Abstract
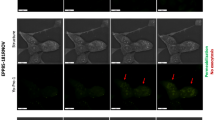
The application of nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs) is a novel method to induce the death of cancer cells. NsPEFs could directly function on the cell membrane and activate the apoptosis pathways, then induce apoptosis in various cell lines. However, the nsPEFs-inducing-apoptosis action sites and the exact pathways are not clear now. In this study, nsPEFs were applied to the human liver cancer cells HepG2 with different parameters. By apoptosis assay, morphological observation, detecting the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨ m), intracellular calcium ion concentration ([Ca2+]i) and the expressions of key apoptosis factors, we demonstrated that nsPEFs could induce the morphology of cell apoptosis, the change in ΔΨ m, [Ca2+]i and the upregulation of some key apoptosis factors, which revealed the responses of liver cancer cells and indicated that cells may undergo apoptosis through the mitochondria-dependent pathway after nsPEFs were applied.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mir LM, Glass LF, Sersa G, Teissié J, Domenge C, Miklavcic D, et al. Effective treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous malignant tumours by electrochemotherapy. Br J Cancer. 1998;77:2336–42.
Glass LF, Pepine ML, Fenske NA, Jaroszeski M, Reintgen DS, Heller R. Bleomycin-mediated electrochemotherapy of metastatic melanoma. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1353–7.
Giardino R, Fini M, Bonazzi V, Cadossi R, Nicolini A, Carpi A. Electrochemotherapy a novel approach to the treatment of metastatic nodules on the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Biomed Pharmacother. 2006;60:458–62.
Neumann E, Schaefer-Ridder M, Wang Y, Hofschneider PH. Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J. 1982;1:841–5.
Mir LM, Orlowski S, Belehradek J, Paoletti C. Electrochemotherapy potentiation of antitumour effect of bleomycin by local electric pulses. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27:68–72.
Davalos RV, Mir LM, Rubinsky B. Tissue ablation with irreversible electroporation. Ann Biomed Eng. 2005;33:223–31.
Beebe SJ, Sain NM, Ren W. Induction of cell death mechanisms and apoptosis by nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs). Cells. 2013;2:136–62.
Beebe SJ. Considering effects of nanosecond pulsed electric fields on proteins. Bioelectrochemistry. 2015;103:52–9.
Wu S, Wang Y, Guo J, Chen Q, Zhang J, Fang J. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields as a novel drug free therapy for breast cancer: an in vivo study. Cancer Lett. 2014;343:268–74.
Ren W, Sain N, Beebe S. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs) activate intrinsic caspase-dependent and caspase-independent cell death in Jurkat cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;421:808–12.
Zhang J, Blackmore PF, Hargrave BY, Xiao S, Beebe SJ, Schoenbach KH. Nanosecond pulse electric field (nanopulse): a novel non-ligand agonist for platelet activation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;471:240–8.
Vernier PT, Ziegler MJ, Sun Y, Gundersen MA, Tieleman DP. Nanopore-facilitated, voltage-driven phosphatidylserine translocation in lipid bilayers—in cells and in silico. Phys Biol. 2006;3:233.
Ren W, Beebe S. An apoptosis targeted stimulus with nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs) in E4 squamous cell carcinoma. Apoptosis. 2011;16:382–93.
Beebe SJ, Fox PM, Rec LJ, Somers K, Stark RH, Schoenbach KH. Nanosecond pulsed electric field (nsPEF) effects on cells and tissues: apoptosis induction and tumor growth inhibition. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci. 2002;30:286–92.
Garon EB, Sawcer D, Vernier PT, Tang T, Sun Y, Marcu L, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation and a case report of intense nanosecond pulsed electric field as a local therapy for human malignancies. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:675–82.
Nuccitelli R, Pliquett U, Chen X, Ford W, Swanson RJ, Beebe SJ, et al. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields cause melanomas to self-destruct. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;343:351–60.
Nuccitelli R, Chen X, Pakhomov AG, Baldwin WH, Sheikh S, Pomicter JL, et al. A new pulsed electric field therapy for melanoma disrupts the tumor’s blood supply and causes complete remission without recurrence. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:438–45.
Pakhomova ON, Gregory BW, Semenov I, Pakhomov AG. Two modes of cell death caused by exposure to nanosecond pulsed electric field. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e70278.
Morotomi-Yano K, Akiyama H, Yano K. Different involvement of extracellular calcium in two modes of cell death induced by nanosecond pulsed electric fields. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014;555–556:47–54.
Morotomi-Yano K, Akiyama H, Yano KI. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields induce poly(ADP-ribose) formation and non-apoptotic cell death in HeLa S3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;438:557–62.
Beebe S, Fox P, Rec L. Nanosecond, high-intensity pulsed electric fields induce apoptosis in human cells. FASEB J. 2003;17:1493–5.
Vernier PT, Li A, Marcu L, Craft CM, Gundersen MA. Ultrashort pulsed electric fields induce membrane phospholipid translocation and caspase activation: differential sensitivities of Jurkat T lymphoblasts and rat glioma C6 cells. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul. 2003;10:795–809.
Schoenbach KH, Joshi RP, Kolb JF, Chen N, Stacey M, Buescher ES, et al. Ultrashort electrical pulses open a new gateway into biological cells. Proc IEEE. 2004;92:1122–37.
Hall E, Schoenbach K, Beebe S. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields induce apoptosis in p53-wildtype and p53-null HCT116 colon carcinoma cells. Apoptosis. 2007;12:1721–31.
Ford WE, Ren W, Blackmore PF, Schoenbach KH, Beebe SJ. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields stimulate apoptosis without release of pro-apoptotic factors from mitochondria in B16f10 melanoma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010;497:82–9.
Beebe S, Schoenbach K. Nanosecond pulsed electric fields: a new stimulus to activate intracellular signaling. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2005;4:297–300.
Nuccitelli R, Lui K, Kreis M, Athos B, Nuccitelli P. Nanosecond pulsed electric field stimulation of reactive oxygen species in human pancreatic cancer cells is Ca(2+)-dependent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;435:580–5.
Beebe SJ, Ford WE, Ren W, Chen X, Schoenbach KH. Non-ionizing radiation with nanosecond pulsed electric fields as a cancer treatment: in vitro studies. IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc Conf. 2009;2009:6509–12.
Xiao D, Yao C, Liu H, Li C, Cheng J, Guo F, et al. Irreversible electroporation and apoptosis in human liver cancer cells induced by nanosecond electric pulses. Bioelectromagnetics. 2013;34:512–20.
Lowe SW, Cepero E, Evan G. Intrinsic tumour suppression. Nature. 2004;432:307–15.
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL, Cho SK, Li CY, et al. Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death. Nature. 2001;410:549–54.
Fulda S, Debatin K-M. Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene. 2006;25:4798–811.
Stacey M, Stickley J, Fox P, Statler V, Schoenbach K, Beebe S, et al. Differential effects in cells exposed to ultra-short, high intensity electric fields: cell survival, DNA damage, and cell cycle analysis. Mutat Res Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2003;542:65–75.
Kotnik T, Miklavcic D. Theoretical evaluation of the distributed power dissipation in biological cells exposed to electric fields. Bioelectromagnetics. 2000;21:385–94.
Esser AT, Smith KC, Gowrishankar TR, Vasilkoskl Z, Weaver JC. Mechanisms for the intracellular manipulation of organelles by conventional electroporation. Biophys J. 2010;98:2506–14.
Schoenbach KH, Katsuki S, Stark RH, Buescher ES, Beebe SJ. Bioelectrics-new applications for pulsed power technology. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci. 2002;30:293–300.
Weaver JC. Electroporation of biological membranes from multicellular to nano scales. IEEE Trans Dielectr Electr Insul. 2003;10:754–68.
Beebe SJ, White J, Blackmore PF, Deng Y, Somers K, Schoenbach KH. Diverse effects of nanosecond pulsed electric fields on cells and tissues. DNA Cell Biol. 2003;22:785–96.
Tang L, Yao C, Sun C. Apoptosis induction with electric pulses—a new approach to cancer therapy with drug free. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;390:1098–101.
Schoenbach KH, Beebe SJ, Buescher ES. Intracellular effect of ultrashort electrical pulses. Bioelectromagnetics. 2001;22:440–8.
Acknowledgements
This study was sponsored by Project No. 106112015CDJZR158804 supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
No human subjects or animals were used in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Xiao, D., Feng, J. et al. Induction of apoptosis of liver cancer cells by nanosecond pulsed electric fields (nsPEFs). Med Oncol 34, 24 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-016-0882-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-016-0882-1