Abstract
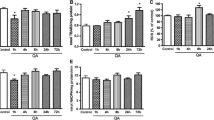
Ciguatoxins (CTXs) cause long-term disturbance of cerebral functions. The primary mechanism of neurotoxicity is related to their interaction with voltage-gated sodium channels. However, until now, the neurological targets for CTXs in the brain of intact animals have not been described. In our study, 1 day following oral exposure to 0.26 ng/g of Pacific ciguatoxin 1 (P-CTX-1), we performed in vivo electrophysiological recordings in the rat anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and identified the increase in spontaneous firings and enhanced responses to visceral noxious stimulation. Local field recordings characterized the P-CTX-1-induced synaptic potentiation and blockage of the induction of electrical stimulation-induced long-term potentiation in the medial thalamus (MT)-ACC pathway. Furthermore, intracerebroventricular administration of P-CTX-1 at doses of 1.0, 5.0, and 10 nM produced a dose-dependent increase in ACC neuronal firings and MT-ACC synaptic transmission. Further studies showed upregulated Na+ channel expression in astrocytes under pathological conditions. We hypothesized that the astrocytes might have been activated in the ciguatera poisoning in vivo. Increases in glial fibrillary acid protein expression were detected in reactive astrocytes in the rat ACC. The activation of astroglia was further indicated by activation of the gap junction protein connexin 43 and upregulation of excitatory amino acid transporter 2 expression suggesting that glutamate was normally rapidly cleared from the synaptic cleft during acute ciguatera poisoning. However, neurotoxicity and reactive astrogliosis were not detected in the ACC after 7 days of P-CTX-1 exposure. The present results are the first characterization of P-CTX-1-invoked brain cortex neuronal excitotoxicity in vivo and supported the theme that neuron and astroglia signals might play roles in acute ciguatera poisoning.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham, W. C., & Bear, M. F. (1996). Metaplasticity: The plasticity of synaptic plasticity. Trends in Neurosciences, 19, 126–130.
Allaman, I., Bélanger, M., & Magistretti, P. J. (2011). Astrocyte–neuron metabolic relationships: For better and for worse. Trends in Neurosciences, 34(2), 76–87.
Arena, P., Levin, B., Fleming, L. E., Friedman, M. A., & Blythe, D. (2004). A pilot study of the cognitive and psychological correlates of chronic ciguatera fish poisoning. Harmful Algae, 3, 51–60.
Bear, M. F., & Malenka, R. C. (1994). Synaptic plasticity: LTP and LTD. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 4, 389–399.
Bottein, M. Y., Wang, Z., & Ramsdell, J. S. (2011). Toxicokinetics of the ciguatoxin P-CTX-1 in rats after intraperitoneal or oral administration. Toxicology, 284, 1–6.
Bowman, C. L., Kimelberg, H. K., Frangakis, M. V., Berwald-Netter, Y., & Edwards, C. (1984). Astrocytes in primary culture have chemically activated sodium channels. Journal of Neuroscience, 4, 1527–1534.
Cao, Z., Wu, X., Chen, S., Fan, J., Zhang, R., Owyang, C., et al. (2008). Anterior cingulate cortex modulates visceral pain as measured by visceromotor responses in viscerally hypersensitive rats. Gastroenterology, 134, 535–543.
Chen, S. L., Wu, X. Y., Cao, Z. J., Fan, J., Wang, M., Owyang, C., et al. (2008). Subdiaphragmatic vagal afferent nerves modulate visceral pain. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 294(6), G1441–G1449.
Danbolt, N. C. (2001). Glutamate uptake. Progress in Neurobiology, 65, 1–105.
Dechraoui, M. Y., Naar, J., Pauillac, S., & Legrand, A. M. (1999). Ciguatoxins and brevetoxins, neurotoxic polyether compounds active on sodium channels. Toxicon, 37, 125–143.
Dermietzel, R., Traub, O., Hwang, T. K., Beyer, E., Bennett, M. V., Spray, D. C., et al. (1989). Differential expression of three gap junction proteins in developing and mature brain tissues. Proceedings of the National Academic Science USA, 86, 10148–10152.
Fan, J., Wu, X., Cao, Z., Chen, S., Owyang, C., & Li, Y. (2009). Up-regulation of anterior cingulate cortex NR2B receptors contributes to visceral pain responses in rats. Gastroenterology, 136(5), 1732–1740.
Gao, J., Wu, X., Owyang, C., & Li, Y. (2006). Enhanced responses of the anterior cingulate cortex neurones to colonic distension in viscerally hypersensitive rats. Journal of Physiology, 570, 169–183.
Gritti, A., Rosati, B., Lecchi, M., Vescovi, A. L., & Wanke, E. (2000). Excitable properties in astrocytes derived from human embryonic CNS stem cells. European Journal of Neuroscience, 12, 3549–3559.
Hedberg, T. G., & Stanton, P. K. (1995). Long-term potentiation and depression of synaptic transmission in rat posterior cingulate cortex. Brain Research, 670, 181–196.
Hogg, R. C., Lewis, R. J., & Adams, D. J. (2002). Ciguatoxin-induced oscillations in membrane potential and action potential firing in rat parasympathetic neurons. European Journal of Neuroscience, 16, 242–248.
Hutchison, W. D., Davis, K. D., Lozano, A. M., Tasker, R. R., & Dostrovsky, J. O. (1999). Pain-related neurons in the human cingulate cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 2, 403–405.
Jourdain, P., Bergersen, L. H., Bhaukaurally, K., Bezzi, P., Santello, M., Domercq, M., et al. (2007). Glutamate exocytosis from astrocytes controls synaptic strength. Nature Neuroscience, 10, 331–339.
Kanai, Y., & Hediger, M. A. (1992). Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature, 360, 467–471.
Karalis, T., Gupta, L., Chu, M., Campbell, B. A., Capra, M. F., & Maywood, P. A. (2000). Three clusters of ciguatera poisoning: Clinical manifestations and public health implications. Medical Journal of Australia, 172(4), 160–162.
Labrakakis, C., Patt, S., Weydt, P., Cervos-Navarro, J., Meyer, R., & Kettenmann, H. (1997). Action potential-generating cells in human glioblastomas. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 56, 243–254.
Lehane, L., & Lewis, R. J. (2000). Ciguatera: Recent advances but the risk remains. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 61, 91–125.
Levin, E. D., & Ramsdell, J. S. (2008). Repeat exposure to ciguatoxin leads to enhanced and sustained thermoregulatory, pain threshold and motor activity responses in mice: Relationship to blood ciguatoxin concentrations. Toxicology, 246, 55–62.
Li, Y., Wu, X. Y., Zhu, J. X., & Owyang, C. (2003). Hypothalamic regulation of pancreatic secretion is mediated by central cholinergic pathway in rat. The Journal of Physiology (London), 552, 571–587.
Li, Y., Zhang, X., Liu, H., Cao, Z., Chen, S., Cao, B., et al. (2012). Phosphorylated CaMKII postsynaptic binding to NR2B subunits in the anterior cingulate cortex mediates visceral pain in visceral hypersensitive rats. Journal of Neurochemistry, 121(4), 662–671.
Liang, C. K., Lo, Y. K., Li, J. Y., & Lai, P. H. (2009). Neurological picture. Reversible corpus callosum lesion in ciguatera poisoning. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 80(6), 587–588.
Mattei, C., Dechraoui, M. Y., Molgo, J., Meunier, F. A., Legrand, A. M., & Benoit, E. (1999). Neurotoxins targeting receptor site 5 of voltage-dependent sodium channels increase the nodal volume of myelinated axons. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 55, 666–673.
Molgo, J., Comella, J. X., & Legrand, A. M. (1990). Ciguatoxin enhances quantal transmitter release from frog motor nerve terminals. British Journal of Pharmacology, 99, 695–700.
Nedergaard, M. (1994). Direct signaling from astrocytes to neurons in cultures of mammalian brain cells. Science, 263, 1768–7171.
Ness, T. J., & Gebhart, G. F. (1990). Visceral pain: A review of experimental studies. Pain, 41, 167–234.
Paxinos, G., & Watson, C. (1998). The rat brain (4th ed.). San Diego, CA: Academic.
Pearn, J. (2001). Neurology of ciguatera. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 70, 4–8.
Peng, Y. G., Taylor, T. B., Finch, R. E., Moeller, P. D., & Ramsdell, J. S. (1995). Neuroexcitatory actions of ciguatoxin on brain regions associated with thermoregulation. NeuroReport, 6, 305–309.
Perez, S., Vale, C., Alonso, E., Alfonso, C., Rodriguez, P., Otero, P., et al. (2011). A comparative study of the effect of ciguatoxins on voltage-dependent Na+ and K+ channels in cerebellar neurons. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 24, 587–596.
Seifert, G., Schilling, K., & Steinhauser, C. (2006). Astrocyte dysfunction in neurological disorders: A molecular perspective. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7, 194–206.
Sofroniew, M. V. (2009). Molecular dissection of reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation. Trends in Neurosciences, 32, 638–647.
Sontheimer, H., Black, J. A., & Waxman, S. G. (1996). Voltage-gated Na+ channels in glia: Properties and possible functions. Trends in Neurosciences, 19, 325–331.
Swift, A. E., & Swift, T. R. (1993). Ciguatera. Journal of Toxicology - Clinical Toxicology, 31, 1–29.
Tian, L., Wang, M., Li, X., Lam, P. K., Wang, D., Chou, H. N., et al. (2011). Proteomic modification in gills and brains of medaka fish (Oryzias melastigma) after exposure to a sodium channel activator neurotoxin, brevetoxin-1. Aquatic Toxicology, 104, 211–217.
Vetter, I., Touska, F., Hess, A., Hinsbey, R., Sattler, S., Lampert, A., et al. (2012). Ciguatoxins activate specific cold pain pathways to elicit burning pain from cooling. EMBO Journal, 31(19), 3795–3808.
Volterra, A., & Meldolesi, J. (2005). Astrocytes, from brain glue to communication elements: The revolution continues. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 6, 626–640.
Wei, F., Li, P., & Zhuo, M. (1999). Loss of synaptic depression in mammalian anterior cingulate cortex after amputation. Journal of Neuroscience, 19, 9346–9354.
Wei, F., & Zhuo, M. (2001). Potentiation of sensory responses in the anterior cingulate cortex following digit amputation in the anaesthetised rat. Journal of Physiology, 532, 823–833.
Wu, X. Y., Fan, J., Cao, Z., Chen, S., Owyang C., & Li, Y. (2008b). Stimulation of the medial thalamus-anterior cingulate cortex synapses is important for learning and triggering pain memories in visceral hypersensitive states. Gastroenterology, 134(S1), A 562.
Wu, X., Gao, J., Yan, J., Fan, J., Owyang, C., & Li, Y. (2008a). Role for NMDA receptors in visceral nociceptive transmission in the anterior cingulate cortex of viscerally hypersensitive rats. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology, 294(4), G918–G927.
Wu, J. J., Mak, Y. L., Murphy, M. B., Lam, J. C., Chan, W. H., Wang, M., et al. (2011). Validation of an accelerated solvent extraction liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for Pacific ciguatoxin-1 in fish flesh and comparison with the mouse neuroblastoma assay. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 400, 3165–3175.
Yan, N., Cao, B., Xu, J., Hao, C., Zhang, X., & Li, Y. (2012). Glutamatergic activation of anterior cingulate cortex mediates the affective component of visceral pain memory in rats. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 97, 156–164.
Yang, J. W., Shih, H. C., & Shyu, B. C. (2006). Intracortical circuits in rat anterior cingulate cortex are activated by nociceptive inputs mediated by medial thalamus. Journal of Neurophysiology, 96, 3409–3422.
Yarowsky, P. J., & Krueger, B. K. (1989). Development of saxitoxin-sensitive and insensitive sodium channels in cultured neonatal rat astrocytes. Journal of Neuroscience, 9, 1055–1061.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Grants Council Hong Kong [160810, 160811, and 160812 to Y. Li], and the National Science Foundation of China [81170353 to Y. Li], the City University of Hong Kong Neuroscience Research Infrastructure Grant [9610211 to Y. Li], Strategic Research Grant [SRG006, 2011 to Y. Li], and Collaborative Research Fund [CityU3/CRF/08/ and CityU (8730026) to P. K. S. Lam]. Professor John Hodgkiss of The University of Hong Kong is thanked for his assistance with the English in this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Cao, B., Wang, J. et al. Neurotoxicity and Reactive Astrogliosis in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Acute Ciguatera Poisoning. Neuromol Med 15, 310–323 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8220-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-013-8220-7