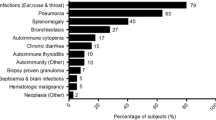
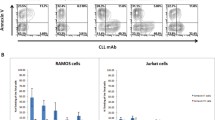
Abstract
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), besides its use as replacement therapy in patients with antibody deficiencies, is broadly used as an immunomodulatory agent for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. The mechanisms of action of IVIG include Fc receptor blockade, inhibition of cytokines and growth factors, modulation of macrophages and dendritic cells, enhancement of regulatory T cells, and modulation of B cells through the FcγRIIB receptor and CD22. Recent studies suggest that in vitro exposure of human B cells to IVIG determines functional changes reminiscent of anergy and that IVIG treatment of patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) induces in B cells ERK activation, a feature of anergy. Here, we show that IVIG therapy drives the B cells of patients with CVID to down-regulate CD21 expression and to assume the peculiar phenotype of the anergic-like, apoptosis-prone CD21low B cells that are spontaneously expanded in a subset of CVID and in some other immunological disorders. The CD21low B cells newly generated after IVIG infusion undergo spontaneous apoptosis upon in vitro culture. Furthermore, IVIG infusion is rapidly followed by a significant, although discrete, decrease in the number of circulating B cells, but not of T cells or of natural killer cells. These findings suggest that IVIG therapy may constrain antibody responses by inducing B cell depletion through differentiation into CD21low B cells that undergo accelerated apoptosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gelfand E. Intravenous immune globulin in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:2015–25.
Ballow M. The IgG molecule as a biological immune response modifier: mechanisms of action of intravenous immune serum globulin in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127:315–23.
Schwab I, Nimmerjahn F. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy: how does IgG modulate the immune system? Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:176–89.
Kaneko Y, Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV. Anti-inflammatory activity of immunoglobulin G resulting from Fc sialylation. Science. 2006;313:670–3.
Seité JF, Cornec D, Renaudineau Y, Youinou P, Mageed RA, Hillion S. IVIg modulates BCR signaling through CD22 and promotes apoptosis in mature human B lymphocytes. Blood. 2010;116:1698–704.
Bayry J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Carbonneil C, Misra N, Donkova V, Pashov A, et al. Inhibition of maturation and function of dendritic cells by intravenous immunoglobulin. Blood. 2003;101:758–65.
Paquin-Proulx D, Santos BA, Carvalho KI, Toledo-Barros M, Oliveira AK, Kokron CM, et al. Dysregulated CD1 profile in myeloid dendritic cells in CVID is normalized by IVIg treatment. Blood. 2013;121:4963–4.
Kessel A, Ammuri H, Peri R, Pavlotzky ER, Blank M, Shoenfeld Y, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy affects T regulatory cells by increasing their suppressive function. J Immunol. 2007;179:5571–5.
Ephrem A, Chamat S, Miquel C, Fisson S, Mouthon L, Caligiuri G, et al. Expansion of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells by intravenous immunoglobulin: a critical factor in controlling experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Blood. 2008;111:715–22.
Cousens LP, Tassone R, Mazer BD, Ramachandiran V, Scott DW, De Groot AS. Tregitope update: mechanism of action parallels IVIg. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12:436–43.
Le Pottier L, Bendaoud B, Dueymes M, Daridon C, Youinou P, Shoenfeld Y, et al. BAFF, a new target for intravenous immunoglobulin in autoimmunity and cancer. J Clin Immunol. 2007;27:257–65.
Le Pottier L, Sapir T, Bendaoud B, Youinou P, Shoenfeld Y, Pers JO. Intravenous immunoglobulin and cytokines: focus on tumor necrosis factor family members BAFF and APRIL. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2007;1110:426–32.
Tackenberg B, Jelcic I, Baerenwaldt A, Oertel WH, Sommer N, Nimmerjahn F, et al. Impaired inhibitory Fcγ receptor IIB expression on B cells in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:4788–92.
Nikolova KA, Tchorbanov AI, Djoumerska-Alexieva IK, Nikolova M, Vassilev TL. Intravenous immunoglobulin up-regulates the expression of the inhibitory FcγIIB receptor on B cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 2009;87:529–33.
Xiang Z, Cutler AJ, Brownlie RJ, Fairfax K, Lawlor KE, Severinson E, et al. FcgammaRIIb controls bone marrow plasma cell persistence and apoptosis. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:419–29.
Séité JF, Goutsmedt C, Youinou P, Pers JO, Hillion S. Intravenous immunoglobulin induces a functional silencing program similar to anergy in human B cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:181–8.
Cambier JC, Gauld SB, Merrell KT, Vilen BJ. B-cell anergy: from transgenic models to naturally occurring anergic B cells? Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:633–43.
Rakhmanov M, Keller B, Gutenberger S, Foerster C, Hoenig M, Driessen G, et al. Circulating CD21low B cells in common variable immunodeficiency resemble tissue homing, innate-like B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:13451–6.
Isnardi I, Ng YS, Menard L, Meyers G, Saadoun D, Srdanovic I, et al. Complement receptor 2/CD21− human naive B cells contain mostly autoreactive unresponsive clones. Blood. 2010;115:5026–36.
Visentini M, Cagliuso M, Conti V, Carbonari M, Mancaniello D, Cibati M, et al. Telomere-dependent replicative senescence of B and T cells from patients with type 1a common variable immunodeficiency. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41:854–62.
Moir S, Ho J, Malaspina A, Wang W, Di Poto AC, O’Shea MA, et al. Evidence for HIV-associated B cell exhaustion in a dysfunctional memory B cell compartment in HIV-infected viremic individuals. J Exp Med. 2008;205:1797–805.
Visentini M, Cagliuso M, Conti V, Carbonari M, Cibati M, Siciliano G, et al. Clonal B cells of HCV-associated mixed cryoglobulinemia patients contain exhausted marginal zone-like and CD21 low cells overexpressing Stra13. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42:1468–76.
Visentini M, Conti V, Cristofoletti C, Lazzeri C, Marrapodi R, Russo G, et al. Clonal expansion and functional exhaustion of monoclonal marginal zone B cells in mixed cryoglobulinemia: the yin and yang of HCV-driven lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2013;12:430–5.
Notarangelo LD, Fischer A, Geha RS, Casanova JL, Chapel H, Conley ME, et al. International union of immunological societies expert committee on primary immunodeficiencies. Primary immunodeficiencies: 2009 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:1161–78.
Warnatz K, Denz A, Dräger R, Braun M, Groth C, Wolff-Vorbeck G, et al. Severe deficiency of switched memory B cells (CD27(+)IgM(−)IgD(−)) in subgroups of patients with common variable immunodeficiency: a new approach to classify a heterogeneous disease. Blood. 2002;99:1544–51.
Ehrhardt GR, Hsu JT, Gartland L, Leu CM, Zhang S, Davis RS, et al. Expression of the immunoregulatory molecule FcRH4 defines a distinctive tissue-based population of memory B cells. J Exp Med. 2005;202:783–91.
Siedlar M, Strach M, Bukowska-Strakova K, Lenart M, Szaflarska A, Węglarczyk K, et al. Preparations of intravenous immunoglobulins diminish the number and proinflammatory response of CD14+ CD16++ monocytes in common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) patients. Clin Immunol. 2011;139:122–32.
Tjon AS, Metselaar HJ, te Boekhorst PA, van Hagen PM, Kwekkeboom J. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin does not reduce the numbers of circulating CD14(+)CD16(++) monocytes in patients with inflammatory disorders. Clin Immunol. 2012;145:11–2.
Wehr C, Kivioja T, Schmitt C, Ferry B, Witte T, Eren E, et al. The EUROclass trial: defining subgroups in common variable immunodeficiency. Blood. 2008;111:77–85.
Paquin-Proulx D, Santos BA, Carvalho KI, Toledo-Barros M, Barreto de Oliveira AK, Kokron CM, et al. IVIg immune reconstitution treatment alleviates the state of persistent immune activation and suppressed CD4 T cell counts in CVID. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:75199.
Toyoda M, Pao A, Petrosian A, Jordan SC. Pooled human gammaglobulin modulates surface molecule expression and induces apoptosis in human B cells. Am J Transplant. 2003;3:156–66.
Paquin Proulx D, Aubin E, Lemieux R, Bazin R. Inhibition of B cell-mediated antigen presentation by intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIg). Clin Immunol. 2010;135:422–9.
Sigman K, Ghibu F, Sommerville W, Toledano B, Bastein Y, Cameron L, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin inhibits IgE production in human B lymphocytes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;102:421–7.
Zhuang Q, Mazer B. Inhibition of IgE production in vitro by intact and fragmented intravenous immunoglobulin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:229–34.
de Grandmont M, Racine C, Roy A, Lemieux R, Neron S. Intravenous immuno-globulins induce the in vitro differentiation of human B lymphocytes and the secretion of IgG. Blood. 2003;101:3065–73.
Séité JF, Guerrier T, Cornec D, Jamin C, Youinou P, Hillion S. TLR9 responses of B cells are repressed by intravenous immunoglobulin through the recruitment of phosphatase. J Autoimmun. 2011;37:190–7.
Christensen SR, Shupe J, Nickerson K, Kashgarian M, Flavell RA, Shlomchik MJ. Toll-like receptor 7 and TLR9 dictate autoantibody specificity and have opposing inflammatory and regulatory roles in a murine model of lupus. Immunity. 2006;25:417–28.
Visentini M, Conti V, Cagliuso M, Tinti F, Siciliano G, Trombetta AC, et al. Regression of systemic lupus erythematosus after development of an acquired toll-like receptor signaling defect and antibody deficiency. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:2767–71.
Visentini M, Marrapodi R, Conti V, Mitrevski M, Camponeschi A, Lazzeri C, et al. Dysregulated extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling associated with impaired B-cell receptor endocytosis in patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:401–10.
Rui L, Vinuesa CG, Blasioli J, Goodnow CC. Resistance to CpG DNA-induced autoimmunity through tolerogenic B cell antigen receptor ERK signaling. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:594–600.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant (C26A12H92L) from the Intramural Research Program of Sapienza University of Rome to M. Fiorilli; M. Visentini was supported by Fondazione Roma, Rome, Italy.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitrevski, M., Marrapodi, R., Camponeschi, A. et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin replacement therapy in common variable immunodeficiency induces B cell depletion through differentiation into apoptosis-prone CD21low B cells. Immunol Res 60, 330–338 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-014-8599-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-014-8599-8