan in Finnish families. Nature Genetics, 14(1), 90–94.
Shaw, J. T., Lovelock, P. K., Kesting, J. B., Cardinal, J., Duffy, D., Wainwright, B., et al. (1998). Novel susceptibility gene for late-onset NIDDM is localized to human chromosome 12q. Diabetes, 47(11), 1793–1796.
Bowden, D. W., Sale, M., Howard, T. D., Qadri, A., Spray, B. J., Rothschild, C. B., et al. (1997). Linkage of genetic markers on human chromosomes 20 and 12 to NIDDM in Caucasian sib pairs with a history of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes, 46(5), 882–886.
Warden, S. M., Richardson, C., O’Donnell, J., Jr., Stapleton, D., Kemp, B. E., & Witters, L. A. (2001). Post-translational modifications of the beta-1 subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase affect enzyme activity and cellular localization. The Biochemical Journal, 354(Pt 2), 275–283.
Hudson, E. R., Pan, D. A., James, J., Lucocq, J. M., Hawley, S. A., Green, K. A., et al. (2003). A novel domain in AMP-activated protein kinase causes glycogen storage bodies similar to those seen in hereditary cardiac arrhythmias. Current Biology, 13(10), 861–866.
Polekhina, G., Gupta, A., Michell, B. J., van Denderen, B., Murthy, S., Feil, S. C., et al. (2003). AMPK beta subunit targets metabolic stress sensing to glycogen. Current Biology, 13(10), 867–871.
Sakoda, H., Fujishiro, M., Fujio, J., Shojima, N., Ogihara, T., Kushiyama, A., et al. (2005). Glycogen debranching enzyme association with beta-subunit regulates AMP-activated protein kinase activity. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology Metabolism, 289(3), E474–E481.
McKay, S. D., White, S. N., Kata, S. R., Loan, R., & Womack, J. E. (2003). The bovine 5′ AMPK gene family: mapping and single nucleotide polymorphism detection. Mammalian Genome, 14(12), 853–858.
Sambrook, J., & Russell, D. W. (2001). Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual (3rd ed., Vol. 3). New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Zhang, C., Wang, Y., Chen, H., Lan, X., & Lei, C. (2007). Enhance the efficiency of single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis by short polyacrylamide gel and modified silver staining. Analytical Biochemistry, 365(2), 286–287.
Barrett, J. C., Fry, B., Maller, J., & Daly, M. J. (2005). Haploview: Analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics, 21(2), 263–265.
Stephens, J. C., Schneider, J. A., Tanguay, D. A., Choi, J., Acharya, T., Stanley, S. E., et al. (2001). Haplotype variation and linkage disequilibrium in 313 human genes. Science, 293(5529), 489–493.
Nakamoto, K., Wang, S., Jenison, R. D., Guo, G. L., Klaassen, C. D., Wan, Y. J., et al. (2006). Linkage disequilibrium blocks, haplotype structure, and htSNPs of human CYP7A1 gene. BMC Genetics, 7, 29.
Saunders, M. A., Hammer, M. F., & Nachman, M. W. (2002). Nucleotide variability at G6pd and the signature of malarial selection in humans. Genetics, 162(4), 1849–1861.
Saunders, M. A., Slatkin, M., Garner, C., Hammer, M. F., & Nachman, M. W. (2005). The extent of linkage disequilibrium caused by selection on G6PD in humans. Genetics, 171(3), 1219–1229.
Toomajian, C., & Kreitman, M. (2002). Sequence variation and haplotype structure at the human HFE locus. Genetics, 161(4), 1609–1623.
Clark, R. M., Linton, E., Messing, J., & Doebley, J. F. (2004). Pattern of diversity in the genomic region near the maize domestication gene tb1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences United States of the America, 101(3), 700–707.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National 863 Program of China (No.2006AA10Z197), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30771544), Keystone Project of transfergene in China (2008ZX08007-002, 2009ZX08009-157B), "13115" Sci-Tech Innovation Program of Shaanxi Province (2008ZDKG-11) and Natural Science Foundation of Xuzhou Normal University (No.2003XY234).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Chen, H., Zhao, S. et al. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Haplotypic Diversity in the Bovine PRKAB1 Gene. Mol Biotechnol 43, 193–199 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9194-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-009-9194-4