Abstract
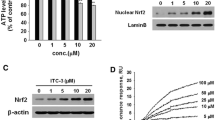
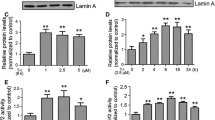
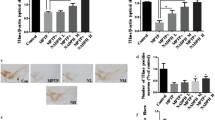
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder associated with a selective loss of the neurons containing dopamine (DA) in the substantia nigra pars compacta. Lines of evidence suggest that oxidative stress is a major factor contributing to the vulnerability of DA cells and that the enzyme NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1) provides protection in these cells. In the present study, we report the synthesis of a novel compound KMS04014 and show that it induces NQO1 gene expression and protects DAergic neuronal cells in both cell culture and animal models of PD. In vitro, KMS04014 increased both mRNA and protein levels of NQO1 and induced nuclear translocation of Nrf2 in the DAergic neuronal cell line CATH.a. It also protected the cells against oxidative stress generated by tetrahydrobiopterin, 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+), and H2O2. In vivo, KMS04014 attenuated the loss of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunopositive DAergic neurons in the substantia nigra and reduced degeneration of the nigral neurons and striatal fibers in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-treated mice, an animal model of PD. Taken together, KMS04014 may be utilized toward development of neuroprotective therapy for PD.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BH4:
-
Tetrahydrobiopterin
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DA:
-
Dopamine
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MPP+ :
-
1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium
- MPTP:
-
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- NQO1:
-
NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase
- Nrf2:
-
Nf-E2-related factor 2
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
- TH:
-
Tyrosine hydroxylase
References
Asanuma M, Miyazaki I, Ogawa N (2003) Dopamine- or L-DOPA-induced neurotoxicity: the role of dopamine quinone formation and tyrosinase in a model of Parkinson's disease. Neurotox Res 5:165–176
Belluzzi E, Bisaglia M, Lazzarini E, Tabares LC, Beltramini M, Bubacco L (2012) Human SOD2 modification by dopamine quinones affects enzymatic activity by promoting its aggregation: possible implications for Parkinson's disease. PLoS One 7:e38026
Beyer RE, Segura-Aguilar J, di Bernardo S et al (1997) The two-electron quinone reductase DT-diaphorase generates and maintains the antioxidant (reduced) form of coenzyme Q in membranes. Mol Asp Med 18(Suppl):S15–S23
Bisaglia M, Soriano ME, Arduini I, Mammi S, Bubacco L (2010) Molecular characterization of dopamine-derived quinones reactivity toward NADH and glutathione: implications for mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802:699–706
Cavelier G, Amzel LM (2001) Mechanism of NAD(P)H:quinone reductase: Ab initio studies of reduced flavin. Proteins 43:420–432
Cho Y, Son HJ, Kim EM et al (2009) Doxycycline is neuroprotective against nigral dopaminergic degeneration by a dual mechanism involving MMP-3. Neurotox Res 16:361–371
Choi HJ, Jang YJ, Kim HJ, Hwang O (2000) Tetrahydrobiopterin is released from and causes preferential death of catecholaminergic cells by oxidative stress. Mol Pharmacol 58:633–640
Choi HJ, Kim SW, Lee SY, Hwang O (2003) Dopamine-dependent cytotoxicity of tetrahydrobiopterin: a possible mechanism for selective neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem 86:143–152
Choi HJ, Lee SY, Cho Y, Hwang O (2005) Inhibition of vesicular monoamine transporter enhances vulnerability of dopaminergic cells: relevance to Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Int 46:329–335
Choi DH, Kim EM, Son HJ et al (2008) A novel intracellular role of matrix metalloproteinase-3 during apoptosis of dopaminergic cells. J Neurochem 106:405–415
Conway KA, Rochet JC, Bieganski RM, Lansbury PT Jr (2001) Kinetic stabilization of the alpha-synuclein protofibril by a dopamine-alpha-synuclein adduct. Science 294:1346–1349
Duffy S, So A, Murphy TH (1998) Activation of endogenous antioxidant defenses in neuronal cells prevents free radical-mediated damage. J Neurochem 71:69–77
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (1997) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 59–67
Fujisawa S, Atsumi T, Kadoma Y, Sakagami H (2002) Antioxidant and prooxidant action of eugenol-related compounds and their cytotoxicity. Toxicology 177:39–54
Fujisawa S, Atsumi T, Kadoma Y, Ishihara M, Ito S, Yokoe I (2004) Kinetic radical scavenging activity and cytotoxicity of 2-methoxy- and 2-t-butyl-substituted phenols and their dimers. Anticancer Res 24:3019–3026
Fujisawa S, Atsumi T, Murakami Y, Kadoma Y (2005) Dimerization, ROS formation, and biological activity of o-methoxyphenols. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 53:28–38
Graham DG, Tiffany SM, Bell WR Jr, Gutknecht WF (1978) Autoxidation versus covalent binding of quinones as the mechanism of toxicity of dopamine, 6-hydroxydopamine, and related compounds toward C1300 neuroblastoma cells in vitro. Mol Pharmacol 14:644–653
Han JM, Lee YJ, Lee SY et al (2007) Protective effect of sulforaphane against dopaminergic cell death. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:249–256
Hara H, Ohta M, Ohta K, Kuno S, Adachi T (2003) Increase of antioxidative potential by tert-butylhydroquinone protects against cell death associated with 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress in neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 119:125–131
Harada S, Fujii C, Hayashi A, Ohkoshi N (2001) An association between idiopathic Parkinson's disease and polymorphisms of phase II detoxification enzymes: glutathione S-transferase M1 and quinone oxidoreductase 1 and 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 288:887–892
Hastings TG, Zigmond MJ (1997) Loss of dopaminergic neurons in parkinsonism: possible role of reactive dopamine metabolites. J Neural Transm Suppl 49:103–110
Hirata A, Murakami Y, Atsumi T et al (2005) Ferulic acid dimer inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. In Vivo 19:849–853
Hwang O, Baker H, Gross S, Joh TH (1998) Localization of GTP cyclohydrolase in monoaminergic but not nitric oxide-producing cells. Synapse 28:140–153
Hwang O, Kim G, Jang YJ et al (2001) Synthetic phytoceramides induce apoptosis with higher potency than ceramides. Mol Pharmacol 59:1249–1255
Inoue M, Suzuki R, Koide T, Sakaguchi N, Ogihara Y, Yabu Y (1994) Antioxidant, gallic acid, induces apoptosis in HL-60RG cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 204:898–904
Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y et al (1999) Keap1 represses nuclear activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes Dev 13:76–86
Jazwa A, Rojo AI, Innamorato NG, Hesse M, Fernandez-Ruiz J, Cuadrado A (2011) Pharmacological targeting of the transcription factor Nrf2 at the basal ganglia provides disease modifying therapy for experimental parkinsonism. Antioxid Redox Signal 14:2347–2360
Jia Z, Zhu H, Misra HP, Li Y (2008) Potent induction of total cellular GSH and NQO1 as well as mitochondrial GSH by 3H-1,2-dithiole-3-thione in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and primary human neurons: protection against neurocytotoxicity elicited by dopamine, 6-hydroxydopamine, 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, or hydrogen peroxide. Brain Res 1197:159–169
Jia Z, Zhu H, Li Y, Misra HP (2009) Cruciferous nutraceutical 3H-1,2-dithiole-3-thione protects human primary astrocytes against neurocytotoxicity elicited by MPTP, MPP(+), 6-OHDA, HNE and acrolein. Neurochem Res 34:1924–1934
Joseph P, Long DJ 2nd, Klein-Szanto AJ, Jaiswal AK (2000) Role of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (DT diaphorase) in protection against quinone toxicity. Biochem Pharmacol 60:207–214
Kim ST, Choi JH, Chang JW, Kim SW, Hwang O (2005) Immobilization stress causes increases in tetrahydrobiopterin, dopamine, and neuromelanin and oxidative damage in the nigrostriatal system. J Neurochem 95:89–98
Kim EM, Shin EJ, Choi JH et al (2010) Matrix metalloproteinase-3 is increased and participates in neuronal apoptotic signaling downstream of caspase-12 during endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem 285:16444–16452
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H et al (2004) Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol 24:7130–7139
LaVoie MJ, Ostaszewski BL, Weihofen A, Schlossmacher MG, Selkoe DJ (2005) Dopamine covalently modifies and functionally inactivates parkin. Nat Med 11:1214–1221
Lee SY, Moon Y, Choi DH, Choi HJ, Hwang O (2007) Particular vulnerability of rat mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons to tetrahydrobiopterin: relevance to Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 25:112–120
Lee JA, Kim JH, Woo SY et al (2014) A novel compound VSC2 has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties in microglia and in Parkinson's disease animal model. Br J Pharmacol. doi:10.1111/bph.12973
Lim JH, Kim KM, Kim SW, Hwang O, Choi HJ (2008) Bromocriptine activates NQO1 via Nrf2-PI3K/Akt signaling: novel cytoprotective mechanism against oxidative damage. Pharmacol Res 57:325–331
Ma ZC, Hong Q, Wang YG et al (2010) Ferulic acid protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells from radiation induced oxidative stress by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. Biol Pharm Bull 33:29–34
Martinez-Vicente M, Talloczy Z, Kaushik S et al (2008) Dopamine-modified alpha-synuclein blocks chaperone-mediated autophagy. J Clin Invest 118:777–788
Maurya DK, Devasagayam TP (2010) Antioxidant and prooxidant nature of hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives ferulic and caffeic acids. Food Chem Toxicol 48:3369–3373
Miyazaki I, Asanuma M, Diaz-Corrales FJ et al (2006) Methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity is regulated by quinone-formation-related molecules. FASEB J 20:571–573
Murakami Y, Shoji M, Ogiwara T, Tanaka S, Yokoe I, Fujisawa S (2006) Preventive effect of ortho dimer of butylated hydroxyanisole on activator protein-1 activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages stimulated by fimbriae of Porphyromonas gingivalis, an oral anaerobe. Anticancer Res 26:2915–2920
Schmued LC, Stowers CC, Scallet AC, Xu L (2005) Fluoro-Jade C results in ultra high resolution and contrast labeling of degenerating neurons. Brain Res 1035:24–31
Sergediene E, Jonsson K, Szymusiak H, Tyrakowska B, Rietjens IM, Cenas N (1999) Prooxidant toxicity of polyphenolic antioxidants to HL-60 cells: description of quantitative structure-activity relationships. FEBS Lett 462:392–396
Siebert A, Desai V, Chandrasekaran K, Fiskum G, Jafri MS (2009) Nrf2 activators provide neuroprotection against 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity in rat organotypic nigrostriatal cocultures. J Neurosci Res 87:1659–1669
Siegel D, Bolton EM, Burr JA, Liebler DC, Ross D (1997) The reduction of alpha-tocopherolquinone by human NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase: the role of alpha-tocopherolhydroquinone as a cellular antioxidant. Mol Pharmacol 52:300–305
Siegel D, Anwar A, Winski SL, Kepa JK, Zolman KL, Ross D (2001) Rapid polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of a mutant form of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1. Mol Pharmacol 59:263–268
Siegel D, Gustafson DL, Dehn DL et al (2004) NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1: role as a superoxide scavenger. Mol Pharmacol 65:1238–1247
Son HJ, Lee JA, Shin N et al (2012) A novel compound PTIQ protects the nigral dopaminergic neurones in an animal model of Parkinson's disease induced by MPTP. Br J Pharmacol 165:2213–2227
Thyagaraju BM, Muralidhara (2008) Ferulic acid supplements abrogate oxidative impairments in liver and testis in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Zool Sci 25:854–860
Van Laar VS, Mishizen AJ, Cascio M, Hastings TG (2009) Proteomic identification of dopamine-conjugated proteins from isolated rat brain mitochondria and SH-SY5Y cells. Neurobiol Dis 34:487–500
van Muiswinkel FL, de Vos RA, Bol JG et al (2004) Expression of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase in the normal and Parkinsonian substantia nigra. Neurobiol Aging 25:1253–1262
Venugopal R, Jaiswal AK (1996) Nrf1 and Nrf2 positively and c-Fos and Fra1 negatively regulate the human antioxidant response element-mediated expression of NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:14960–14965
Wang N, Wang Y, Yu G, Yuan C, Ma J (2011) Quinoprotein adducts accumulate in the substantia nigra of aged rats and correlate with dopamine-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Res 36:2169–2175
Woo SY, Kim JH, Moon MK et al (2014) Discovery of vinyl sulfones as a novel class of neuroprotective agents toward Parkinson's disease therapy. J Med Chem 57:1473–1487
Yeh CT, Ching LC, Yen GC (2009) Inducing gene expression of cardiac antioxidant enzymes by dietary phenolic acids in rats. J Nutr Biochem 20:163–171
Zafar KS, Inayat-Hussain SH, Siegel D, Bao A, Shieh B, Ross D (2006a) Overexpression of NQO1 protects human SK-N-MC neuroblastoma cells against dopamine-induced cell death. Toxicol Lett 166:261–267
Zafar KS, Siegel D, Ross D (2006b) A potential role for cyclized quinones derived from dopamine, DOPA, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid in proteasomal inhibition. Mol Pharmacol 70:1079–1086
Zahid M, Saeed M, Yang L, Beseler C, Rogan E, Cavalieri EL (2011) Formation of dopamine quinone-DNA adducts and their potential role in the etiology of Parkinson's disease. IUBMB Life 63:1087–1093
Zhou ZD, Lim TM (2009) Dopamine (DA) induced irreversible proteasome inhibition via DA derived quinones. Free Radic Res 43:417–430
Zhou ZD, Lim TM (2010) Glutathione conjugates with dopamine-derived quinones to form reactive or non-reactive glutathione-conjugates. Neurochem Res 35:1805–1818
Acknowledgments
Hyo Jin Son and Ji Hyun Choi made equal contributions. This work was supported by the National Agenda Project from Korea Research Council of Fundamental Science and Technology (OH) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2009-0081675, OH; NRF-2013-R1A1A22059669, HJS).
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, H.J., Choi, J.H., Lee, J.A. et al. Induction of NQO1 and Neuroprotection by a Novel Compound KMS04014 in Parkinson’s Disease Models. J Mol Neurosci 56, 263–272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0516-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0516-7