Abstract
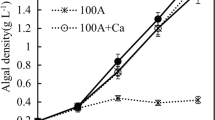
This study is aimed at controlling eutrophication through converting the nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus into microbial protein and simultaneously inhibiting the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa by Candida utilis. C. utilis and M. aeruginosa (initial cell density was 2.25 × 107 and 4.15 × 107 cells·mL−1) were cultured together in the absence or presence of a carbon source (glucose) during a 10-day experiment. In the absence of carbon source, the measured removal efficiencies of NH4 +–N and PO4 3−–P were 41.39 ± 2.19 % and 82.93 ± 3.95 %, respectively, at the second day, with the removal efficiency of 67.82 ± 2.29 % for M. aeruginosa at the fourth day. In contrast, the removal efficiencies of NH4 +–N and PO4 3−–P were increased to 87.45 ± 4.25 % and 83.73 ± 3.55 %, respectively, while the removal efficiency of M. aeruginosa decreased to 37.89 ± 8.41 % in the presence of the carbon source (C/N = 2:1). These results showed that the growth of M. aeruginosa was inhibited by C. utilis. Our finding sheds light on a novel potential approach for yeast to consume nutrients and control harmful algal during bloom events.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA. (1998). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (20th ed.). Washington, DC: American Public Health Association (APHA).
Arnold, J. L., Knapp, J. S., & Johnson, C. L. (2000). Water Research, 34, 3699–3708.
Auesukaree, C., Homma, T., Tochio, H., Shirakawa, M., Kaneko, Y., & Harashima, S. (2004). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 17289–17294.
Avnimelech, Y. (1999). Aquaculture, 176, 227–235.
Chang, H.-Q., Yang, X.-E., Fang, Y.-Y., Pu, P.-M., Li, Z.-K., & Rengel, Z. (2006). Journal of Zhejiang University. Science. B, 7, 521–531.
Conley, D. J., Paerl, H. W., Howarth, R. W., Boesch, D. F., Seitzinger, S. P., Havens, K. E., et al. (2009). Science, 323, 1014–1015.
Davis, J. R., & Koop, K. (2006). Hydrobiologia, 559, 23–76.
Figueiredo, D. R., Azeiteiro, U. M., Esteves, S. M., Goncalves, F. J. M., & Pereira, M. J. (2004). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 59, 151–163.
Figueredo, C. C., & Giani, A. (2001). Hydrobiologia, 445, 165–174.
Gao, G., Qin, B. Q., Sommaruga, R., & Psenner, R. (2007). Hydrobiologia, 581, 177–188.
Hansson, L. A., Annadotter, H., Bergman, E., Hamrin, S. F., Jeppesen, E., Kairesalo, T., et al. (1998). Ecosystems, 1, 558–574.
Huett, D. O., Morris, S. G., Smith, G., & Hunt, N. (2005). Water Research, 39, 3259–3272.
Ikawa, M., Sasner, J. J., & Haney, J. F. (2001). Hydrobiologia, 443, 19–22.
Jeong, H. J., Kim, J. S., Yoo, Y. D., Kim, S. T., Song, J. Y., Kim, T. H., et al. (2008). Harmful Algae, 7, 368–377.
Ke, Z. X., Xie, P., Guo, L. G., Liu, Y. Q., & Yang, H. (2007). Aquaculture, 265, 127–138.
Li, M., Wu, Y. J., Yu, Z. L., Sheng, G. P., & Yu, H. Q. (2007). Water Research, 41, 3152–3158.
Marazioti, C., Kornaros, M., & Lyberatos, G. (2003). Water Research, 37, 1239–1251.
Oberholster, P. J., Botha, A. M., & Ashton, P. J. (2009). Ecotoxicology, 18, 34–46.
Pitois, S., Jackson, M. H., & Wood, B. J. B. (2001). Journal of Environmental Health, 64, 25–32.
Qin, B. Q., Yang, L. Y., Chen, F. Z., Zhu, G. W., Zhang, L., & Chen, Y. Y. (2006). Chinese Science Bulletin, 51, 2401–2412.
Rippka, R., Deruelles, J., Waterbury, J. B., Herdman, M., & Stanier, R. Y. (1979). Journal of General Microbiology, 111, 1–61.
Singhal, V., & Rai, J. P. N. (2003). Bioresource Technology, 86, 221–225.
Smith, V. H., Tilman, G. D., & Nekola, J. C. (1999). Environmental Pollution, 100, 179–196.
Sondergaard, M., Liboriussen, L., Pedersen, A. R., & Jeppesen, E. (2008). Ecosystems, 11, 1291–1305.
Song, L. R., Chen, W., Peng, L., Wan, N., Gan, N. Q., & Zhang, X. M. (2007). Water Research, 41, 2853–2864.
Tucker, S., & Pollard, P. (2005). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 71, 629–635.
Tang, X. Q., Wu, M., Yang, W. J., Yin, W., Jin, F., Ye, M., et al. (2012). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223, 723–737.
Watanabe, T., Masaki, K., Iwashita, K., Fujii, T., & Iefuji, H. (2009). Bioresource Technology, 100, 1781–1785.
Watanabe, T., Ozaki, N., Iwashita, K., Fujii, T., & Iefuji, H. (2008). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 80, 331–338.
White, S. H., Duivenvoorden, L. J., & Fabbro, L. D. (2005). Hydrobiologia, 548, 117–126.
Wicks, R. J., & Thiel, P. G. (1990). Environmental Science & Technology, 24, 1413–1418.
Yang, X. E., Wu, X., Hao, H. L., & He, Z. L. (2008). Journal of Zhejiang University. Science. B, 9, 197–209.
Yoshida, T., Takashima, Y., Tomaru, Y., Shirai, Y., Takao, Y., Hiroishi, S., et al. (2006). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72, 1239–1247.
Zhang, X., Hu, H. Y., Men, Y. J., Yang, J., & Christoffersen, K. (2009). Water Research, 43, 2953–2960.
Zhu, L., Ding, W., Feng, L. J., Kong, Y., Xu, J., & Xu, X. Y. (2012). Bioresource Technology, 108, 1–7.
Zohary, T. (1985). Journal of Plankton Research, 7, 399–409.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by a grant from the Science and Technology R & D Program of Wuhan, China (No. 200960223065 and No. 201120637175-4). We would like to thank Dr. Nathan Moore (Department of Geography, Michigan State University) for the help of checking English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Y., Xu, X., Zhu, L. et al. Control of the Harmful Alga Microcystis aeruginosa and Absorption of Nitrogen and Phosphorus by Candida utilis . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169, 88–99 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9946-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9946-7