Abstract
Fat-splitting enzymes (lipases), due to their natural, industrial, and medical relevance, attract enough attention as fats do in our lives. Starting from the paper that we write, cheese and oil that we consume, detergent that we use to remove oil stains, biodiesel that we use as transportation fuel, to the enantiopure drugs that we use in therapeutics, all these applications are facilitated directly or indirectly by lipases. Due to their uniqueness, versatility, and dexterity, decades of research work have been carried out on microbial lipases. The hunt for novel lipases and strategies to improve them continues unabated as evidenced by new families of microbial lipases that are still being discovered mostly by metagenomic approaches. A separate database for true lipases termed LIPABASE has been created recently which provides taxonomic, structural, biochemical information about true lipases from various species. The present review attempts to summarize new approaches that are employed in various aspects of microbial lipase research, viz., screening, isolation, production, purification, improvement by protein engineering, and surface display. Finally, novel applications facilitated by microbial lipases are also presented.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrato, F., Carriere, F., Sarda, L., & Verger, R. (1997). A critical reevaluation of the phenomenon of interfacial activation. Methods in Enzymology, 286, 327–347.
Ollis, D. L., Cheah, E., Cygler, M., Dijkstra, B., Frolow, F., et al. (1992). The alpha/beta hydrolase fold. Protein Engineering, 5, 197–211.
Svendsen, A. (2000). Lipase protein engineering. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1543, 223–238.
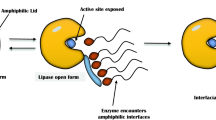
Brzozowski, A. M., Derewenda, U., Derewenda, Z. S., Dodson, G. G., Lawson, D. M., et al. (1991). A model for interfacial activation in lipases from the structure of a fungal lipase-inhibitor complex. Nature, 351, 491–494.
Jaeger, K. E., & Reetz, M. T. (1998). Microbial lipases form versatile tools for biotechnology. Trends in Biotechnology, 16, 396–403.
Patton, J. S., & Carey, M. C. (1979). Watching fat digestion. Science, 204, 145–148.
Brockman, H. L., Law, J. H., & Kezdy, F. J. (1973). Catalysis by adsorbed enzymes. The hydrolysis of tripropionin by pancreatic lipase adsorbed to siliconized glass beads. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 248, 4965–4970.
Panaitov, I., & Verger, R. (2000). In A. Baszkin & W. Norde (Eds.), Physical chemistry of biological interfaces (pp. 359–400). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Reis, P., Holmberg, K., Watzke, H., Leser, M. E., & Miller, R. (2009). Lipases at interfaces: a review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 147–148, 237–250.
Reis, P., Holmberg, K., Miller, R., Kragel, J., Grigoriev, D. O., et al. (2008). Competition between lipases and monoglycerides at interfaces. Langmuir, 24, 7400–7407.
Reis, P., Witula, T., & Holmberg, K. (2008). Mesoporous materials as host for an entrapped enzyme. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 110, 355–362.
Reis, P., Miller, R., Kragel, J., Leser, M., Fainerman, V. B., et al. (2008). Lipases at interfaces: unique interfacial properties as globular proteins. Langmuir, 24, 6812–6819.
Reis, P., Miller, R., Leser, M., Watzke, H., Fainerman, V. B., et al. (2008). Adsorption of polar lipids at the water-oil interface. Langmuir, 24, 5781–5786.
Akbari, N., Daneshjoo, S., Akbari, J., & Khajeh, K. (2011). Isolation, characterization, and catalytic properties of a novel lipase which is activated in ionic liquids and organic solvents. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 165, 785–794.
Idris, A., & Bukhari, A. (2012). Immobilized Candida antarctica lipase B: hydration, stripping off and application in ring opening polyester synthesis. Biotechnology Advances, 30, 550–563.
Ou, G., He, B., & Yuan, Y. (2011). Lipases are soluble and active in glycerol carbonate as a novel biosolvent. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 49, 167–170.
Fischer, F., Mutschler, J., & Zufferey, D. (2011). Enzyme catalysis with small ionic liquid quantities. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 38, 477–487.
Kaar, J. L. (2011). Lipase activation and stabilization in room-temperature ionic liquids. Methods in Molecular Biology, 679, 25–35.
Willerding, A. L., de Oliveira, L. A., Moreira, F. W., Germano, M. G., & Chagas, A. F., Jr. (2011). Lipase activity among bacteria isolated from Amazonian soils. Enzyme Res, 2011, 720194.
Morohoshi, T., Oikawa, M., Sato, S., Kikuchi, N., Kato, N., et al. (2011). Isolation and characterization of novel lipases from a metagenomic library of the microbial community in the pitcher fluid of the carnivorous plant Nepenthes hybrida. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 112, 315–320.
Sarda, L., & Desnuelle, P. (1958). Actions of pancreatic lipase on esters in emulsions. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 30, 513–521.
Jaeger, K. E., Ransac, S., Dijkstra, B. W., Colson, C., van Heuvel, M., et al. (1994). Bacterial lipases. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 15, 29–63.
Ali, Y. B., Verger, R., & Abousalham, A. (2012). Lipases or esterases: does it really matter? Toward a new bio-physico-chemical classification. Methods in Molecular Biology, 861, 31–51.
Messaoudi, A., Belguith, H., Ghram, I., & Hamida, J. B. (2011). LIPABASE: a database for ‘true’ lipase family enzymes. International Journal of Bioinformatics Research and Applications, 7, 390–401.
Widmann, M., Juhl, P. B., & Pleiss, J. (2010). Structural classification by the lipase engineering database: a case study of Candida antarctica lipase A. BMC Genomics, 11, 123.
Lotti, M., & Alberghina, L. (2007). In J. Polaina & A. P. Maccabe (Eds.), Industrial enzymes (pp. 263–281). New York: Springer.
Brady, L., Brzozowski, A. M., Derewenda, Z. S., Dodson, E., Dodson, G., et al. (1990). A serine protease triad forms the catalytic centre of a triacylglycerol lipase. Nature, 343, 767–770.
Van Pouderoyen, G., Eggert, T., Jaeger, K. E., & Dijkstra, B. W. (2001). The crystal structure of Bacillus subtilis lipase: a minimal alpha/beta hydrolase fold enzyme. Journal of Molecular Biology, 309, 215–226.
Derewenda, Z. S., Derewenda, U., & Dodson, G. G. (1992). The crystal and molecular structure of the Rhizomucor miehei triacylglyceride lipase at 1.9 A resolution. Journal of Molecular Biology, 227, 818–839.
Brocca, S., Secundo, F., Ossola, M., Alberghina, L., Carrea, G., et al. (2003). Sequence of the lid affects activity and specificity of Candida rugosa lipase isoenzymes. Protein Science, 12, 2312–2319.
Bassegoda, A., Pastor, F. I., & Diaz, P. (2012). Rhodococcus sp. strain CR-53 LipR, the first member of a new bacterial lipase family (family X) displaying an unusual Y-type oxyanion hole, similar to the Candida antarctica lipase clan. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78, 1724–1732.
Lou, Z., Li, M., Sun, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., et al. (2010). Crystal structure of a secreted lipase from Gibberella zeae reveals a novel “double-lock” mechanism. Protein & Cell, 1, 760–770.
Cherukuvada, S. L., Seshasayee, A. S., Raghunathan, K., Anishetty, S., & Pennathur, G. (2005). Evidence of a double-lid movement in Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipase: insights from molecular dynamics simulations. PLoS Computational Biology, 1, e28.
Xu, T., Liu, L., Hou, S., Xu, J., Yang, B., et al. (2012). Crystal structure of a mono- and diacylglycerol lipase from Malassezia globosa reveals a novel lid conformation and insights into the substrate specificity. Journal of Structural Biology, 178, 363–369.
Mancheno, J. M., Pernas, M. A., Martinez, M. J., Ochoa, B., Rua, M. L., et al. (2003). Structural insights into the lipase/esterase behavior in the Candida rugosa lipases family: crystal structure of the lipase 2 isoenzyme at 1.97A resolution. Journal of Molecular Biology, 332, 1059–1069.
Akoh, C. C., Lee, G. C., & Shaw, J. F. (2004). Protein engineering and applications of Candida rugosa lipase isoforms. Lipids, 39, 513–526.
Piamtongkam, R., Duquesne, S., Bordes, F., Barbe, S., Andre, I., et al. (2011). Enantioselectivity of Candida rugosa lipases (Lip1, Lip3, and Lip4) towards 2-bromo phenylacetic acid octyl esters controlled by a single amino acid. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 108, 1749–1756.
Pleiss, J., Scheib, H., & Schmid, R. D. (2000). The His gap motif in microbial lipases: a determinant of stereoselectivity toward triacylglycerols and analogs. Biochimie, 82, 1043–1052.
Mala, J. G., & Takeuchi, S. (2008). Understanding structural features of microbial lipases—an overview. Analytical Chemistry Insights, 3, 9–19.
Mukherjee, K. D. (1994). Plant lipases and their application in lipid biotransformations. Progress in Lipid Research, 33, 165–174.
Barros, M., Fleuri, L. F., & Macedo, G. A. (2010). Seed lipases sources applications and properties—a review. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 27, 15–29.
Dominguez de Maria, P., Sinisterra, J. V., Tsai, S. W., & Alcantara, A. R. (2006). Carica papaya lipase (CPL): an emerging and versatile biocatalyst. Biotechnology Advances, 24, 493–499.
Abdelkafi, S., Barouh, N., Fouquet, B., Fendri, I., Pina, M., et al. (2011). Carica papaya lipase: a naturally immobilized enzyme with interesting biochemical properties. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition, 66, 34–40.
Rivera, I., Mateos-Diaz, J. C., & Sandoval, G. (2012). Plant lipases: partial purification of Carica papaya lipase. Methods in Molecular Biology, 861, 115–122.
Wong, H., & Schotz, M. C. (2002). The lipase gene family. Journal of Lipid Research, 43, 993–999.
Hui, D. Y., & Howles, P. N. (2002). Carboxyl ester lipase: structure-function relationship and physiological role in lipoprotein metabolism and atherosclerosis. Journal of Lipid Research, 43, 2017–2030.
Kurtovic, I., Marshall, S. N., Zhao, X., & Simpson, B. K. (2009). Lipases from mammals and fishes. Reviews in Fisheries Science, 17, 18–40.
Amara, S., Fendri, A., Ben Salem, N., Gargouri, Y., & Miled, N. (2010). Snail hepatopancreatic lipase: a new member of invertebrates lipases' group. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 942–952.
Zouari, N., Miled, N., Rouis, S., & Gargouri, Y. (2007). Scorpion digestive lipase: a member of a new invertebrate's lipase group presenting novel characteristics. Biochimie, 89, 403–409.
Cherif, S., Fendri, A., Miled, N., Trabelsi, H., Mejdoub, H., et al. (2007). Crab digestive lipase acting at high temperature: purification and biochemical characterization. Biochimie, 89, 1012–1018.
Vulfson, E. (1994). In P. Wooley & S. B. Peterson (Eds.), Lipases their structure biochemistry and applications (pp. 271–288). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Saxena, R. K., Sheoran, A., Giri, B., & Davidson, W. S. (2003). Purification strategies for microbial lipases. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 52, 1–18.
Jaeger, K. E., Dijkstra, B. W., & Reetz, M. T. (1999). Bacterial biocatalysts: molecular biology, three-dimensional structures, and biotechnological applications of lipases. Annual Review of Microbiology, 53, 315–351.
Jaeger, K. E., & Eggert, T. (2002). Lipases for biotechnology. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 13, 390–397.
Pandey, A., Benjamin, S., Soccol, C. R., Nigam, P., Krieger, N., et al. (1999). The realm of microbial lipases in biotechnology. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 29(Pt 2), 119–131.
Singh, A. K., & Mukhopadhyay, M. (2012). Overview of fungal lipase: a review. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 166, 486–520.
Derewenda, U., Swenson, L., Green, R., Wei, Y., Yamaguchi, S., et al. (1994). Current progress in crystallographic studies of new lipases from filamentous fungi. Protein Engineering, 7, 551–557.
Houde, A., Kademi, A., & Leblanc, D. (2004). Lipases and their industrial applications: an overview. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 118, 155–170.
Gunasekaran, V., & Das, D. (2005). Lipase fermentation progress and prospects. Indian Journal of Biotechnology, 4, 437–445.
Cardenas, F., de Castro, M. S., Sanchez-Montero, J. M., Sinisterra, J. V., Valmaseda, M., et al. (2001). Novel microbial lipases: catalytic activity in reactions in organic media. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 28, 145–154.
Ghosh, P. K., Saxena, R. K., Gupta, R., Yadav, R. P., & Davidson, S. (1996). Microbial lipases: productions and applications. Science Progress, 79, 119–157.
Singh, A. K., & Mukhopadhyay, M. (2012). Overview of fungal lipase: a review. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 166, 486–520.
Gandhi, N. N. (1997). Applications of lipase. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 74, 621–634.
Lin, E.-S., & Ko, H.-C. (2005). Glucose stimulates production of the alkaline-thermostable lipase of the edible basidiomycete Antrodia cinnamomea. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 37, 261–265.
Gutarra, M. L., Godoy, M. G., Maugeri, F., Rodrigues, M. I., Freire, D. M., et al. (2009). Production of an acidic and thermostable lipase of the mesophilic fungus Penicillium simplicissimum by solid-state fermentation. Bioresource Technology, 100, 5249–5254.
Velasco-Lozano, S., Volke-Sepulveda, T., & Favela-Torres, E. (2012). Lipases production by solid-state fermentation: the case of Rhizopus homothallicus in perlite. Methods in Molecular Biology, 861, 227–237.
Gutarra, M. L., de Godoy, M. G., Silva Jdo, N., Guedes, I. A., Lins, U., et al. (2009). Lipase production and Penicillium simplicissimum morphology in solid-state and submerged fermentations. Biotechnology Journal, 4, 1450–1459.
Mala, J. G., Edwinoliver, N. G., Kamini, N. R., & Puvanakrishnan, R. (2007). Mixed substrate solid state fermentation for production and extraction of lipase from Aspergillus niger MTCC 2594. Journal of General and Applied Microbiology, 53, 247–253.
Maheshwari, R., Bharadwaj, G., & Bhat, M. K. (2000). Thermophilic fungi: their physiology and enzymes. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 64, 461–488.
Saisubramanian, N., Edwinoliver, N. G., Nandakumar, N., Kamini, N. R., & Puvanakrishnan, R. (2006). Efficacy of lipase from Aspergillus niger as an additive in detergent formulations: a statistical approach. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 33, 669–676.
Contesini, F., Lopes, D., Macedo, G., Nascimento, M., & Carvalho, P. (2010). Aspergillus sp. lipase: potential biocatalyst for industrial use. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 67, 163–171.
Dominguez de Maria, P., Sanchez-Montero, J. M., Sinisterra, J. V., & Alcantara, A. R. (2006). Understanding Candida rugosa lipases: an overview. Biotechnology Advances, 24, 180–196.
Liou, Y.-C., Marangoni, A. G., & Yada, R. Y. (1998). Aggregation behavior of Candida rugosa lipase. Food Research International, 31, 243–248.
de Maria, P. D., Sanchez-Montero, J. M., Alcantara, A. R., Valero, F., & Sinisterra, J. V. (2005). Rational strategy for the production of new crude lipases from Candida rugosa. Biotechnology Letters, 27, 499–503.
Lopez, N., Pernas, M. A., Pastrana, L. M., Sanchez, A., Valero, F., et al. (2004). Reactivity of pure Candida rugosa lipase isoenzymes (Lip1, Lip2, and Lip3) in aqueous and organic media. influence of the isoenzymatic profile on the lipase performance in organic media. Biotechnology Progress, 20, 65–73.
Benjamin, S., & Pandey, A. (1998). Candida rugosa lipases: molecular biology and versatility in biotechnology. Yeast, 14, 1069–1087.
Vakhlu, J., Kour, A. (2006). Yeast lipases: enzyme purification, biochemical properties and gene cloning. Electronic Journal of Biotechnology, 9.
Fickers, P., Marty, A., & Nicaud, J. M. (2011). The lipases from Yarrowia lipolytica: genetics, production, regulation, biochemical characterization and biotechnological applications. Biotechnology Advances, 29, 632–644.
Lee, K. H., Park, C. H., & Lee, E. Y. (2010). Biosynthesis of glycerol carbonate from glycerol by lipase in dimethyl carbonate as the solvent. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 33, 1059–1065.
Neta, N. S., Peres, A. M., Teixeira, J. A., & Rodrigues, L. R. (2011). Maximization of fructose esters synthesis by response surface methodology. New Biotechnology, 28, 349–355.
Kirk, O., & Christensen, M. W. (2002). Lipases from Candida antarctica: unique biocatalysts from a unique origin. Organic Process Research & Development, 6, 446–451.
Goncalves, C., Lopes, M., Ferreira, J. P., & Belo, I. (2009). Biological treatment of olive mill wastewater by non-conventional yeasts. Bioresource Technology, 100, 3759–3763.
Holmquist, M. (1998). Insights into the molecular basis for fatty acyl specificities of lipases from Geotrichum candidum and Candida rugosa. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 93, 57–66.
Ciafardini, G., Zullo, B. A., Cioccia, G., & Iride, A. (2006). Lipolytic activity of Williopsis californica and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in extra virgin olive oil. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 107, 27–32.
Deive, F. J., Costas, M., & Longo, M. A. (2003). Production of a thermostable extracellular lipase by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biotechnology Letters, 25, 1403–1406.
Bussamara, R., Fuentefria, A. M., de Oliveira, E. S., Broetto, L., Simcikova, M., et al. (2010). Isolation of a lipase-secreting yeast for enzyme production in a pilot-plant scale batch fermentation. Bioresource Technology, 101, 268–275.
Gupta, R., Gupta, N., & Rathi, P. (2004). Bacterial lipases: an overview of production, purification and biochemical properties. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 64, 763–781.
El Khattabi, M., Ockhuijsen, C., Bitter, W., Jaeger, K. E., & Tommassen, J. (1999). Specificity of the lipase-specific foldases of gram-negative bacteria and the role of the membrane anchor. Molecular and General Genetics, 261, 770–776.
Arpigny, J. L., & Jaeger, K. E. (1999). Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochemical Journal, 343(Pt 1), 177–183.
Rosenau, F., & Jaeger, K. (2000). Bacterial lipases from Pseudomonas: regulation of gene expression and mechanisms of secretion. Biochimie, 82, 1023–1032.
Rosenstein, R., & Gotz, F. (2000). Staphylococcal lipases: biochemical and molecular characterization. Biochimie, 82, 1005–1014.
Snellman, E. A., & Colwell, R. R. (2004). Acinetobacter lipases: molecular biology, biochemical properties and biotechnological potential. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 31, 391–400.
Angkawidjaja, C., & Kanaya, S. (2006). Family I.3 lipase: bacterial lipases secreted by the type I secretion system. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 63, 2804–2817.
Guncheva, M., & Zhiryakova, D. (2011). Catalytic properties and potential applications of Bacillus lipases. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 68, 1–21.
Rosenau, F., Tommassen, J., & Jaeger, K. E. (2004). Lipase-specific foldases. Chembiochem, 5, 152–161.
Reetz, M. T., & Jaeger, K. E. (1998). Overexpression, immobilization and biotechnological application of Pseudomonas lipases. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 93, 3–14.
Horchani, H., Aissa, I., Ouertani, S., Zarai, Z., Gargouri, Y., & Sayari, A. (2012). Staphylococcal lipases: biotechnological applications. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 76, 125–132.
Cherif, S., Mnif, S., Hadrich, F., Abdelkafi, S., & Sayadi, S. (2011). A newly high alkaline lipase: an ideal choice for application in detergent formulations. Lipids in Health and Disease, 10, 221.
Han, S. J., Back, J. H., Yoon, M. Y., Shin, P. K., Cheong, C. S., et al. (2003). Expression and characterization of a novel enantioselective lipase from Acinetobacter species SY-01. Biochimie, 85, 501–510.
Martinez, D. A., & Nudel, B. C. (2002). The improvement of lipase secretion and stability by addition of inert compounds into Acinetobacter calcoaceticus cultures. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 48, 1056–1061.
Wang, H., Zhang, J., Wang, X., Qi, W., & Dai, Y. (2012). Genome shuffling improves production of the low-temperature alkalophilic lipase by Acinetobacter johnsonii. Biotechnology Letters, 34, 145–151.
Khoramnia, A., Ebrahimpour, A., Beh, B.K., & Lai, O.M. (2011). Production of a solvent, detergent, and thermotolerant lipase by a newly isolated Acinetobacter sp. in submerged and solid-state fermentations. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, Article ID 702179. doi:10.1155/2011/702179.
Ahmed, E. H., Raghavendra, T., & Madamwar, D. (2010). An alkaline lipase from organic solvent tolerant Acinetobacter sp. EH28: application for ethyl caprylate synthesis. Bioresource Technology, 101, 3628–3634.
Snellman, E. A., & Colwell, R. R. (2008). Transesterification activity of a novel lipase from Acinetobacter venetianus RAG-1. Antonie Leeuwenhoek, 94, 621–625.
Saisubramanian, N., Sivasubramanian, S., Nandakumar, N., Indirakumar, B., Chaudhary, N. A., et al. (2008). Two step purification of Acinetobacter sp. lipase and its evaluation as a detergent additive at low temperatures. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 150, 139–156.
Haki, G. D., & Rakshit, S. K. (2003). Developments in industrially important thermostable enzymes: a review. Bioresource Technology, 89, 17–34.
Kittikun, H., Prasertsan, P., Zimmermann, W., Seesuriyachan, P., & Chaiyaso, T. (2012). Sugar ester synthesis by thermostable lipase from Streptomyces thermocarboxydus ME168. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 166, 1969–1982.
Faoro, H., Glogauer, A., Couto, G. H., de Souza, E. M., Rigo, L. U., et al. (2012). Characterization of a new Acidobacteria-derived moderately thermostable lipase from a Brazilian Atlantic Forest soil metagenome. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 81, 386–394.
Ali, M. S., Yun, C. C., Chor, A. L., Rahman, R. N., Basri, M., et al. (2012). Purification and characterisation of an F16L mutant of a thermostable lipase. The Protein Journal, 31, 229–237.
Cordenons, A., Gonzalez, R., Kok, R., Hellingwerf, K. J., & Nudel, C. (1996). Effect of nitrogen sources on the regulation of extracellular lipase production in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus strains. Biotechnology Letters, 18, 633–638.
Ahmad, S., Kamal, M. Z., Sankaranarayanan, R., & Rao, N. M. (2008). Thermostable Bacillus subtilis lipases: in vitro evolution and structural insight. Journal of Molecular Biology, 381, 324–340.
Le, Q. A., Joo, J. C., Yoo, Y. J., & Kim, Y. H. (2012). Development of thermostable Candida antarctica lipase B through novel in silico design of disulfide bridge. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 109, 867–876.
Sharma, P. K., Kumar, R., Mohammad, O., Singh, R., & Kaur, J. (2012). Engineering of a metagenome derived lipase toward thermal tolerance: effect of asparagine to lysine mutation on the protein surface. Gene, 491, 264–271.
Chakravorty, D., Parameswaran, S., Dubey, V. K., & Patra, S. (2011). In silico characterization of thermostable lipases. Extremophiles, 15, 89–103.
Joseph, B., Ramteke, P. W., & Thomas, G. (2008). Cold active microbial lipases: Some hot issues and recent developments. Biotechnology Advances, 26, 457–470.
Rashid, N., Shimada, Y., Ezaki, S., Atomi, H., & Imanaka, T. (2001). Low-temperature lipase from psychrotrophic Pseudomonas sp. strain KB700A. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 4064–4069.
Kim, H. R., Kim, I. H., Hou, C. T., Kwon, K. I., & Shin, B. S. (2010). Production of a novel cold-active lipase from Pichia lynferdii Y-7723. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58, 1322–1326.
Jeon, J. H., Kim, J. T., Lee, H. S., Kim, S. J., Kang, S. G., et al. (2011). Novel lipolytic enzymes identified from metagenomic library of deep-sea sediment. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2011, 271419.
Gerday, C., Aittaleb, M., Arpigny, J. L., Baise, E., Chessa, J. P., et al. (1997). Psychrophilic enzymes: a thermodynamic challenge. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1342, 119–131.
Alquati, C., De Gioia, L., Santarossa, G., Alberghina, L., Fantucci, P., et al. (2002). The cold-active lipase of Pseudomonas fragi. Heterologous expression, biochemical characterization and molecular modeling. European Journal of Biochemistry, 269, 3321–3328.
Suzuki, T., Nakayama, T., Kurihara, T., Nishino, T., & Esaki, N. (2001). Cold-active lipolytic activity of psychrotrophic Acinetobacter sp. strain no. 6. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 92, 144–148.
Qi, W., Shao, J., Wang, H. K., Wei, Y. J., & Zhang, J. (2011). A novel low-temperature alkaline lipase from Acinetobacter johnsonii LP28 suitable for detergent formulation. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 49, 96–102.
Sidhu, P., Sharma, R., Soni, S. K., & Gupta, J. K. (1998). Production of extracellular alkaline lipase by a new thermophilic Bacillus sp. Folia Microbiologica, 43, 51–54.
Masahiro, M., Ehsan, A., Du, D., & Park, E. Y. (2009). Characterization and optimization of extracellular alkaline lipase production by Alcaligenes sp. using stearic acid as carbon source. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 14, 193–201.
Gupta, N., Sahaib, V., & Gupta, R. (2007). Alkaline lipase from a novel strain Burkholderia multivorans: statistical medium optimization and production in a bioreactor. Process Biochemistry, 42, 518–526.
Lin, S. F., Chiou, C. M., Yeh, C. M., & Tsai, Y. C. (1996). Purification and partial characterization of an alkaline lipase from Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes F-111. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 1093–1095.
Joshi, G. K., Kumar, S., Tripathi, B. N., & Sharma, V. (2006). Production of alkaline lipase by Corynebacterium paurometabolum, MTCC 6841 isolated from Lake Naukuchiatal, Uttaranchal State, India. Current Microbiology, 52, 354–358.
Bouaziz, A., Horchani, H., Ben Salem, N., Gargouri, Y., & Sayari, A. (2011). Expression, purification of a novel alkaline Staphylococcus xylosus lipase acting at high temperature. Biochemical Eng J, 54, 93–102.
Mander, P., Cho, S. S., Simkhada, J. R., Choi, Y. H., Park, D. J., et al. (2012). An organic solvent-tolerant alkaline lipase from Streptomyces sp. CS268 and its application in biodiesel production. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 17, 67–75.
Dai, D., & Xia, L. (2005). Enhanced production of Penicillium expansum PED-03 lipase through control of culture conditions and application of the crude enzyme in kinetic resolution of racemic allethrolone. Biotechnology Progress, 21, 1165–1168.
HueyMin, H., Liu, R., Jiang, X., Mou, H., Guan, H., Huang, H., et al. (2009). A novel low-temperature resistant alkaline lipase from a soda lake fungus strain Fusarium solani N4-2 for detergent formulation. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 46, 265–270.
Yoo, H. Y., Simkhada, J. R., Cho, S. S., Park, D. H., Kim, S. W., et al. (2011). A novel alkaline lipase from Ralstonia with potential application in biodiesel production. Bioresource Technology, 102, 6104–6111.
Salameh, M. A., & Wiegel, J. (2010). Effects of detergents on activity, thermostability and aggregation of two alkalithermophilic lipases from Thermosyntropha lipolytica. Open Biochemistry Journal, 4, 22–28.
Romdhane, I. B., Frikha, F., Maalej-Achouri, I., Gargouri, A., & Belghith, H. (2012). Gene cloning and molecular characterization of the Talaromyces thermophilus lipase catalyzed efficient hydrolysis and synthesis of esters. Gene, 494, 112–118.
Kim, E. Y., Oh, K. H., Lee, M. H., Kang, C. H., Oh, T. K., et al. (2009). Novel cold-adapted alkaline lipase from an intertidal flat metagenome and proposal for a new family of bacterial lipases. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 75, 257–260.
Mahadik, N. D., Puntambekar, U. S., Bastawde, K. B., Khire, J. M., & Gokhale, D. V. (2002). Production of acidic lipase by Aspergillus niger in solid state fermentation. Process Biochemistry, 38, 715–721.
Colin, V. L., Baigori, M. D., & Pera, L. M. (2010). Effect of environmental conditions on extracellular lipases production and fungal morphology from Aspergillus niger MYA 135. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 50, 52–58.
Doukyu, N., & Ogino, H. (2010). Organic solvent tolerant enzymes. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 48, 270–282.
Shu, Z. Y., Wu, J. G., Cheng, L. X., Chen, D., Jiang, Y. M., et al. (2012). Production and characteristics of the whole-cell lipase from organic solvent tolerant Burkholderia sp. ZYB002. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 166, 536–548.
Xu, J.-H., Zhao, L.-L., Zhao, J., Pan, J., & Wang, Z.-L. (2008). An organic solvent tolerant lipase from Serratia marcescens ECU1010: biochemical characterization and practical application. Journal of Biotechnology, 136, S51.
Grognux, J., & Reymond, J. L. (2004). Classifying enzymes from selectivity fingerprints. Chembiochem, 5, 826–831.
Jensen, R. G. (1983). Detection and determination of lipase (acylglycerol hydrolase) activity from various sources. Lipids, 18, 650–657.
Beisson, F., Tiss, A., Riviere, C., & Verger, R. (2000). Methods for lipase detection and assay: a critical review. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology, 102, 133–153.
Gupta, R., Rathi, P., Gupta, N., & Bradoo, S. (2003). Lipase assays for conventional and molecular screening: an overview. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 37, 63–71.
Zhang, J.-H., Lin, Y., Sun, Y.-F., Ye, Y.-R., Zheng, S.-P., et al. (2012). High-throughput screening of B factor saturation mutated Rhizomucor miehei lipase thermostability based on synthetic reaction. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 50, 325–330.
Saisuburamaniyan, N., Krithika, L., Dileena, K. P., Sivasubramanian, S., & Puvanakrishnan, R. (2004). Lipase assay in soils by copper soap colorimetry. Analytical Biochemistry, 330, 70–73.
Feist, A. M., Herrgard, M. J., Thiele, I., Reed, J. L., & Palsson, B. O. (2009). Reconstruction of biochemical networks in microorganisms. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 7, 129–143.
Steele, H. L., Jaeger, K. E., Daniel, R., & Streit, W. R. (2009). Advances in recovery of novel biocatalysts from metagenomes. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 16, 25–37.
Fernandez-Arrojo, L., Guazzaroni, M. E., Lopez-Cortes, N., Beloqui, A., & Ferrer, M. (2010). Metagenomic era for biocatalyst identification. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 21, 725–733.
Lee, S. W., Won, K., Lim, H. K., Kim, J. C., Choi, G. J., et al. (2004). Screening for novel lipolytic enzymes from uncultured soil microorganisms. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 65, 720–726.
Cieslinski, H., Bialkowskaa, A., Tkaczuk, K., Dlugolecka, A., Kur, J., et al. (2009). Identification and molecular modeling of a novel lipase from an Antarctic soil metagenomic library. Polish Journal of Microbiology, 58, 199–204.
Couto, G. H., Glogauer, A., Faoro, H., Chubatsu, L. S., Souza, E. M., et al. (2010). Isolation of a novel lipase from a metagenomic library derived from mangrove sediment from the south Brazilian coast. Genetics and Molecular Research, 9, 514–523.
Tuffin, M., Anderson, D., Heath, C., & Cowan, D. A. (2009). Metagenomic gene discovery: how far have we moved into novel sequence space? Biotechnology Journal, 4, 1671–1683.
Glogauer, A., Martini, V. P., Faoro, H., Couto, G. H., Muller-Santos, M., et al. (2011). Identification and characterization of a new true lipase isolated through metagenomic approach. Microbial Cell Factories, 10, 54.
Martini, V. P., Glogauer, A., Iulek, J., Souza, E. M., Pedrosa, F. O., et al. (2012). Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of LipC12, a true lipase isolated through a metagenomics approach. Acta Crystallographica. Section F, Structural Biology and Crystallization Communications, 68, 175–177.
Simon, C., & Daniel, R. (2011). Metagenomic analyses: past and future trends. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 77, 1153–1161.
Rao, L., Xue, Y., Zhou, C., Tao, J., Li, G., et al. (2011). A thermostable esterase from Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis opening up a new family of bacterial lipolytic enzymes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1814, 1695–1702.
Nacke, H., Will, C., Herzog, S., Nowka, B., Engelhaupt, M., et al. (2011). Identification of novel lipolytic genes and gene families by screening of metagenomic libraries derived from soil samples of the German Biodiversity Exploratories. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 78, 188–201.
Vieites, J. M., Guazzaroni, M. E., Beloqui, A., Golyshin, P. N., & Ferrer, M. (2009). Metagenomics approaches in systems microbiology. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 33, 236–255.
Kalyuzhnaya, M. G., Lapidus, A., Ivanova, N., Copeland, A. C., McHardy, A. C., et al. (2008). High-resolution metagenomics targets specific functional types in complex microbial communities. Nature Biotechnology, 26, 1029–1034.
Jehmlich, N., Schmidt, F., von Bergen, M., Richnow, H. H., & Vogt, C. (2008). Protein-based stable isotope probing (protein-SIP) reveals active species within anoxic mixed cultures. ISME Journal, 2, 1122–1133.
Bomar, L., Maltz, M., Colston, S., & Graf, J. (2011). Directed culturing of microorganisms using metatranscriptomics. MBio, 2(2), e00012-11. doi:10.1128/mBio.00012-11.
Uchiyama, T., & Miyazaki, M. (2009). Functional metagenomics for enzyme discovery: challenges of efficient screening. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 20, 616–622.
Shangguan, J. J., Liu, Y. Q., Wang, F. J., Zhao, J., Fan, L. Q., et al. (2011). Expression and characterization of a novel lipase from Aspergillus fumigatus with high specific activity. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 165, 949–962.
Najjar, A., Robert, S., Guerin, C., Violet-Asther, M., & Carriere, F. (2011). Quantitative study of lipase secretion, extracellular lipolysis, and lipid storage in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica grown in the presence of olive oil: analogies with lipolysis in humans. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 89, 1947–1962.
Jermsuntiea, W., Aki, T., Toyoura, R., Iwashita, K., Kawamoto, S., et al. (2011). Purification and characterization of intracellular lipase from the polyunsaturated fatty acid-producing fungus Mortierella alliacea. New Biotechnology, 28, 158–164.
Ham, H. J., Rho, H. J., Shin, S. K., & Yoon, H. J. (2010). The TGL2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes an active acylglycerol lipase located in the mitochondria. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 3005–3013.
Deive, F. J., Carvalho, E., Pastrana, L., Rua, M. L., Longo, M. A., et al. (2009). Strategies for improving extracellular lipolytic enzyme production by Thermus thermophilus HB27. Bioresource Technology, 100, 3630–3637.
D'Annibale, A., Sermanni, G. G., Federici, F., & Petruccioli, M. (2006). Olive-mill wastewaters: a promising substrate for microbial lipase production. Bioresource Technology, 97, 1828–1833.
Dutta, S., & Ray, L. (2009). Production and characterization of an alkaline thermostable crude lipase from an isolated strain of Bacillus cereus C(7). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 159, 142–154.
Shariff, F. M., Leow, T. C., Mukred, A. D., Salleh, A. B., Basri, M., et al. (2007). Production of L2 lipase by Bacillus sp. strain L2: nutritional and physical factors. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 47, 406–412.
Chander, H., Bathish, V. K., Sannabhadti, S. S., & Srinivasan, R. A. (2006). Factors affecting lipase production in Aspergillus wentii. Journal of Food Science, 45, 598–600.
Joseph, B., Ramteke, P. W., & Kumar, P. A. (2006). Studies on the enhanced production of extracellular lipase by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Journal of General and Applied Microbiology, 52, 315–320.
Maia, M. M., Heasley, A., Camargo de Morais, M. M., Melo, E. H., Morais, M. A., Jr., et al. (2001). Effect of culture conditions on lipase production by Fusarium solani in batch fermentation. Bioresource Technology, 76, 23–27.
Ben Rebah, F., Frikha, F., Kamoun, W., Belbahri, L., Gargouri, Y., et al. (2008). Culture of Staphylococcus xylosus in fish processing by-product-based media for lipase production. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 47, 549–554.
Kambourova, M., Emanuilova, E., & Dimitrov, P. (1996). Influence of culture conditions on thermostable lipase production by a thermophilic alkalitolerant strain of Bacillus sp. Folia Microbiol (Praha), 41, 146–148.
Show, P. L., Tan, C. P., Shamsul Anuar, M., Ariff, A., Yusof, Y. A., et al. (2012). Extractive fermentation for improved production and recovery of lipase derived from Burkholderia cepacia using a thermoseparating polymer in aqueous two-phase systems. Bioresource Technology, 116, 226–233.
Fickers, P., Destain, J., & Thonart, P. (2009). Improvement of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase production by fed-batch fermentation. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 49, 212–215.
Montesinos, J. L., Dalmau, E., & Casas, C. (2003). Lipase production in continuous culture of Candida rugosa. J Chem Tech Biot, 78, 753–761.
Deive, F. J., Sanroman, M. A., & Longo, M. A. (2010). A comprehensive study of lipase production by Yarrowia lipolytica CECT 1240 (ATCC 18942): from shake flask to continuous bioreactor. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology, 85, 258–266.
Moftah, O. A., Grbavcic, S., Zuza, M., Lukovic, N., Bezbradica, D., et al. (2012). Adding value to the oil cake as a waste from oil processing industry: production of lipase and protease by Candida utilis in solid state fermentation. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 166, 348–364.
Lopez, E., Deive, F. J., Longo, M. A., & Sanroman, M. A. (2010). Strategies for utilisation of food-processing wastes to produce lipases in solid-state cultures of Rhizopus oryzae. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 33, 929–935.
Kempka, A. P., Lipke, N. L., da Luz Fontoura Pinheiro, T., Menoncin, S., Treichel, H., et al. (2008). Response surface method to optimize the production and characterization of lipase from Penicillium verrucosum in solid-state fermentation. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 31, 119–125.
Kumar, S., Katiyar, N., Ingle, P., & Negi, S. (2011). Use of evolutionary operation (EVOP) factorial design technique to develop a bioprocess using grease waste as a substrate for lipase production. Bioresource Technology, 102, 4909–4912.
Edwinoliver, N. G., Thirunavukarasu, K., Naidu, R. B., Gowthaman, M. K., Kambe, T. N., et al. (2010). Scale up of a novel tri-substrate fermentation for enhanced production of Aspergillus niger lipase for tallow hydrolysis. Bioresource Technology, 101, 6791–6796.
Treichel, H., de Oliveria, D., Mazutti, M. A., Luccio, M. D., & Oliveira, J. V. (2010). A review on microbial lipases production. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 3, 182–196.
Shimada, Y., Sugihara, A., & Tominaga, Y. (1994). Microbial lipase: structure and production. Bioprocess Technology, 19, 359–371.
Resina, D., Maurer, M., Cos, O., Arnau, C., Carnicer, M., et al. (2009). Engineering of bottlenecks in Rhizopus oryzae lipase production in Pichia pastoris using the nitrogen source-regulated FLD1 promoter. New Biotechnology, 25, 396–403.
Bas, D., & Boyaci, H. I. (2007). Modeling and optimization II: comparison of estimation capabilities of response surface methodology with artificial neural networks in a biochemical reaction. Journal of Food Engineering, 78, 846–854.
Sifour, M., Zaghloul, T. I., Saeed, H. M., Berekaa, M. M., & Abdel-Fattah, Y. R. (2010). Enhanced production of lipase by the thermophilic Geobacillus stearothermophilus strain-5 using statistical experimental designs. New Biotechnology, 27, 330–336.
Olusesan, A. T., Azura, L. K., Abubakar, F., Mohamed, A. K., Radu, S., et al. (2011). Enhancement of thermostable lipase production by a genotypically identified extremophilic Bacillus subtilis NS 8 in a continuous bioreactor. Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, 20, 105–115.
Gupta, N., Mehra, G., & Gupta, R. (2004). A glycerol-inducible thermostable lipase from Bacillus sp.: medium optimization by a Plackett-Burman design and by response surface methodology. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 50, 361–368.
Ebrahimpour, A., Abd Rahman, R. N., Ean Ch’ng, D. H., Basri, M., & Salleh, A. B. (2008). A modeling study by response surface methodology and artificial neural network on culture parameters optimization for thermostable lipase production from a newly isolated thermophilic Geobacillus sp. strain ARM. BMC Biotechnology, 8, 96.
Contesini, F. J., da Silva, V. C., Maciel, R. F., de Lima, R. J., Barros, F. F., et al. (2009). Response surface analysis for the production of an enantioselective lipase from Aspergillus niger by solid-state fermentation. Journal of Microbiology, 47, 563–571.
Chennupati, S., Potumarthi, R., Gopal Rao, M., Manga, P. L., Sridevi, M., et al. (2009). Multiple responses optimization and modeling of lipase production by Rhodotorula mucilaginosa MTCC-8737 using response surface methodology. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 159, 317–329.
Teng, Y., & Xu, Y. (2008). Culture condition improvement for whole-cell lipase production in submerged fermentation by Rhizopus chinensis using statistical method. Bioresource Technology, 99, 3900–3907.
Lan, D., Hou, S., Yang, N., Whiteley, C., Yang, B., et al. (2011). Optimal production and biochemical properties of a lipase from Candida albicans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12, 7216–7237.
Rajendran, A., & Thangavelu, V. (2007). Optimization of medium composition for lipase production by Candida rugosa NCIM 3462 using response surface methodology. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 53, 643–655.
Holland, J. H. (1992). Adaptation in natural and artificial systems: an introductory analysis with applications to biology, control, and artificial intelligence (p. 207). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Eberhart, R.C., Kennedy, J. (1995). A new optimizer using particle swarm theory. Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium. Micro Machine and Human Science, Indianapolis, IN, pp. 39–43.
Garlapati, V. K., Vundavilli, P. R., & Banerjee, R. (2010). Evaluation of lipase production by genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization and their comparative study. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 1350–1361.
Talukder, M. R., Susanto, D., Feng, G., Wu, J., Choi, W. J., et al. (2007). Improvement in extraction and catalytic activity of Mucor javanicus lipase by modification of AOT reverse micelle. Biotechnology Journal, 2, 1369–1374.
Yu, Y. C., Chu, Y., & Ji, J. Y. (2003). Study of the factors affecting the forward and back extraction of yeast-lipase and its activity by reverse micelles. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 267, 60–64.
Taipa, M. A., Aires-Barros, M. R., & Cabral, J. M. (1992). Purification of lipases. Journal of Biotechnology, 26, 111–142.
Yujun, W., Jian, X., Guangsheng, L., & Youyuan, D. (2008). Immobilization of lipase by ultrafiltration and cross-linking onto the polysulfone membrane surface. Bioresource Technology, 99, 2299–2303.
Aires-Barros, M. R., & Cabral, J. M. (1991). Selective separation and purification of two lipases from Chromobacterium viscosum using AOT reversed micelles. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 38, 1302–1307.
Yao, H., Zhang, T., Xue, H., Tang, K., & Li, R. (2011). Biomimetic affinity purification of Candida antarctica lipase B. Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 879, 3896–3900.
Juntachai, W., Oura, T., & Kajiwara, S. (2011). Purification and characterization of a secretory lipolytic enzyme, MgLIP2, from Malassezia globosa. Microbiology, 157, 3492–3499.
Sikdar, S. K., Cole, K. D., Stewart, R. M., Szlag, D. C., Todd, P., et al. (1991). Aqueous two-phase extraction in bioseparations: an assessment. Biotechnology (N. Y), 9, 254–256.
Gupta, R., Bradoo, S., & Saxena, R. K. (1999). Aqueous two-phase systems: an attractive technology for downstream processing of biomolecules. Current Science, 77, 520–523.
Srinivas, N. D., Barhate, R. S., & Raghavarao, K. S. M. S. (2002). Aqueous two-phase extraction in combination with ultrafiltration for downstream processing of Ipomoea peroxidase. Journal of Food Engineering, 54, 1–6.
Terstappen, G. C., Geerts, A. J., & Kula, M. R. (1992). The use of detergent-based aqueous two-phase systems for the isolation of extracellular proteins: purification of a lipase from Pseudomonas cepacia. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 16, 228–235.
Bompensieri, S., Mahler, G. F., Castaneda, N., Miranda, M. V., Cascone, O., et al. (1998). Rapid purification of a lipase from Acenitobacter calcoaceticus by temperature-induced aqueous two-phase systems. Biotechnology Techniques, 12, 611–613.
Barbosa, J. M., Souza, R. L., Fricks, A. T., Zanin, G. M., Soares, C. M., et al. (2011). Purification of lipase produced by a new source of Bacillus in submerged fermentation using an aqueous two-phase system. Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 879, 3853–3858.
Volpato, G., Filice, M., de las Rivas, B., Rodrigues, R. C., Heck, J. X., et al. (2011). Purification, immobilization, and characterization of a specific lipase from Staphylococcus warneri EX17 by enzyme fractionating via adsorption on different hydrophobic supports. Biotechnology Progress, 27, 717–723.
Volpato, G., Filice, M., Ayub, M. A., Guisan, J. M., & Palomo, J. M. (2010). Single-step purification of different lipases from Staphylococcus warneri. Journal of Chromatography A, 1217, 73–478.
Ventura, S. P., Sousa, S. G., Freire, M. G., Serafim, L. S., Lima, A. S., et al. (2011). Design of ionic liquids for lipase purification. Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences, 879, 2679–2687.
Levasseur, A., Gouret, P., Lesage-Meessen, L., Asther, M., Record, E., et al. (2006). Tracking the connection between evolutionary and functional shifts using the fungal lipase/feruloyl esterase A family. BMC Evolutionary Biology, 6, 92.
Takwa, M., Larsen, M. W., Hult, K., & Martinelle, M. (2011). Rational redesign of Candida antarctica lipase B for the ring opening polymerization of D,D-lactide. Chemical Communications (Cambridge), 47, 7392–7394.
Brundiek, H. B., Evitt, A. S., Kourist, R., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2012). Creation of a lipase highly selective for trans fatty acids by protein engineering. Angewandte Chemie (International Ed. in English), 51, 412–414.
Gumulya, Y., & Reetz, M. T. (2011). Enhancing the thermal robustness of an enzyme by directed evolution: least favorable starting points and inferior mutants can map superior evolutionary pathways. ChemBioChem, 12, 2502–2510.
Kolling, D. J., Bertoldo, J. B., Brod, F. C., Vernal, J., Terenzi, H., et al. (2010). Biochemical and structural characterization of two site-directed mutants of Staphylococcus xylosus lipase. Molecular Biotechnology, 46, 168–175.
Reetz, M. T., & Carballeira, J. D. (2007). Iterative saturation mutagenesis (ISM) for rapid directed evolution of functional enzymes. Nature Protocols, 2, 891–903.
Wong, H., Davis, R. C., Hill, J. S., Yang, D., & Schotz, M. C. (1997). Lipase engineering: a window into structure-function relationships. Methods in Enzymology, 284, 171–184.
Alberghina, L. (Ed.). (2000). Protein engineering in industrial biotechnology. Reading: Harwood Academic Publishers. pp 376.
Acharya, P., Rajakumara, E., Sankaranarayanan, R., & Rao, N. M. (2004). Structural basis of selection and thermostability of laboratory evolved Bacillus subtilis lipase. Journal of Molecular Biology, 341, 1271–1281.
Reetz, M. T., Prasad, S., Carballeira, J. D., Gumulya, Y., & Bocola, M. (2010). Iterative saturation mutagenesis accelerates laboratory evolution of enzyme stereoselectivity: rigorous comparison with traditional methods. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 132, 9144–9152.
Prasad, S., Bocola, M., & Reetz, M. T. (2011). Revisiting the lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: directed evolution of substrate acceptance and enantioselectivity using iterative saturation mutagenesis. Chemphyschem, 12, 1550–1557.
Park, C. G., Kwon, M. A., Song, J. K., & Kim, D. M. (2011). Cell-free synthesis and multifold screening of Candida antarctica lipase B (CalB) variants after combinatorial mutagenesis of hot spots. Biotechnology Progress, 27, 47–53.
Schmidt, M., & Bornscheuer, U. T. (2005). High-throughput assays for lipases and esterases. Biomolecular Engineering, 22, 51–56.
Sandström, A. G., Wikmark, Y., Engström, K., Nyhlén, J., & Bäckvall, J. E. (2012). Combinatorial reshaping of the Candida antarctica lipase A substrate pocket for enantioselectivity using an extremely condensed library. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 109, 78–83.
Shu, Z., Duan, M., Yang, J., Xu, L., & Yan, Y. (2009). Aspergillus niger lipase: heterologous expression in Pichia pastoris, molecular modeling prediction and the importance of the hinge domains at both sides of the lid domain to interfacial activation. Biotechnology Progress, 25, 409–416.
Shu, Z., Wu, J., Xue, L., Lin, R., Jiang, Y., et al. (2011). Construction of Aspergillus niger lipase mutants with oil-water interface independence. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 48, 129–133.
Becker, S., Theile, S., Heppeler, N., Michalczyk, A., Wentzel, A., et al. (2005). A generic system for the Escherichia coli cell-surface display of lipolytic enzymes. FEBS Letters, 579, 1177–1182.
Lee, S. H., Choi, J. I., Han, M. J., Choi, J. H., & Lee, S. Y. (2005). Display of lipase on the cell surface of Escherichia coli using OprF as an anchor and its application to enantioselective resolution in organic solvent. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 90, 223–230.
Jung, H. C., Kwon, S. J., & Pan, J. G. (2006). Display of a thermostable lipase on the surface of a solvent-resistant bacterium, Pseudomonas putida GM730, and its applications in whole-cell biocatalysis. BMC Biotechnology, 6, 23.
Kobayashi, G., Fujii, K., Serizawa, M., Yamamoto, H., & Sekiguchi, J. (2002). Simultaneous display of bacterial and fungal lipases on the cell surface of Bacillus subtilis. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 93, 15–19.
Mormeneo, M., Andres, I., Bofill, C., Diaz, P., & Zueco, J. (2008). Efficient secretion of Bacillus subtilis lipase A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by translational fusion to the Pir4 cell wall protein. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 80, 437–445.
Ueda, M., & Tanaka, A. (2000). Cell surface engineering of yeast: construction of arming yeast with biocatalyst. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 90, 125–136.
Kato, M., Fuchimoto, J., Tanino, T., Kondo, A., Fukuda, H., et al. (2007). Preparation of a whole-cell biocatalyst of mutated Candida antarctica lipase B (mCALB) by a yeast molecular display system and its practical properties. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 75, 549–555.
Tanino, T., Aoki, T., Chung, W. Y., Watanabe, Y., Ogino, C., et al. (2009). Improvement of a Candida antarctica lipase B-displaying yeast whole-cell biocatalyst and its application to the polyester synthesis reaction. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 82, 59–66.
Liu, W., Zhao, H., Jia, B., Xu, L., & Yan, Y. (2010). Surface display of active lipase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using Cwp2 as an anchor protein. Biotechnology Letters, 32, 255–260.
Liu, W. S., Pan, X. X., Jia, B., Zhao, H. Y., Xu, L., et al. (2010). Surface display of active lipases Lip7 and Lip8 from Yarrowia lipolytica on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 88, 885–891.
Han, S. Y., Zhang, J. H., Han, Z. L., Zheng, S. P., & Lin, Y. (2011). Combination of site-directed mutagenesis and yeast surface display enhances Rhizomucor miehei lipase esterification activity in organic solvent. Biotechnology Letters, 33, 2431–2438.
Baek, J. H., Han, M. J., Lee, S. H., & Lee, S. Y. (2010). Enhanced display of lipase on the Escherichia coli cell surface, based on transcriptome analysis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 76, 971–973.
Ribeiro, B. D., de Castro, A. M., Coelho, M. A., & Freire, D. M. (2011). Production and use of lipases in bioenergy: a review from the feedstocks to biodiesel production. Enzyme Research, 2011, 16.
Tan, T., Lu, J., Nie, K., Deng, L., & Wang, F. (2010). Biodiesel production with immobilized lipase: a review. Biotechnology Advances, 28, 628–634.
Bisen, P. S., Sanodiya, B. S., Thakur, G. S., Baghel, R. K., & Prasad, G. B. (2010). Biodiesel production with special emphasis on lipase-catalyzed transesterification. Biotechnology Letters, 32, 1019–1030.
Wang, X., Liu, X., Yan, X., Zhao, P., Ding, Y., et al. (2011). Enzyme-nanoporous gold biocomposite: excellent biocatalyst with improved biocatalytic performance and stability. PLoS One, 6, e24207.
Tzialla, A. A., Pavlidis, I. V., Felicissimo, M. P., Rudolf, P., Gournis, D., et al. (2010). Lipase immobilization on smectite nanoclays: characterization and application to the epoxidation of alpha-pinene. Bioresource Technology, 101, 1587–1594.
Rao, A., Bankar, A., Shinde, A., Ravi Kumar, A., Gosavi, S., et al. (2011). Phyto-inspired silica nanowires: characterization and application in lipase immobilization. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 4, 871–877.
Baldessari, A., & Iglesias, L. E. (2012). Lipases in green chemistry: acylation and alcoholysis on steroids and nucleosides. Methods in Molecular Biology, 861, 457–469.
Gross, R. A., Kalra, B., & Kumar, A. (2001). Polyester and polycarbonate synthesis by in vitro enzyme catalysis. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 55, 655–660.
Kim, D. Y., & Dordick, J. S. (2001). Combinatorial array-based enzymatic polyester synthesis. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 76, 200–206.
Wang, H. Y., Zhou, Y. J., Wang, Z., Wang, N., Li, K., et al. (2011). Enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of a novel thermosensitive polyester with pendant ketoprofen. Macromolecular Bioscience, 11, 595–599.
Brust, B., Lecoufle, M., Tuaillon, E., Dedieu, L., Canaan, S., et al. (2011). Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipolytic enzymes as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of active tuberculosis. PLoS One, 6, e25078.
Pinijsuwan, S., Shipovskov, S., Surareungchai, W., Ferapontova, E. E., & Gothelf, K. V. (2011). Development of a lipase-based optical assay for detection of DNA. Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry, 9, 6352–6356.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagarajan, S. New Tools for Exploring “Old Friends—Microbial Lipases”. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 168, 1163–1196 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9849-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-012-9849-7