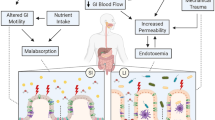
Abstract
This article reviews the literature regarding gastrointestinal disturbances specifically in runners. Upper gastrointestinal problems such as reflux, nausea, vomiting, and gastritis are reviewed. Exercise has been found to alter esophageal motility. These symptoms worsen with increased exertion as well. H2 blockers have been found helpful for reflux and nausea. The lower intestinal problems of motility and blood loss are discussed. These problems are generally more common and more directly related to running. Also reviewed are endotoxin involvement and transient abdominal pain. Much of the literature deals with marathon and ultramarathon running, showing the extreme effects of running and exertional stress on the body; however, recreational runners may not be so afflicted as these study participants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Clayton D: Runners World. May 1979:72.
Gil SM, Yazaki E, Evans DF: Aetiology of running-related gastrointestinal dysfunction. How far is the finishing line? Sports Med 1998, 26:365–378.
Costil DL, Wilmore JH: Cardiorespiratory function and performance. In Physiology of Sport and Exercise, edn 2. Edited by Costil DL, Wilmore JH. Champaign: Human Kinetics; 1999:205–242.
Sullivan SN, Wong C, Heidenheim P: Does running cause gastrointestinal symptoms? A survey of 93 randomly selected runners compared with controls. N Z Med J 1994, 107:328–330.
Clark CS, Kraus BB, Sinclair J, Castell DO: Gastroesophageal relux induced by exercise in healthy volunteers. JAMA 1989, 261:3599–3601.
Kruass BB, Sinclair JW, Castell DO: Gastroesophageal reflux in runners. Ann Intern Med 1990, 112:429–433.
Collins KL, Pratt FP, Rodriguez-Stanley S, et al.: Esophageal reflux in conditioned runners, cyclists, and weightlifters. Med Sci Sport Exerc 2003, 35:730–735.
Peters HP, Bos M, Seebregts L, et al.: Gastrointestinal symptoms in long-distance runners, cyclists, and triathletes: prevalence, medication, and etiology. Am J Gastroenterol 1999, 94:1570–1581.
Rehrer NJ, Brouns F, Beckers EJ, et al.: Physiologic changes and gastrointestinal symptoms as a results of ultraendurance running. Eur J Appl Physiol 1992, 64:1–8.
Glace B, Murphy C, McHugh M: Food and fluid intake and disturbances in gastrointestinal and mental function during and ultramarathon. Intl J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 2002, 12:414–427.
Peters HP, Zweers M, Backx FJ, et al.: Gastrointestinal symptoms during long-distance walking. Med Sci Sports Exerc 1999, 31:767–773.
Soffer EE, Merchant RK, Duethman G, et al.: Effect of graded exercise on esophageal motility and gastroesophageal reflux in trained athletes. Dig Dis Sci 1993, 38:220–224.
van Nieuwenhoven MA, Brouns F, Brummer RJ: The effect of physical exercise on parameters of gastrointestinal function. Neurogastroenterol Motil 1999, 11:431–439.
Choi SC, Yoo KH, Kim TH, et al.: Effect of graded running on esophageal motility and gastroesophageal reflux in fed volunteers. J Korean Med Sci 2001, 16:183–187.
Weiner P, Konson N, Sternberg A, et al.: Is gastro-oesophageal reflux a factor in exercise-induced asthma. Respir Med 1998, 92:1071–1075.
DeMeester TR, O’Sullivan GC, Bermudez G, et al.: Esophageal function in patients with anginal-type chest pain and normal coronary angiograms. Ann Surg 1982, 196:488–498.
Schofield PM, Bennett DH, Whorwell PJ, et al.: Exertional gastro-esophageal reflux: a mechanism for symptoms in patients with angina pectoris and normal coronary angiograms. BMJ 1987, 294:1459–1461.
Bovero E, Torre F, Poletti M, DeIaco F: Exertional gastroesophageal pH-metry: a new provocative physiological test in the diagnosis of chest pain. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 1993, 17:4–8.
Kondo T: Exercise-induced nausea is exaggerated by eating. Appetite 2001, 36:119–125.
Baska RS, Moses FM, Deuster PA: Cimetidine reduces runningassociated gastrointestinal bleeding. Dig Dis Sci 1990, 35:956–960.
Smetanka RD, Lambert GP, Murray R, et al.: Intestinal permeability in runners in the 1996 Chicago marathon. Int J Sport Nutr 1999, 9:426–433.
Ryan AJ, Chang RT, Gisolfi CV: Gastrointestinal permeability following aspirin intake and prolonged running. Med Sci Sport Exer 1996, 28:698–705.
Lambert GP, Broussard LJ, Mason BL, et al.: Gastrointestinal permeability during exercise: effects of aspirin and energycontaining beverages. J Appl Physiol 2001, 90:2075–2080.
Choi SC, Choi SJ, Kim JA, et al.: The role of gastrointestinal endoscopy in long-distance runners with gastrointestinal symptoms. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2001, 13:1089–1094. In this study of 16 competitive runners, the authors directly assessed mucosal damage with endoscopy. Additionally, they compare the findings with hematologic parameters.
Moses FM, Baska RS, Peura DA, Deuster PA: Effect of cimetidine on marathon-associated gastrointestinal bleeding. Dig Dis Sci 1992, 36:1390–1394.
Cheng Y, Macera CA, Davis DR, Blair SN: Physical activity and peptic ulcers. West J Med 2000, 173:101–107.
Morton DP, Callister R: Characteristics and etiology of exercise-related transient abdominal pain. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2000, 32:432–438.
Morton DP, Callister R: Factors influencing exercise-related transient abdominal pain. Med Sci Sport Exerc 2002, 34:745–749. This survey of runners expands the previous reference to define factors that influence the prevalence of this transient abdominal pain.
Loudon CP, Corroll V, Butcher J, et al.: The effects of physical exercise on patients with Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol 1999, 94:697–703.
Putukian M, Potera C. Don’t miss gastrointestinal disorders in athletes. Phys Sportsmed 1997, 25:80–84.
Lustyk MK, Jarrett ME, Bennett JC, Heitkemper MM: Does a physically active lifestyle improve symptoms in women with irritable bowel syndrome? Gastroenterol Nurs 2001, 24:129–137.
Keefe EB, Lowe DK, Goss JR, Wayne R: Gastrointestinal symptoms of marathon runners. West J Med 1984, 141:481–484.
Worobetz LJ, Gerrard DF: Gastrointestinal symptoms during exercise in endurance athletes: prevalence and speculations on the aetiology. N Z Med J 1985, 98:644–646.
Toilet Training. http://www.coolrunning.com.au/editorials/ 1998e007.shtml
Rehrer NJ, Meijer GA: Biomechanical vibration of the abdominal region during running and bicycling. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 1991, 31:231–234.
Rehrer NJ, Janssen ME, Brouns F, Saris WH: Fluid intake and gastrointestinal problems in runners competing in a 25 km race and a marathon. Int J Sports Med 1989, 10(Suppl 1):S22-S25.
Brouns F, Beckers E: Is the gut an athletic organ? Digestion, absorption and exercise. Sports Med 1993, 15:242–257.
O’Connor AM, Johnston CF, Buchanan KD, et al.: Circulating gastrointestinal hormone changes in marathon running. Int J Sports Med 1995, 16:283–287.
Jeukendrup AE, Vet-Joop K, Sturk A, et al.: Relationship between gastro-intestinal complaints and endotoxaemia, cytokine release and the acute-phase reaction during and after a long-distance triathlon in highly trained men. Clin Sci 2000, 98:47–55.
Brock-Utne JG, Gaffin SL, Wells MT, et al.: Endotoxaemia in exhausted runners after a long-distance race. S Afr Med J 1988, 73:533–536.
Walsh M, Moriarity J, Peterson J, et al.: Portal venous thrombosis in a backpacker: the role of exercise. Phys Sportsmed 1996, 24:75.
Moses FM, Brewer TG, Peura DA: Running associated proximal hemorrhagic colitis. Ann Intern Med 1988, 108:385–386.
Green GA: Gastrointestinal disorders in the athlete. Clin Sports Med 1992, 11:453–470. Excellent and comprehensive general review of GI disorders.
Buchman AL, Killip D, Ou CN, et al.: Short-term vitamin E supplementation before marathon running: a placebo controlled trial. Nutrition 1999, 15:278–283.
Buchman AL, O’Brien W, Ou CN, et al.: The effect of arginine or glycine supplementation on gastrointestinal function, muscle injury, serum amino acid concentrations and performance during a marathon run. Int J Sports Med 1999, 20:31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simons, S.M., Kennedy, R.G. Gastrointestinal problems in runners. Curr Sports Med Rep 3, 112–116 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11932-004-0011-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11932-004-0011-3