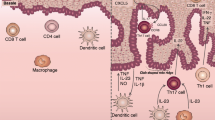
Abstract
Genetic epidemiological studies have demonstrated a significant genetic basis to both psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Although candidate gene association studies had identified genes for disease susceptibility, recent genome-wide association studies have demonstrated robust associations both within and outside the major histocompatibility region on chromosome 6p. The susceptibility genes identified include HLA-C, IL13, IL4, TNFAIP3, IL23A, IL23R, IL28RA, REL, IFIH1, ERAP, TRAF3IP2, NFKBIA, TYK2, ZNF313, NOS2, FBXL19 and NFKBIA in subjects of European ethnicity and HLA-C, IL12B, LCE3D, ERAP1, TNIP1, PTTG1, CSMD1, GJB2, SERPINB8 and ZNF816A in subjects of Chinese ethnicity. These associations provide us with a model for the pathogenesis of psoriasis involving skin barrier function, innate and adaptive immunity. Gene–gene and gene–environmental interaction effects have also been demonstrated. However, loci identified to date do not fully account for the high heritability of psoriasis and PsA, and therefore many genetic as well as environmental factors and interaction effects remain to be determined. This article reviews the current status of genetic studies in psoriasis and PsA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurd SK, Gelfand JM (2009) The prevalence of previously diagnosed and undiagnosed psoriasis in US adults: results from NHANES 2003–2004. J Am Acad Dermatol 60:218–224, Erratum in: J Am Acad Dermatol 61, 507
Nestle FO, Kaplan DH, Barker J (2009) Psoriasis. N Engl J Med 361:496–509
Moll JM, Wright V (1973) Psoriatic arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 3:55–78
Chandran V, Raychaudhuri SP (2010) Geoepidemiology and environmental factors of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Autoimmun 34:J314–J321
Henseler T, Christophers E (1985) Psoriasis of early and late onset: characterization of two types of psoriasis vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol 13:450–456
Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P et al (2006) Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum 54:2665–2673
Gelfand JM, Stern RS, Nijsten T, Feldman SR, Thomas J, Kist J et al (2005) The prevalence of psoriasis in African Americans: results from a population-based study. J Am Acad Dermatol 52:23–26
Gelfand JM, Gladman DD, Mease PJ, Smith N, Margolis DJ, Nijsten T et al (2005) Epidemiology of psoriatic arthritis in the population of the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol 53:573–577
Risch N (1990) Linkage strategies for genetically complex traits I. Multilocus models. Am J Hum Genet 46:222–228
Rahman P, Elder JT (2005) Genetic epidemiology of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64(Suppl 2):ii37–ii39, discussion ii40–ii41
Elder JT, Nair RP, Guo SW, Henseler T, Christophers E, Voorhees JJ (1994) The genetics of psoriasis. Arch Dermatol 130:216–224
Moll JM, Wright V (1973) Familial occurrence of psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 32:181–201
Chandran V, Schentag CT, Brockbank JE et al (2009) Familial aggregation of psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 68:664–667
Karason A, Love TJ, Gudbjornsson B (2009) A strong heritability of psoriatic arthritis over four generations—the Reykjavik Psoriatic Arthritis Study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:1424–1428
Pedersen OB, Svendsen AJ, Ejstrup L, Skytthe A, Junker P (2008) On the heritability of psoriatic arthritis. Disease concordance among monozygotic and dizygotic twins. Ann Rheum Dis 67:1417–1421
Burden AD, Javed S, Bailey M, Hodgins M, Connor M, Tillman D (1998) Genetics of psoriasis: paternal inheritance and a locus on chromosome 6p. J Invest Dermatol 110:958–960
Tomfohrde J, Silverman A, Barnes R et al (1994) Gene for familial psoriasis susceptibility mapped to the distal end of human chromosome 17q. Science 264:1141–1145
Matthews D, Fry L, Powles A et al (1996) Evidence that a locus for familial psoriasis maps to chromosome 4q. Nat Genet 14:231–233
Capon F, Semprini S, Chimenti S et al (2001) Fine mapping of the PSORS4 psoriasis susceptibility region on chromosome 1q21. J Invest Dermatol 116:728–730
Enlund F, Samuelsson L, Enerbäck C et al (1999) Psoriasis susceptibility locus in chromosome region 3q21 identified in patients from southwest Sweden. Eur J Hum Genet 7:783–790
Hensen P, Windemuth C, Hüffmeier U et al (2003) Association scan of the novel psoriasis susceptibility region on chromosome 19: evidence for both susceptible and protective loci. Exp Dermatol 12:490–496
Veal CD, Clough RL, Barber RC et al (2001) Identification of a novel psoriasis susceptibility locus at 1p and evidence of epistasis between PSORS1 and candidate loci. J Med Genet 38:7–13
International Psoriasis Genetics Consortium (2003) The International Psoriasis Genetics Study: assessing linkage to 14 candidate susceptibility loci in a cohort of 942 affected sib pairs. Am J Hum Genet 73:430–437
Sagoo GS, Tazi-Ahnini R, Barker JW et al (2004) Meta-analysis of genome-wide studies of psoriasis susceptibility reveals linkage to chromosomes 6p21 and 4q28-q31 in Caucasian and Chinese Hans population. J Invest Dermatol 122:1401–1405
Asumalahti K, Laitinen T, Lahermo P et al (2003) Psoriasis susceptibility locus on 18p revealed by genome scan in Finnish families not associated with PSORS1. J Invest Dermatol 121:735–740
Karason A, Gudjonsson JE, Upmanyu R et al (2003) A susceptibility gene for psoriatic arthritis maps to chromosome 16q: evidence for imprinting. Am J Hum Genet 72:125–131
Risch N, Merikangas K (1996) The future of genetic studies of complex human diseases. Science 273:1516–1517
Duffin KC, Chandran V, Gladman DD, Krueger GG, Elder JT, Rahman P (2008) Genetics of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: update and future direction. J Rheumatol 35:1449–1453
Gladman DD, Anhorn KA, Schachter RK, Mervart H (1986) HLA antigens in psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol 13:586–592
Ho PY, Barton A, Worthington J, Thomson W, Silman AJ, Bruce IN (2007) HLA-Cw6 and HLA-DRB1*07 together are associated with less severe joint disease in psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:807–811
Holm SJ, Sánchez F, Carlén LM, Mallbris L, Ståhle M, O'Brien KP (2005) HLA-Cw*0602 associates more strongly to psoriasis in the Swedish population than variants of the novel 6p21.3 gene PSORS1C3. Acta Derm Venereol 85:2–8
Gonzalez S, Martinez-Borra J, Del Río JS et al (2000) The OTF3 gene polymorphism confers susceptibility to psoriasis independent of the association of HLA-Cw*0602. J Invest Dermatol 115:824–828
Asumalahti K, Veal C, Laitinen T et al (2002) Coding haplotype analysis supports HCR as the putative susceptibility gene for psoriasis at the MHC PSORS1 locus. Hum Mol Genet 11:589–597
Holm SJ, Carlén LM, Mallbris L, Ståhle-Bäckdahl M, O'Brien KP (2003) Polymorphisms in the SEEK1 and SPR1 genes on 6p21.3 associate with psoriasis in the Swedish population. Exp Dermatol 12:435–444
Orrù S, Giuressi E, Carcassi C, Casula M, Contu L (2005) Mapping of the major psoriasis-susceptibility locus (PSORS1) in a 70-Kb interval around the corneodesmosin gene (CDSN). Am J Hum Genet 76:164–171
Li C, Wang G, Gao Y, Liu L, Gao T (2007) TNF-alpha gene promoter −238G>A and −308G>A polymorphisms alter risk of psoriasis vulgaris: a meta-analysis. J Invest Dermatol 127:1886–1892
Reich K, Hüffmeier U, König IR et al (2007) TNF polymorphisms in psoriasis: association of psoriatic arthritis with the promoter polymorphism TNF*-857 independent of the PSORS1 risk allele. Arthritis Rheum 56:2056–2064
Nair RP, Stuart PE, Nistor I et al (2006) Sequence and haplotype analysis supports HLA-C as the psoriasis susceptibility 1 gene. Am J Hum Genet 78:827–851
Gonzalez S, Martinez-Borra J, Torre-Alonso JC et al (1999) The MICA-A9 triplet repeat polymorphism in the transmembrane region confers additional susceptibility to the development of psoriatic arthritis and is independent of the association of Cw*0602 in psoriasis. Arthritis Rheum 42:1010–1016
Pollock R, Chandran V, Barrett J et al (2011) Differential major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related A allele associations with skin and joint manifestations of psoriatic disease. Tissue Antigens 77:554–561
Rahman P, Siannis F, Butt C et al (2006) TNFalpha polymorphisms and risk of psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 65:919–923
Rahman P, Roslin NM, Pellett FJ et al (2011) High resolution mapping in the major histocompatibility complex region identifies multiple independent novel loci for psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 70:690–694
Cargill M, Schrodi SJ, Chang M et al (2007) A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes. Am J Hum Genet 80:273–290
Liu Y, Helms C, Liao W et al (2008) A genome-wide association study of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis identifies new disease loci. PLoS Genet 4:e1000041
Nair RP, Duffin KC, Helms C et al (2009) Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-kappaB pathways. Nat Genet 41:199–204
Zhang XJ, Huang W, Yang S et al (2009) Psoriasis genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility variants within LCE gene cluster at 1q21. Nat Genet 41:205–210
Feng BJ, Sun LD, Soltani-Arabshahi R et al (2009) Multiple loci within the major histocompatibility complex confer risk of psoriasis. PLoS Genet 5:e1000606
Genetic Analysis of Psoriasis Consortium & the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2, Strange A, Capon F et al (2010) A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat Genet 42:985–990
Ellinghaus E, Ellinghaus D, Stuart PE et al (2010) Genome-wide association study identifies a psoriasis susceptibility locus at TRAF3IP2. Nat Genet 42:991–995
Stuart PE, Nair RP, Ellinghaus E et al (2010) Genome-wide association analysis identifies three psoriasis susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 42:1000–1004
Sun LD, Cheng H, Wang ZX et al (2010) Association analyses identify six new psoriasis susceptibility loci in the Chinese population. Nat Genet 42:1005–1009
Rahman P, Inman RD, Maksymowych WP, Reeve JP, Peddle L, Gladman DD (2009) Association of interleukin 23 receptor variants with psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol 36:137–140
Rahman P, Sun S, Peddle L et al (2006) Association between the interleukin-1 family gene cluster and psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54:2321–2325
Nelson GW, Martin MP, Gladman D, Wade J, Trowsdale J, Carrington M (2004) Cutting edge: heterozygote advantage in autoimmune disease: hierarchy of protection/susceptibility conferred by HLA and killer Ig-like receptor combinations in psoriatic arthritis. J Immunol 173:273–276
Eder L, Chandran V, Pellet F, Shanmugarajah S, Rosen CF, Bull SB, Gladman DD (2011) Human leucocyte antigen risk alleles for psoriatic arthritis among patients with psoriasis. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/ard.2011.155044
Hüffmeier U, Uebe S, Ekici AB et al (2010) Common variants at TRAF3IP2 are associated with susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Nat Genet 42:996–999
Conrad DF, Pinto D, Redon R et al (2010) Origins and functional impact of copy number variation in the human genome. Nature 464:704–712
Hollox EJ, Huffmeier U, Zeeuwen PL et al (2008) Psoriasis is associated with increased beta-defensin genomic copy number. Nat Genet 40:23–25
de Cid R, Riveira-Munoz E, Zeeuwen PL et al (2009) Deletion of the late cornified envelope LCE3B and LCE3C genes as a susceptibility factor for psoriasis. Nat Genet 41:211–215
Hüffmeier U, Estivill X, Riveira-Munoz E et al (2010) Deletion of LCE3C and LCE3B genes at PSORS4 does not contribute to susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis in German patients. Ann Rheum Dis 69:876–878
Bowes J, Flynn E, Ho P et al (2010) Variants in linkage disequilibrium with the late cornified envelope gene cluster deletion are associated with susceptibility to psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:2199–2203
Australo-Anglo-American Spondyloarthritis Consortium (TASC), Reveille JD, Sims AM et al (2010) Genome-wide association study of ankylosing spondylitis identifies non-MHC susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 42:123–127
Brown MA, Wellcome Trust Case-Control Consortium 2, Australo-Anglo-American Spondyloarthritis Consortium (2010) Genome-wide association study of ankylosing spondylitis identifies new loci, a tag SNP for HLA-B27, and an interaction between HLA-B27 and variants of ERAP. Arthritis Rheum 62(Supplement):S562
Zheng HF, Zuo XB, Lu WS et al (2011) Variants in MHC, LCE and IL12B have epistatic effects on psoriasis risk in Chinese population. J Dermatol Sci 61:124–128
Gudjonsson JE, Thorarinsson AM, Sigurgeirsson B, Kristinsson KG, Valdimarssonn H (2003) Streptococcal throat infections and exacerbation of chronic plaque psoriasis: a prospective study. Br J Dermatol 149:530–534
Gudjonsson JE, Karason A, Runarsdottir EH et al (2006) Distinct clinical differences between HLA-Cw*0602 positive and negative psoriasis patients—an analysis of 1019 HLA-C- and HLA-B-typed patients. J Invest Dermatol 126:740–745
Patel RV, Weinberg JM (2008) Psoriasis in the patient with human immunodeficiency virus, part 1: review of pathogenesis. Cutis 82:117–122
Jin Y, Yang S, Zhang F et al (2009) Combined effects of HLA-Cw6 and cigarette smoking in psoriasis vulgaris: a hospital-based case-control study in China. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 23:132–137
Setty AR, Curhan G, Choi HK (2007) Smoking and the risk of psoriasis in women: Nurses' Health Study II. Am J Med 120:953–959
Setty AR, Curhan G, Choi HK (2007) Obesity, waist circumference, weight change, and the risk of psoriasis in women: Nurses' Health Study II. Arch Intern Med 167:1670–1675
Pattison E, Harrison BJ, Griffiths CE, Silman AJ, Bruce IN (2008) Environmental risk factors for the development of psoriatic arthritis: results from a case–control study. Ann Rheum Dis 67:672–676
Eder L, Loo T, Chandran V et al (2011) The association between environmental factors and onset of psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). doi:10.1002/acr.20496
Rakkhit T, Wong B, Nelson TS et al (2007) Time to development of psoriatic arthritis decreases with smoking prior to psoriasis onset and increases with smoking after psoriasis onset. J Invest Derm 127(Suppl 1):S52
Duffin KC, Freeny IC, Schrodi SJ et al (2009) Association between IL13 polymorphisms and psoriatic arthritis is modified by smoking. J Invest Dermatol 129:2777–2783
Eder L, Chandran V, Pellett F, Pollock R, Shanmugarajah S, Rosen CF, Rahman P, Gladman DD (2011) IL13 Gene Polymorphism is a marker for psoriatic arthritis among psoriasis patients. Ann Rheum Dis 70:1594–1598
Griffiths CE, Barker JN (2007) Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 370:263–271
Fan X, Yang S, Sun LD et al (2007) Comparison of clinical features of HLA-Cw*0602-positive and -negative psoriasis patients in a Han Chinese population. Acta Derm Venereol 87:335–340
Gladman DD, Farewell VT (1995) The role of HLA antigens as indicators of disease progression in psoriatic arthritis. Multivariate relative risk model. Arthritis Rheum 38:845–850
Gladman DD, Farewell VT, Kopciuk KA, Cook RJ (1998) HLA markers and progression in psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol 25:730–733
Korendowych E, Dixey J, Cox B, Jones S, McHugh N (2003) The influence of the HLA-DRB1 rheumatoid arthritis shared epitope on the clinical characteristics and radiological outcome of psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol 30:96–101
Rahman P, Snelgrove T, Peddle L et al (2008) A variant of the IL4 I50V single-nucleotide polymorphism is associated with erosive joint disease in psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:2207–2208
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandran, V. The Genetics of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 44, 149–156 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-012-8303-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-012-8303-5