Abstract
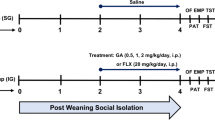
Laquinimod is a novel oral immunomodulatory drug for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS). Considering the frequent co-morbidity of MS with anxiety and depression, we sought to assess the antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of laquinimod in mouse models. Laquinimod (0.5–25 mg/kg), fluoxetine (10 mg/kg) or vehicle were administered for 4–14 days to adult Balb/c mice, followed by behavioral tests and brain BDNF analysis. Following a 4-day administration of laquinimod (5 and 25 mg/kg), an increase in motivated behavior was observed in the forced swim test (p < 0.01 vs. controls). In the open field test, laquinimod (0.5–5 mg/kg), but not fluoxetine, significantly increased motility (p < 0.05), whereas both decreased anxiety behavior (p < 0.01), evident only for laquinimod (5 mg/kg) in the elevated plus maze (p < 0.05). Following 7 days of administration, both drugs decreased anxiety behavior in the elevated plus maze and marble burying tests (p < 0.001 and p < 0.02, respectively). After 14 days, only laquinimod (5 mg/kg) demonstrated anxiolytic efficacy in the open field test (p < 0.05), with evidence of increased BDNF in response to 5–25 mg/kg in the hippocampus, but not frontal cortex (p < 0.05). In conclusion, laquinimod may possess anxiolytic and antidepressant effects, possibly associated with hippocampal BDNF increase, offering promise for MS patients suffering from psychiatric co-morbidity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharoni R, Saada R, Eilam R, Hayardeny L, Sela M, Arnon R (2012) Oral treatment with laquinimod augments regulatory T-cells and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression and reduces injury in the CNS of mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 251(1–2):14–24
American Psychiatric Association (2010) Practice guideline for the treatment of patients with major depressive disorder, 3rd edn. American Psychiatric Association, Arlington
Bakshi R, Czarnecki D, Shaikh ZA et al (2000) Brain MRI lesions and atrophy are related to depression in multiple sclerosis. Neuroreport 11(6):1153–1158
Beiske AG, Svensson E, Sandanger I et al (2008) Depression and anxiety amongst multiple sclerosis patients. Eur J Neurol 15(3):239–245
Borras C, Rio J, Porcel J, Barrios M, Tintore M, Montalban X (1999) Emotional state of patients with relapsing-remitting MS treated with interferon beta-1b. Neurology 52(8):1636–1639
Bruck W, Wegner C (2011) Insight into the mechanism of laquinimod action. J Neurol Sci 306(1–2):173–179
Castren E, Hen R (2013) Neuronal plasticity and antidepressant actions. Trends Neurosci 36(5):259–267
Castren E, Rantamaki T (2010) The role of BDNF and its receptors in depression and antidepressant drug action: reactivation of developmental plasticity. Dev Neurobiol 70(5):289–297
Comi G, Jeffery D, Kappos L et al (2012) Placebo-controlled trial of oral laquinimod for multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 366(11):1000–1009
Comi G, Pulizzi A, Rovaris M et al (2008) Effect of laquinimod on MRI-monitored disease activity in patients with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIb study. Lancet 371(9630):2085–2092
Cowansage KK, LeDoux JE, Monfils MH (2010) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a dynamic gatekeeper of neural plasticity. Curr Mol Pharmacol 3(1):12–29
De Santi L, Annunziata P, Sessa E, Bramanti P (2009) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB receptor in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 287(1–2):17–26
Dranovsky A, Hen R (2006) Hippocampal neurogenesis: regulation by stress and antidepressants. Biol Psychiatry 59(12):1136–1143
Dwivedi Y, Rizavi HS, Conley RR, Roberts RC, Tamminga CA, Pandey GN (2003) Altered gene expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and receptor tyrosine kinase B in postmortem brain of suicide subjects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60(8):804–815
Feinstein A (2000) Multiple sclerosis, disease modifying treatments and depression: a critical methodological review. Mult Scler 6(5):343–348
Feinstein A, Roy P, Lobaugh N, Feinstein K, O’Connor P, Black S (2004) Structural brain abnormalities in multiple sclerosis patients with major depression. Neurology 62(4):586–590
Galeazzi GM, Ferrari S, Giaroli G et al (2005) Psychiatric disorders and depression in multiple sclerosis outpatients: impact of disability and interferon beta therapy. Neurol Sci 26(4):255–262
Groves JO (2007) Is it time to reassess the BDNF hypothesis of depression? Mol Psychiatry 12(12):1079–1088
Hagemeier K, Bruck W, Kuhlmann T (2012) Multiple sclerosis—remyelination failure as a cause of disease progression. Histol Histopathol 27(3):277–287
Holick KA, Lee DC, Hen R, Dulawa SC (2008) Behavioral effects of chronic fluoxetine in BALB/cJ mice do not require adult hippocampal neurogenesis or the serotonin 1A receptor. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(2):406–417
Jacobs BL, van Praag H, Gage FH (2000a) Adult brain neurogenesis and psychiatry: a novel theory of depression. Mol Psychiatry 5(3):262–269
Jacobs LD, Beck RW, Simon JH et al (2000b) Intramuscular interferon beta-1a therapy initiated during a first demyelinating event in multiple sclerosis. CHAMPS Study Group. N Engl J Med 343(13):898–904
Janssens AC, van Doorn PA, de Boer JB, van der Meche FG, Passchier J, Hintzen RQ (2003) Impact of recently diagnosed multiple sclerosis on quality of life, anxiety, depression and distress of patients and partners. Acta Neurol Scand 108(6):389–395
Julian LJ, Vella L, Frankel D, Minden SL, Oksenberg JR, Mohr DC (2009) ApoE alleles, depression and positive affect in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 15(3):311–315
Kahl KG, Kruse N, Faller H, Weiss H, Rieckmann P (2002) Expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma mRNA in blood cells correlates with depression scores during an acute attack in patients with multiple sclerosis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 27(6):671–681
Korostil M, Feinstein A (2007) Anxiety disorders and their clinical correlates in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler 13(1):67–72
Liguori M, Fera F, Gioia MC et al (2007) Investigating the role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Genes Brain Behav 6(2):177–183
Liguori M, Fera F, Patitucci A et al (2009) A longitudinal observation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA levels in patients with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Brain Res 1256:123–128
Malberg JE, Schechter LE (2005) Increasing hippocampal neurogenesis: a novel mechanism for antidepressant drugs. Curr Pharm Des 11(2):145–155
Nicolas LB, Kolb Y, Prinssen EP (2006) A combined marble burying-locomotor activity test in mice: a practical screening test with sensitivity to different classes of anxiolytics and antidepressants. Eur J Pharmacol 547(1–3):106–115
Overstreet DH (2012) Modeling depression in animal models. Methods Mol Biol 829:125–144
Paparrigopoulos T, Ferentinos P, Kouzoupis A, Koutsis G, Papadimitriou GN (2010) The neuropsychiatry of multiple sclerosis: focus on disorders of mood, affect and behaviour. Int Rev Psychiatry 22(1):14–21
Patten SB, Metz LM (2001) Interferon beta-1 a and depression in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: an analysis of depression data from the PRISMS clinical trial. Mult Scler 7(4):243–248
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open:closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14(3):149–167
Peruga I, Hartwig S, Thone J et al (2011) Inflammation modulates anxiety in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Behav Brain Res 220(1):20–29
Pinheiro SH, Zangrossi H Jr, Del-Ben CM, Graeff FG (2007) Elevated mazes as animal models of anxiety: effects of serotonergic agents. An Acad Bras Cienc 79(1):71–85
Porcel J, Rio J, Sanchez-Betancourt A et al (2006) Long-term emotional state of multiple sclerosis patients treated with interferon beta. Mult Scler 12(6):802–807
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M (1977) Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 266(5604):730–732
Prut L, Belzung C (2003) The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: a review. Eur J Pharmacol 463(1–3):3–33
Pujol J, Bello J, Deus J, Marti-Vilalta JL, Capdevila A (1997) Lesions in the left arcuate fasciculus region and depressive symptoms in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 49(4):1105–1110
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C et al (2003) Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 301(5634):805–809
Schiffer RB, Weitkamp LR, Wineman NM, Guttormsen S (1988) Multiple sclerosis and affective disorder. Family history, sex, and HLA-DR antigens. Arch Neurol 45(12):1345–1348
Sen S, Duman R, Sanacora G (2008) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression, and antidepressant medications: meta-analyses and implications. Biol Psychiatry 64(6):527–532
Siegert RJ, Abernethy DA (2005) Depression in multiple sclerosis: a review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(4):469–475
Smith SJ, Young CA (2000) The role of affect on the perception of disability in multiple sclerosis. Clin Rehabil 14(1):50–54
Tanis KQ, Newton SS, Duman RS (2007) Targeting neurotrophic/growth factor expression and signaling for antidepressant drug development. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 6(2):151–160
Thone J, Ellrichmann G, Seubert S et al (2012) Modulation of autoimmune demyelination by laquinimod via induction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Am J Pathol 180(1):267–274
Thone J, Gold R (2011) Laquinimod: a promising oral medication for the treatment of relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 7(3):365–370
Tselis A (2010) Laquinimod, a new oral autoimmune modulator for the treatment of relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 11(5):577–585
Yan HC, Cao X, Das M, Zhu XH, Gao TM (2010) Behavioral animal models of depression. Neurosci Bull 26(4):327–337
Zivadinov R, Zorzon M, Tommasi MA et al (2003) A longitudinal study of quality of life and side effects in patients with multiple sclerosis treated with interferon beta-1a. J Neurol Sci 216(1):113–118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Irit Gil-Ad and Ben H. Amit are equal contributors and co-authors of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gil-Ad, I., Amit, B.H., Hayardeni, L. et al. Effects of the Anti-Multiple Sclerosis Immunomodulator Laquinimod on Anxiety and Depression in Rodent Behavioral Models. J Mol Neurosci 55, 552–560 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0387-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0387-3