Abstract
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension (SIH) is caused by leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), with resultant CSF hypovolemia and intracranial hypotension. Although in some patients SIH may be preceded by minor trauma, it often occurs in the absence of any identifiable initiating event. Orthostatic headache is the primary clinical manifestation, usually accompanied by one or more other symptoms of SIH. Diagnosis can be reached by a combination of imaging studies, which may include MRI with gadolinium, nuclear cisternography, and myelography. Treatment ranges from conservative management, such as bed rest and hydration, to invasive procedures, such as lumbar puncture with autologous blood patch, CT-guided fibrin glue injection at the site of the leak, and open surgical intervention. Outcomes vary from complete resolution of CSF leak with alleviation of symptoms to continued and/or recurrent leaks with chronic unremitting symptomatology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Schievink WI, Gordon OK, Tourje J: Connective tissue disorders with spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid leaks and intracranial hypotension: a prospective study. Neurosurgery 2004, 54:65–71.
Mokri B, Maher CO, Sencakova D: Spontaneous CSF leaks: underlying disorders of connective tissue. Neurology 2002, 58:814–816.
Mokri B: Low cerebrospinal fluid pressure syndromes. Neurol Clin N Am 2004, 22:55–74.
Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. The International classification of headache disorders. Cephalalgia 2004, 24(Suppl 1):1–151.
Mokri B, Atkinson JLK, Piepgras DG: Absent headache despite CSF volume depletion (intracranial hypotension). Neurology 2000, 55:573–575.
Mokri B: Spontaneous CSF leaks mimicking benign exertional headaches. Cephalalgia 2002, 22:780–783.
Scheivink WI, Wijdicks EFM, Meyer FB, Sonntag VK: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension mimicking aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2001, 48:513–517.
Mokri B: Headaches caused by decreased intracranial pressure: diagnosis and management. Curr Opin Neurol 2003, 16:319–326.
Albayram S, Wasserman BA, Yousem DM, Wityk R: Intracranial hypotension as a cause of radiculopathy from cervical epidural venous engorgement. Case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002, 23:618–621.
Hong M, Shah GV, Adams KM, et al.: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension causing reversible frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 2002, 58:1285–1287.
Evans RW, Mokri B: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension resulting in coma. Headache 2002, 42:159–160.
Schievink WI, Maya MM, Moser FG, Tourje J: Spectrum of subdural fluid collections in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. J Neurosurg 2005, 103:608–613.
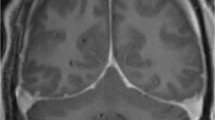
Mokri B, Piepgras DG, Miller GM: Syndrome of orthostatic headaches and diffuse pachymeningeal gadolinium enhancement. Mayo Clin Proc 1997, 72:400–413.
Rice DH: Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea: diagnosis and treatment. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2003, 11:19–22.
Zlab MK, Moore GF, Daly DT, Yonkers AJ: Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea: a review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J 1992, 71:314–317.
Lund VJ: Endoscopic management of cerebrospinal fluid leaks. Am J Rhinol 2002, 16:17–23.
Eros EJ, Dodick DW, Nelson KD: Orthostatic headache syndrome with CSF leak secondary to bony pathology of the cervical spine. Cephalalgia 2002, 22:439–443.
Vishteh AG, Schievink WI, Baskin JJ, Sonntag VKH: Cervical bony spur presenting with spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Case report. J Neurosurg 1998, 89:483–484.
Schievink WI: Spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks and intracranial hypotension. JAMA 2006, 295:2286–2296.
Portier F, Minteguiaga C, Racy E, et al.: Spontaneous intracranial hypotension: a rare cause of labyrinthe hydrops. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2002, 111:817–820.
Lin WC, Lirng JF, Fuh JL, et al.: MR findings of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Acta Radiol 2002, 43:249–255.
Berroir S, Loisel B, Ducros A, et al.: Early epidural blood patch in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurology 2004, 63:1950–1951.
Schievink WI, Maya MM, Louy C: Cranial MRI predicts outcome of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurology 2005, 64:1282–1284.
Chen CJ, Lee TH, Hsu HL, et al.: Spinal MR findings in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neuroradiology 2002, 44:996–1003.
Molins A, Alvarez J, Sumalla J, et al.: Cisternographic pattern of spontaneous liquoral hypotension. Cephalalgia 1990, 10:59–65.
Grantham VV, Blakley B, Winn J: Technical review and considerations for a cerebrospinal fluid leakage study. J Nucl Med Technol 2006, 34:48–51.
Matsumura A, Anno I, Kimura H, et al.: Diagnosis of spontaneous intracranial hypotension by using magnetic resonance myelography. J Neurosurg 2000, 92:873–876.
Luetmer PH, Mokri B: Dynamic CT myelography: a technique for localizing high-flow spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003, 24:1711–1714.
Zlab MK, Moore GF, Daly DT, Yonkers AJ: Cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea: a review of the literature. Ear Nose Throat J 1992, 71:314–317.
Hull HF, Morrow G: Glucorrhea revisited. JAMA 1975, 234:1052–1053.
Mokri B: Spontaneous low cerebrospinal pressure/volume headaches. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2004, 4:117–124.
Karst M, Hollenhorst J, Fink M, Conrad I: Computerized tomography-guided epidural blood patch in the treatment of spontaneous low cerebrospinal fluid pressure headache. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2001, 45:649–651.
Duffy PJ, Crosby ET: The epidural blood patch. Resolving the controversies. Can J Anaesth 1999, 46:878–886.
Sencakova D, Mokri B, McClelland RL: The efficacy of epidural blood patch in spontaneous CSF leaks. Neurology 2001, 57:1921–1923.
Schievink WI, Maya MM, Moser FM: Treatment of spontaneous intracranial hypotension with percutaneous placement of a fibrin sealant. J Neurosurg 2004, 100:1098–1100.
Gladstone JP, Nelson K, Patel N, Dodick DW: Spontaneous CSF leak treated with percutaneous CT-guided fibrin glue. Neurology 2005, 64:1818–1819.
Schievink WI, Morreale VM, Atkinson JL, et al.: Surgical treatment of spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks. J Neurosurg 1998, 88:243–246.
Kong DS, Park K, Nam DH, et al.: Clinical features and long-term results of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurosurgery 2005, 57:91–96.
Schievink WI, Maya MM, Riedinger M: Recurrent spontaneous spinal cerebrospinal fluid leaks and intracranial hypotension: a prospective study. J Neurosurg 2003, 99:840–842.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwedt, T.J., Dodick, D.W. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Curr Pain Headache Rep 11, 56–61 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-007-0023-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-007-0023-9