Abstract
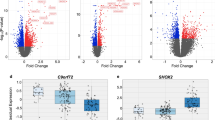
Focal cortical dysplasias (FCDs) are frequently associated with the medical refractory epilepsy in both children and adults. Transient receptor potential canonical channel 5 (TRPC5), a receptor-operated cation channel, has been well recognized as a regulator in the central nervous system. Here, we examined the expression and cellular distribution of TRPC5 in the specimens from patients with FCDIa (n = 14), FCDIIa (n = 12), and FCDIIb (n = 12) compared with the age-matched control cortex (CTX). TRPC5 mRNA and protein levels were significantly higher in FCDs compared with CTX. Immunohistochemical data showed that TRPC5 was strongly expressed in the misshapen cells, particularly in neuronal microcolumns, dysmorphic neurons, and balloon cells. Moreover, the double-label immunofluorescence analyses demonstrated that TRPC5 localized on NeuN-positive neurons. In addition, its co-localization with glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) indicated that TRPC5 was distributed on both glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons. Taken together, these results suggested that increased expression of TRPC5 in FCDs and the cell-specific distribution patterns of TRPC5 in the misshapen neurons in FCDs could potentially contribute to the epileptogenesis of FCDs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andre VM, Flores-Hernandez J, Cepeda C et al (2004) NMDA receptor alterations in neurons from pediatric cortical dysplasia tissue. Cereb Cortex 14:634–646
Antonio R, Andrew DM, Cesar M et al (2002) RNA distribution analysis of human TRPC family in CNS and peripheral tissues. Mol Brain Res 109:95–104
Bezzerides VJ, Ramsey IS, Kotecha S, Greka A, Clapham DE (2004) Rapid vesicular translocation and insertion of TRP channels. Nat Cell Biol 6:709–720
Blumcke I, Thom M, Aronica E et al (2011) The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: a consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission. Epilepsia 52:158–174
Crino PB, Eberwine J (1997) Cellular and molecular basis of cerebral dysgenesis. J Neurosci Res 50:907–916
Davare MA, Fortin DA, Saneyoshi T et al (2009) Transient receptor potential canonical 5 channels activate Ca2+/calmodulin kinase Igamma to promote axon formation in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 29:9794–9808
Fowler MA, Sidiropoulou K, Ozkan ED, Phillips CW, Cooper DC (2007) Corticolimbic expression of TRPC4 and TRPC5 channels in the rodent brain. PLoS One 2:e573
Freichel M, Vennekens R, Olausson J et al (2004) Functional role of TRPC proteins in vivo: Lessons from TRPC-deficient mouse models. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 322:1352–1358
Gomez T (2005) Neurobiology: channels for pathfinding. Nature 434:835–838
Greka A, Navarro B, Oancea E, Duggan A, Clapham DE (2003) TRPC5 is a regulator of hippocampal neurite length and growth cone morphology. Nat Neurosci 6:837–845
Gross SA, Guzman GA, Wissenbach U et al (2009) TRPC5 is a Ca2+-activated channel functionally coupled to Ca2+-selective ion channels. J Biol Chem 284:34423–34432
He ZH, Jia CX, Feng SJ et al (2012) TRPC5 Channel is the mediator of neurotrophin-3 in regulating dendritic growth via CaMKII in rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 32:9383–9395
He JJ, Li S, Shu HF et al (2013) The interleukin 17 systemin cortical lesions in focal cortical dysplasias. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 72:152–163
Heo DK, Chung WY, Park HW, Yuan JP, Lee MG, Kim JY (2012) Opposite regulatory effects of TRPC1 and TRPC5 on neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. Cell Signal 24:899–906
Hertz L, Zielke HR (2004) Astrocytic control of glutamatergic activity: astrocytes as stars of the show. TRENDS Neurosci 27:735–743
Jia Y, Zhou J, Tai Y, Wang Y (2007) TRPC channels promote cerebellar granule neuron survival. Nat Neurosci 10:559–567
Kaczmarek JS, Riccio A, Clapham DE (2012) Calpain cleaves and activates the TRPC5 channel to participate in semaphorin 3A-induced neuronal growth cone collapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:7888–7892
Malarkey EB, Ni Y, Parpura V (2008) Ca2+ entry through TRPC1 channels contributes to intracellular Ca2+ dynamics and consequent glutamate release from rat astrocytes. Glia 56:821–835
Mathern GW, Andres M, Salamon N et al (2007) A hypothesis regarding the pathogenesis and epileptogenesis of pediatric cortical dysplasia and hemimegalencephaly based on MRI cerebral volumes and NeuN cortical cell densities. Epilepsia 48 (Suppl. 5): 74-78.
Montell C. (2005) The TRP superfamily of cation channels. Sci STKE 272, re3: DOI: 10.1126.
Najm IM, Tilelli CQ, Oghlakian R (2007) Pathophysiological mechanisms of focal cortical dysplasia: a critical review of human tissue studies and animal models. Epilepsia 48(Suppl 2):21–32
Oh HS, Lee MC, Kim HS et al (2008) Pathophysiologic characteristics of balloon cells in cortical dysplasia. Childs Nerv Syst 24:175–183
Palmini A, Najm I, Avanzini G et al (2004) Terminology and classification of the cortical dysplasias. Neurology 62:S2–S8
Parent JM (2007) Adult neurogenesis in the intact and epileptic dentate gyrus. Prog Brain Res 163:529–540
Phelan KD, Shwe UT, Abramowitz J et al (2012) Canonical Transient receptor channel 5 (TRPC5) and TRPC1/4 contribute to seizure and excitotoxicity by distinct cellular mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol 83:429–438
Philipp S, Hambrecht J, Braslavski L et al (1998) A novel capacitative calcium entry channel expressed in excitable cells. EMBO J 17:4274–4282
Puram SV, Riccio A, Koirala S et al (2011) A TRPC5-regulated calcium signaling pathway controls dendrite patterning in the mammalian brain. Genes Dev 25:2659–2673
Shin HY, Hong YH, Jang SS et al (2010) A role of canonical transient receptor potential 5 channel in neuronal differentiation from A2B5 neural progenitor cells. PLoS One 5:e10359
Shu HF, Zhang CQ, Yin Q et al (2010) Expression of the interleukin 6 system in cortical lesions from patients with tuberous sclerosis complex and focal cortical dysplasia type IIb. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69(8):838–849
Sossey-Alaoui K, Lyon JA, Jones L et al (1999) Molecular cloning and characterization of TRPC5 (HTRP5), the human homologue of a mouse brain receptor-activated capacitative Ca2+ entry channel. Genomics 60:330–340
Spreafico R, Blumcke I (2010) Focal cortical dysplasias: clinical implication of neuropathological classification systems. Acta Neuropathol 120:359–367
Strubing C, Krapivinsky G, Krapivinsky L, Clapham DE (2001) TRPC1 and TRPC5 form a novel cation channel in mammalian brain. Neuron 29:645–655
Tai C, Hines DJ, Choi HB, MacVicar BA (2011) Plasma membrane insertion of TRPC5 channels contributes to the cholinergic plateau potential in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Hippocampus 21:958–967
Tassi L, Colombo N, Garbelli R et al (2002) Focal cortical dysplasia: neuropathological subtypes, EEG, neuroimaging and surgical outcome. Brain 125:1719–1732
Tassi L, Garbelli R, Colombo N et al (2010) Type I focal cortical dysplasia: surgical outcome is related to histopathology. Epileptic Disord 12:181–191
Tassi L, Garbelli R, Colombo N et al (2012) Electroclinical, MRI and surgical outcomes in 100 epileptic patients with type II FCD. Epileptic Disord 14:257–266
Taylor DC, Falconer MA, Bruton CJ, Corsellis JA (1971) Focal dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 34:369–387
Wong M (2008) Mechanisms of epileptogenesis in tuberous sclerosis complex and related malformations of cortical development with abnormal glioneuronal proliferation. Epilepsia 49:8–21
Wong RO, Ghosh A (2002) Activity-dependent regulation of dendritic growth and patterning. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:803–812
Yuste R, Bonhoeffer T (2001) Morphological changes in dendritic spines associated with long-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1071–1089
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank the patients and their families for their participation in this work. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81071043, 81100975, 81070953), Natural Science Foundation Project of CQ CSTC (No. 2011JJ0124), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (NO. 2012 T50850).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guang-Zhen Xu and Hai-feng Shu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, GZ., Shu, Hf., Yue, HY. et al. Increased Expression of TRPC5 in Cortical Lesions of the Focal Cortical Dysplasia. J Mol Neurosci 55, 561–569 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0390-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0390-8