Abstract
Background
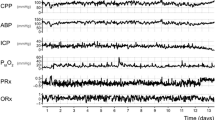
Transcranial Doppler-derived indices of cerebral autoregulation are related to outcome after TBI. We analyzed our retrospective material to identify thresholds discriminative of outcome for these indices.
Methods
248 sedated and ventilated patients after head injury were eligible for the study. The indices of autoregulation derived from transcranial Doppler were calculated as correlation coefficients of blood flow velocity with cerebral perfusion pressure (index Mx) or arterial blood pressure (index Mxa). 2 × 2 tables were created grouping patients according to survival–death or favorable–unfavorable outcomes and varying thresholds for Mx and Mxa. Pearson’s chi-square was calculated. Thresholds returning the highest chi-square value were assumed to have the best discriminative value between survival–death and favorable–unfavorable outcomes.
Results
Mx and Mxa demonstrated that worse autoregulation is associated with poorer outcome and greater mortality (P = 0.0033 for Mx and P = 0.047 for Mxa). Both indices were more effective for prediction of favorable outcome than mortality. Chi-square for Mx showed a double peak with thresholds at 0.05 and 0.3. Mxa had only one peak at 0.3. Peak chi-square for Mx (11.3) was greater than for Mxa (8.7), indicating that Mx was a better discriminant of outcome than Mxa.
Conclusions
We propose that Mx greater than 0.3 indicates definitely disturbed autoregulation and lower than 0.05 good autoregulation. For values between 0.05 and 0.3 the state of autoregulation is uncertain.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Piechnik S, Steiner LA, Pickard JD. Cerebral autoregulation following head injury. J Neurosurg. 2001;95:756–63.
Brady KM, Shaffner DH, Lee JK, Easley RB, Smielewski P, Czosnyka M, Jallo GI, Guerguerian AM. Continuous monitoring of cerebrovascular pressure reactivity after traumatic brain injury in children. Pediatrics. 2009;124:e1205–12.
Panerai RB, Kerins V, Fan L, Yeoman PM, Hope T, Evans DH. Association between dynamic cerebral autoregulation and mortality in severe head injury. Br J Neurosurg. 2004;18:471–9.
Castellani G, Zweifel C, Kim DJ, Carrera E, Radolovich DK, Smielewski P, Hutchinson PJ, Pickard JD, Czosnyka M. Plateau waves in head injured patients requiring neurocritical care. Neurocrit Care. 2009;11:143–50.
Tzeng YC, Willie CK, Atkinson G, Lucas SJ, Wong A, Ainslie PN. Cerebrovascular regulation during transient hypotension and hypertension in humans. Hypertension. 2010;56:268–73.
Rangel-Castilla L, Rivera Lara L, Gopinath SP, Swank PR, Valadka A, Robertson C. Cerebral hemodynamic effects of acute hyperoxia and hyperventilation after severe traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2010;27:1853–63.
Immink RV, van den Born BJ, van Montfrans GA, Koopmans RP, Karemaker JM, van Lieshout JJ. Impaired cerebral autoregulation in patients with malignant hypertension. Circulation. 2004;110:2241–5.
Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Kirkpatrick P, Menon DK, Pickard JD. Monitoring of cerebral autoregulation in head-injured patients. Stroke. 1996;27:1829–34.
Lewis PM, Smielewski P, Pickard JD, Czosnyka M. Dynamic cerebral autoregulation: should intracranial pressure be taken into account? Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2007;149:549–55.
Lang EW, Mehdorn HM, Dorsch NW, Czosnyka M. Continuous monitoring of cerebrovascular autoregulation: a validation study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2002;72:583–6.
Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Czosnyka Z, Piechnik S, Steiner LA, Schmidt E, Gooskens I, Soehle M, Lang EW, Matta BF, Pickard JD. Continuous assessment of cerebral autoregulation: clinical and laboratory experience. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2003;86:581–5.
Lang EW, Lagopoulos J, Griffith J, Yip K, Mudaliar Y, Mehdorn HM, Dorsch NW. Non invasive cerebrovascular autoregulation assessment in traumatic brain injury: validation and utility. J Neurotrauma. 2003;20:69–75.
Soehle M, Czosnyka M, Pickard JD, Kirkpatrick PJ. Continuous assessment of cerebral autoregulation in subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anesth Analg. 2004;98:1133–9.
Reinhard M, Neunhoeffer F, Gerds TA, Niesen WD, Buttler KJ, Timmer J, Schmidt B, Czosnyka M, Weiller C, Hetzel A. Secondary decline of cerebral autoregulation is associated with worse outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage. Intensive Care Med. 2010;36:264–71.
Rosner MJ, Rosner SD, Johnson AH. Cerebral perfusion pressure: management protocol and clinical results. J Neurosurg. 1995;83:949–62.
Helmy A, Vizcaychipi M, Gupta AK. Traumatic brain injury: intensive care management. Br J Anaesth. 2007;99:32–42.
Guendling K, Smielewski P, Czosnyka M, Lewis P, Nortje J, Timofeev I, Hutchinson PJ, Pickard JD. Use of ICM+ software for on-line analysis of intracranial and arterial pressures in head-injured patients. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2006;96:108–13.
Cold GE. Jensen FT: cerebral autoregulation in unconscious patients with brain injury. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1978;22:270–80.
Enevoldsen EM, Jensen FT. Autoregulation and CO2 responses of cerebral blood flow in patients with acute severe head injury. J Neurosurg. 1978;48:689–703.
Muizelaar JP, Ward JD, Marmarou A, Newlon PG, Wachi A. Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in severely head-injured children. Part 2: autoregulation. J Neurosurg. 1989;71:72–6.
Overgaard J, Tweed WA. Cerebral circulation after head injury. 1. Cerebral blood flow and its regulation after closed head injury with emphasis on clinical correlations. J Neurosurg. 1974;41:531–41.
Balestreri M, Czosnyka M, Steiner LA, Hiler M, Schmidt EA, Matta B, Menon D, Hutchinson P, Pickard JD. Association between outcome, cerebral pressure reactivity and slow ICP waves following head injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2005;95:25–8.
Steiner LA, Czosnyka M, Piechnik SK, Smielewski P, Chatfield D, Menon DK, Pickard JD. Continuous monitoring of cerebrovascular pressure reactivity allows determination of optimal cerebral perfusion pressure in patients with traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Med. 2002;30:733–8.
Steiner LA, Pfister D, Strebel SP, Radolovich D, Smielewski P, Czosnyka M. Near-infrared spectroscopy can monitor dynamic cerebral autoregulation in adults. Neurocrit Care. 2009;10:122–8.
Brady KM, Mytar JO, Kibler KK, Hogue CW Jr, Lee JK, Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Easley RB. Non invasive autoregulation monitoring with and without intracranial pressure in the naive piglet brain. Anesth Analg. 2010;111:191–5.
Steiner LA, Johnston AJ, Chatfield DA, Czosnyka M, Coleman MR, Coles JP, Gupta AK, Pickard JD, Menon DK. The effects of large-dose propofol on cerebrovascular pressure autoregulation in head-injured patients. Anesth Analg. 2003;97(2):572–6.
Steiner LA, Balestreri M, Johnston AJ, Coles JP, Chatfield DA, Pickard JD, Menon DK. Czosnyka M effects of moderate hyperventilation on cerebrovascular pressure-reactivity after head injury. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2005;95:17–20.
Piechnik SK, Yang X, Czosnyka M, Smielewski P, Fletcher SH, Jones AL, Pickard JD. The continuous assessment of cerebrovascular reactivity: a validation of the method in healthy volunteers. Anesth Analg. 1999;89(4):944–9.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the National Institute of Health Research, Biomedical Research Center, Cambridge University Hospital Foundation Trust—Neurosciences Theme and Senior Investigator Awards (JDP), Technology Foresight Challenge Fund (Grant FCA 234/95), MRC Program Grant (MRC G9439390). Clifford and Mary Corbridge Trust (KPB), and Foundation for Polish Science (MK).
Many thanks to all colleagues participating in head injury monitoring program in Cambridge, UK in 1991–2009, whose experience, knowledge, and clinical material helped us to write this study: Mrs. P. Al-Rawi, Mrs. D. Chattfield, Mrs. A. Menkdelov, Mrs. C. Turner, Dr. M. Balestreri, Miss. M. Hiler, Dr. S.K. Piechnik, Dr. L.A. Steiner, Mr. P.J. Hutchinson, Mr. P. Kirkpatrick, Mr. E. Guazzo, Mr. P.C. Whetfield, Mr. P. Minhas, Dr. M. Soehle, Mr. R. Kett-White, Dr. E. Schmidt, Mr. I. Timofeev, Mr. A. Helmy, Mr. P.J Kirkpatrick, Dr. J. Coles, Prof. A. Gupta, Prof. D. Menon, and nursing and research staff from Neurosciences Critical Care Unit and Wolfson Brain Imaging Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dr. M. Czosnyka is on leave from Warsaw University of Technology, Poland.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sorrentino, E., Budohoski, K.P., Kasprowicz, M. et al. Critical Thresholds for Transcranial Doppler Indices of Cerebral Autoregulation in Traumatic Brain Injury. Neurocrit Care 14, 188–193 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-010-9492-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-010-9492-5