Abstract
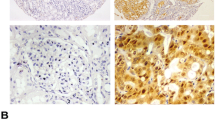
Cullin 1 (Cul1) is a rigid scaffold protein of a major class of E3 ubiquitin ligase, also known as the Skp1/cullin1/F-box (SCF) complex, which is involved in cell-cycle progression. The aberrant expression of Cul1 is involved in the dysfunction of SCF E3 ligase. Previous studies have revealed an association between increased Cul1 expression and tumor progression and poor outcome in several different tumors. We constructed a tissue microarray containing 103 papillary carcinoma tissues of the thyroid and 66 normal thyroid tissues. Cul1 expression and Cyclin D1 expression were evaluated by immunohistochemistry staining, and the relationship between their expression and clinicopathological parameters were analyzed. Cytoplasmic expression of Cul1 was correlated with tumor occurrence (p < 0.001), N stage (p = 0.027), and Cyclin D1 expression (p < 0.001). Cyclin D1 expression showed a correlation with tumor occurrence (p < 0.001) and T stage (p = 0.009). On the other hand, nuclear expression of Cul1 showed a negative correlation with tumor occurrence (p < 0.001) and Cyclin D1 expression (p < 0.001). Cytoplasmic Cul1 expression was associated with tumor development and higher nodal metastasis status, supporting the idea that the SCF complex is involved in cell-cycle regulation and promotes cell proliferation. Nuclear expression of Cul1 showed inverse relationship between tumor aggressiveness factors. Our data suggest that the expression site of Cul1 may affect the function of the SFC complex and play a role in tumor progression.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hundahl SA, Cady B, Cunningham MP, Mazzaferri E, McKee RF, Rosai J, Shah JP, Fremgen AM, Stewart AK, Holzer S (2000) Initial results from a prospective cohort study of 5583 cases of thyroid carcinoma treated in the United States during 1996. U.S. and German Thyroid Cancer Study Group. An American College of Surgeons Commission on Cancer Patient Care Evaluation Study. Cancer 89 (1):202-217. doi:10.1002/1097-0142(20000701)89:1<202::AID-CNCR27>3.0.CO;2-A
Davies L, Welch HG (2006) Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the United States, 1973-2002. JAMA 295 (18):2164-2167. doi:10.1001/jama.295.18.2164
Ito Y, Higashiyama T, Takamura Y, Miya A, Kobayashi K, Matsuzuka F, Kuma K, Miyauchi A (2007) Risk factors for recurrence to the lymph node in papillary thyroid carcinoma patients without preoperatively detectable lateral node metastasis: validity of prophylactic modified radical neck dissection. World J Surg 31 (11):2085-2091. doi:10.1007/s00268-007-9224-y
Mercante G, Frasoldati A, Pedroni C, Formisano D, Renna L, Piana S, Gardini G, Valcavi R, Barbieri V (2009) Prognostic factors affecting neck lymph node recurrence and distant metastasis in papillary microcarcinoma of the thyroid: results of a study in 445 patients. Thyroid 19 (7):707-716. doi:10.1089/thy.2008.0270
Moreno-Egea A, Rodriguez-Gonzalez JM, Sola-Perez J, Soria-Cogollos T, Parrilla-Paricio P (1995) Multivariate analysis of histopathological features as prognostic factors in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Br J Surg 82 (8):1092-1094
Ciechanover A (1994) The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway. Cell 79 (1):13-21. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90396-4
Reinstein E, Ciechanover A (2006) Narrative review: protein degradation and human diseases: the ubiquitin connection. Ann Intern Med 145 (9):676-684
Saltman B, Singh B, Hedvat CV, Wreesmann VB, Ghossein R (2006) Patterns of expression of cell cycle/apoptosis genes along the spectrum of thyroid carcinoma progression. Surgery 140 (6):899-905; discussion 905-896. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2006.07.027
Nakayama KI, Nakayama K (2006) Ubiquitin ligases: cell-cycle control and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6 (5):369-381. doi:10.1038/nrc1881
Petroski MD, Deshaies RJ (2005) Function and regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6 (1):9-20. doi:10.1038/nrm1547
Van Rechem C, Black JC, Abbas T, Allen A, Rinehart CA, Yuan GC, Dutta A, Whetstine JR (2011) The SKP1-Cul1-F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 4 (SCF-FbxL4) ubiquitin ligase regulates lysine demethylase 4A (KDM4A)/Jumonji domain-containing 2A (JMJD2A) protein. J Biol Chem 286 (35):30462-30470. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.273508
Chen G, Li G (2010) Increased Cul1 expression promotes melanoma cell proliferation through regulating p27 expression. Int J Oncol 37 (5):1339-1344
Kawaida R, Yamada R, Kobayashi K, Tokuhiro S, Suzuki A, Kochi Y, Chang X, Sekine A, Tsunoda T, Sawada T, Furukawa H, Nakamura Y, Yamamoto K (2005) CUL1, a component of E3 ubiquitin ligase, alters lymphocyte signal transduction with possible effect on rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun 6 (3):194-202. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6364177
Bai J, Zhou Y, Chen G, Zeng J, Ding J, Tan Y, Zhou J, Li G (2011) Overexpression of Cullin1 is associated with poor prognosis of patients with gastric cancer. Hum Pathol 42 (3):375-383. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2010.09.003
Min KW, Kim DH, Do SI, Sohn JH, Chae SW, Pyo JS, Park CH, Oh YH, Jang KS, Kim HL, Kim M (2012) Diagnostic and prognostic relevance of Cullin1 expression in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. J Clin Pathol 65 (10):896-901. doi:10.1136/jclinpath-2012-200847
Skaar JR, Pagano M (2009) Control of cell growth by the SCF and APC/C ubiquitin ligases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21 (6):816-824. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2009.08.004
Antonaci A, Consorti F, Mardente S, Natalizi S, Giovannone G, Della Rocca C (2008) Survivin and cyclin D1 are jointly expressed in thyroid papillary carcinoma and microcarcinoma. Oncol Rep 20 (1):63-67
Khoo ML, Beasley NJ, Ezzat S, Freeman JL, Asa SL (2002) Overexpression of cyclin D1 and underexpression of p27 predict lymph node metastases in papillary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87 (4):1814-1818
Khoo ML, Ezzat S, Freeman JL, Asa SL (2002) Cyclin D1 protein expression predicts metastatic behavior in thyroid papillary microcarcinomas but is not associated with gene amplification. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87 (4):1810-1813
Wang S, Lloyd RV, Hutzler MJ, Safran MS, Patwardhan NA, Khan A (2000) The role of cell cycle regulatory protein, cyclin D1, in the progression of thyroid cancer. Mod Pathol 13 (8):882-887. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880157
Fan XC, Steitz JA (1998) Overexpression of HuR, a nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling protein, increases the in vivo stability of ARE-containing mRNAs. EMBO J 17 (12):3448-3460. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.12.3448
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Medical Research Funds from Kangbuk Samsung Hospital.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Do, SI., Kim, K., Lee, H. et al. Aberrant Expression Pattern and Location of Cullin 1 are Associated With the Development of Papillary Carcinoma in Thyroid and Cyclin D1 Expression. Endocr Pathol 25, 282–287 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-014-9321-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12022-014-9321-z