Abstract
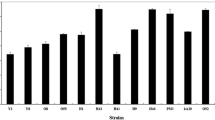
Production of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) starter with raw material has received much scientific investigation, but little information is available on the influences of some trace elements on the growth and fermentative activity of LAB. Based on this fact, this paper aimed to investigate the effects of Mn2+ on the performance of Lactobacillus plantarum CX-15 starter with Jerusalem artichoke (JA) as the main medium substrate. The results showed that Mn2+ addition had a significant beneficial affect on the fermentative activity of L. plantarum CX-15 starter. In contrast, the lack of Mn2+ would cause the subsequent fermentation significantly slower, whether the cell density in starter culture was higher or lower. The possible mechanism of these phenomenons was further elucidated by the time course analysis of the specific activities of metabolism key enzymes during the culture processes of L. plantarum CX-15 starter. Compared to the fermentation processes without Mn2+ addition, it was found that Mn2+ addition would enhance the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity but reduce the activities of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) and ATPase activity. Therefore, it could be concluded that the improvement of L. plantarum starter fermentative activity was probably a consequence of Mn2+ acting as “metabolic switch,” which regulated the metabolic flux from pyruvic acid to lactic acid and other metabolism pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Settanni, L., Gaglio, R., Guarcello, R., Francesca, N., Carpino, S., Sannino, C., & Todaro, M. (2013). International Dairy Journal, 32(2), 126–132.
Møller, K. K., Rattray, F. P., & Ardö, Y. (2013). International Dairy Journal, 33(2), 163–174.
Rubio, R., Jofré, A., Martín, B., Aymerich, T., & Garriga, M. (2013). Food Microbiology, 38, 303–311.
Coda, R., Cagno, D. R., Gobbetti, M., & Rizzello, C. G. (2014). Food Microbiology, 37, 51–58.
Lee, Y. M., Kim, J. S., & Kim, W. J. (2012). Food Science and Biotechnology, 21(3), 653–659.
Xiong, T., Song, S., Huang, X., Feng, C., Liu, G., Huang, J., & Xie, M. (2013). Journal of Food Science, 78(1), 84–89.
Soomro, A., Masud, T., & Anwaar, K. (2002). Pakistan Journal of Nutrition, 1(1), 20–24.
Chang, J. H., Shim, Y., Cha, S. K., & Chee, K. (2010). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 109(1), 220–230.
Leroy, F., & De Vuyst, L. (2004). Trends in Food Science and Technology, 15(2), 67–78.
Hugo, A., De Antoni, G., & Pérez, P. (2006). International Journal of Food Microbiology, 111(3), 191–196.
Gardner, N. J., Savard, T., Obermeier, P., Caldwell, G., & Champagne, C. P. (2001). International Journal of Food Microbiology, 64(3), 261–275.
Schiraldi, C., Adduci, V., Valli, V., Maresca, C., Giuliano, M., Lamberti, M., Cartenì, M., & De Rosa, M. (2003). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 82(2), 213–222.
Jianling, B., Shuping, M., Wanling, Z., & Yingtuan, H. (2007). Food and Fermentation Industries, 33(2), 79–83.
Siaterlis, A., Deepika, G., & Charalampopoulos, D. (2009). Letters in Applied Microbiology, 48(3), 295–301.
Carvalho, A. S., Silva, J., Ho, P., Teixeira, P., Malcata, F. X., & Gibbs, P. (2004). International Dairy Journal, 14(10), 835–847.
Fitzpatrick, J. J., Ahrens, M., & Smith, S. (2001). Process Biochemistry, 36(7), 671–675.
Raccach, M., & Marshall, P. (1985). Journal of Food Science, 50(3), 665–668.
Senthuran, A., Senthuran, V., Mattiasson, B., & Kaul, R. (1997). Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 55(6), 841–853.
Choi, H. Y., Ryu, H. K., Park, K. M., Lee, E. G., Lee, H., Kim, S.-W., & Choi, E.-S. (2012). Bioresource Technology, 114, 745–747.
Bajpai, P. K., & Bajpai, P. (1991). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 13(4), 359–362.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Analytical Chemistry, 31(3), 426–428.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). Analytical Biochemistry, 72(1), 248–254.
Sun, Y., Oberley, L. W., & Li, Y. (1988). Clinical Chemistry, 34(3), 497–500.
Xu, G. Q., Chu, J., Zhuang, Y. P., Wang, Y. H., & Zhang, S.-L. (2008). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 38(2), 189–197.
Wang, X., Bohlscheid, J., & Edwards, C. (2003). Journal of Applied Microbiology, 94(3), 349–359.
Kisser, M., Kubicek, C., & Röhr, M. (1980). Archives of Microbiology, 128(1), 26–33.
Solaini, G., Sgarbi, G., & Baracca, A. (2011). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Bioenergetics, 1807(6), 534–542.
Condon, S. (1987). Fems Microbiology Letters, 46(3), 269–280.
Archibald, F. S., & Fridovich, I. (1981). Journal of Bacteriology, 146(3), 928–936.
Acknowledgments
This research was partially funded by the Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, X., Dong, Y., Su, P. et al. Improvement of the Fermentative Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Starter Culture by the Addition of Mn2+ . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174, 1752–1760 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1156-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1156-z