Abstract
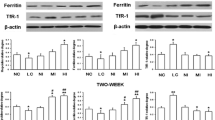
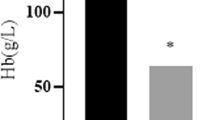
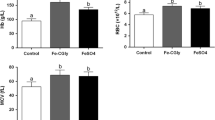
This study aims to investigate the effects of a tripeptide iron (REE-Fe) on iron-deficiency anemia rats. Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into seven groups: a normal control group, an iron-deficiency control group, and iron-deficiency groups treated with ferrous sulfate (FeSO4), ferrous glycinate (Fe-Gly), or REE-Fe at low-, medium-, or high-dose groups. The rats in the iron-deficiency groups were fed on an iron-deficient diet to establish iron-deficiency anemia (IDA) model. After the model established, different iron supplements were given to the rats once a day by intragastric administration for 21 days. The results showed that REE-Fe had effective restorative action returning body weight, organ coefficients, and hematological parameters in IDA rats to normal level. In addition, comparing with FeSO4 or Fe-Gly, high-dose REE-Fe was more effective on improving the levels of renal coefficient, total iron-binding capacity, and transferrin. Furthermore, the liver hepcidin messenger RNA (mRNA) expression in the high-dose group was significantly higher (p < 0.05) than that in the FeSO4 or Fe-Gly group and showed no significant difference (p > 0.05) with the normal control group. The findings suggest that REE-Fe is an effective source of iron supplement for IDA rats and might be exploited as a new iron fortifier.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hentze MW, Muckenthaler MU, Andrews NC (2004) Balancing acts: molecular control of mammalian iron metabolism. Cell 117(3):285–297
Lee SH, Song KB (2009) Purification of an iron-binding nona-peptide from hydrolysates of porcine blood plasma protein. Process Biochem 44(3):378–381
Naigamwalla DZ, Webb JA, Giger U (2012) Iron deficiency anemia. Can Vet J 53 (3):250-256
Low M, Farrell A, Biggs BA, et al. (2013) Effects of daily iron supplementation in primary-school-aged children: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Can Med Assoc J 185(17):E791–E802
Gkouvatsos K, Papanikolaou G, Pantopoulos K (2012) Regulation of iron transport and the role of transferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1820(3):188–202
Beard JL (2001) Iron biology in immune function, muscle metabolism and neuronal functioning. J Nutr 131(2):568S–579S
Duque X, Martinez H, Vilchis-Gil J, et al. (2014) Effect of supplementation with ferrous sulfate or iron bis-glycinate chelate on ferritin concentration in Mexican school children: a randomized controlled trial. Nutr J 13(71):71–80
Mimura ÉCM, Breganó JW, Dichi JB, et al. (2008) Comparison of ferrous sulfate and ferrous glycinate chelate for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in gastrectomized patients. Nutrition 24(7):663–668
Ballot DE, Macphail AP, Bothwell TH, et al. (1989) Fortification of curry powder with Fe(III)EDTA in an iron-deficient population. Report of a controlled iron-fortification trial. Am J Clin Nutr 49(1):162–169
Bovell-Benjamin AC, Viteri FE, Allen LH (2000) Iron absorption from ferrous bisglycinate and ferric trisglycinate in whole maize is regulated by iron status. Am J Clin Nutr 71(6):1563–1569
Guo L, Harnedy PA, Li B, et al. (2014) Food protein-derived chelating peptides: biofunctional ingredients for dietary mineral bioavailability enhancement. Trends Food Sci Technol 37(2):92–105
Webb K, Matthews J, DiRienzo D (1992) Peptide absorption: a review of current concepts and future perspectives. J Anim Sci 70(10):3248–3257
Zhou J, Mao XY, Wang X, et al. (2014) Anti-anaemia efficacy of β-lactoglobulin hydrolysate-iron complex on iron-deficient anaemic rats. Eur J Nutr 53(3):877–884
Ldl H, VSND S, Morgano MA, et al. (2014) Small peptides from enzymatic whey hydrolyzates increase dialyzable iron. Int Dairy J 38(2):145–147
Meisel H, FitzGerald RJ (2003) Biofunctional peptides from milk proteins: mineral binding and cytomodulatory effects. Curr Pharm Des 9(16):1289–1295
Torres-Fuentes C, Alaiz M, Vioque J (2012) Iron-chelating activity of chickpea protein hydrolysate peptides. Food Chem 134(3):1585–1588
Lv Y, Liu Q, Bao X, et al. (2009) Identification and characteristics of iron-chelating peptides from soybean protein hydrolysates using IMAC-Fe3+. J Agric Food Chem 57(11):4593–4597
Chan W, White PD (2000) Fmoc solid phase peptide synthesis: a practical approach, 1st edn. Oxford University, New York
Ghasemi S, Khoshgoftarmanesh AH, Hadadzadeh H (2012) Synthesis of iron-amino acid chelates and evaluation of their efficacy as iron source and growth stimulator for tomato in nutrient solution culture. J Plant Growth Regul 31(4):498–508
Mahoney AW, Vanorden CC, Hendricks DG (1974) Efficiency of converting food iron into hemoglobin by the anemic rat. Nutr Metab 17(4):223–230
Tang N, Chen LQ, Zhuang H (2014) Effects of heme iron enriched peptide on iron deficiency anemia in rats. Food Funct 5(2):390–399
Zielińska-Dawidziak M, Hertig I, Staniek H, et al. (2014) Effect of iron status in rats on the absorption of metal ions from plant ferritin. Plant Food Hum Nutr 69(2):101–107
Yun S, Zhang T, Li M, et al. (2011) Proanthocyanidins inhibit iron absorption from soybean (glycine max) seed ferritin in rats with iron deficiency anemia. Plant Food Hum Nutr 66(3):212–217
Kuvibidila SR, Velez M, Gardner R, et al. (2012) Iron deficiency reduces serum and in vitro secretion of interleukin-4 in mice independent of altered spleen cell proliferation. Nutr Res 32(2):107–115
Linberg R, Conover CD, Shum KL, et al. (1998) Hemoglobin based oxygen carriers: how much methemoglobin is too much? Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol 26(2):133–148
Thymann T, Le Huërou-Luron I, Petersen Y, et al. (2014) Glucagon-like peptide 2 treatment may improve intestinal adaptation during weaning. J Anim Sci 92(5):2070–2079
Modepalli N, Jo S, Repka MA, et al. (2013) Microporation and 'iron'tophoresis for treating iron deficiency anemia. Pharm Res 30(3):889–898
Clark VL, Kruse JA (1990) Clinical methods: the history, physical, and laboratory examinations. JAMA 264(21):2808–2809
Mahoney AW, Hendricks DG (1982) Efficiency of hemoglobin regeneration as a method of assessing iron bioavailability in food products. In: Kies C (ed) Nutritional bioavailability of iron, vol 203. Acs Symposium Series, 2 edn. American Chemical Society, Washington, pp. 1–10
Huh MH, Shin MH, Lee YB, et al. (1999) Effect of soybean hull iron on growth, iron bioavailability, and behavioral function in anemic rats induced by iron deficiency during gestation or lactation. Nutr Res 19(12):1749–1761
Sanchez-Rivera L, Martinez-Maqueda D, Cruz-Huerta E, et al. (2014) Peptidomics for discovery, bioavailability and monitoring of dairy bioactive peptides. Food Res Int 63:S170–S181
Yamanishi H, Iyama S, Yamaguchi Y, et al. (2003) Total iron-binding capacity calculated from serum transferrin concentration or serum iron concentration and unsaturated iron-binding capacity. Clin Chem 49(1):175–178
Wang FR, Xie ZG, Ye XQ, et al. (2014) Effectiveness of treatment of iron deficiency anemia in rats with squid ink melanin-Fe. Food Funct 5(1):123–128
Linder MC (2013) Mobilization of stored iron in mammals: a review. Nutrients 5(10):4022–4050
Naito Y, Hosokawa M, Sawada H, et al. (2014) Hepcidin is increased in the hypertrophied heart of Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Int J Cardiol 172(1):e45–e47
Saini RK, Manoj P, Shetty NP, et al. (2014) Dietary iron supplements and Moringa oleifera leaves influence the liver hepcidin messenger RNA expression and biochemical indices of iron status in rats. Nutr Res 34(7):630–638
Nicolas G, Chauvet C, Viatte L, et al. (2002) The gene encoding the iron regulatory peptide hepcidin is regulated by anemia, hypoxia, and inflammation. J Clin Invest 110(7):1037–1044
David MF, Sarah JW, Erika MB, et al. (2002) Hepcidin expression inversely correlates with the expression of duodenal iron transporters and iron absorption in rats. Gastroenterology 123(3):835–844
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, C., Lei, X., Wang, Q. et al. Effects of a Tripeptide Iron on Iron-Deficiency Anemia in Rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 169, 211–217 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0412-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0412-6