Abstract
Background
Sporadic Burkitt lymphoma (BL), characterised by translocation-associated C-MYC upregulation is a rare, aggressive lymphoma with a cure rate up to 90 % using the R-CODOX-M/R-IVAC (RCRI) protocol. RCRI is active in HIV-associated BL in combination with HAART. The WHO classification system defines lymphomas intermediate between DLBCL and BL, in which lymphomas with t(14;18)(q32;q21) and C-MYC-carrying translocation, i.e. ‘double-hit’ are included (BL-DH), and these patients are conventionally treated with RCRI.
Result
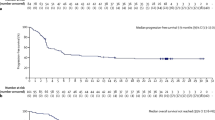
We describe the SJH experience of 25 patients with BL, BL + HIV and BL-DH treated with RCRI between 2002 and 2011. Twelve BL patients (8M/4F), median age 49.1 years (range 20–73 years); of whom 9 had extensive disease, including 8 with marrow and 2 with CNS involvement. Eleven patients remain in remission at 80.5 months (range 37–147 months) from completion of treatment and one died of progressive BL giving an OS of 91.6 % at 1 year with no late relapses. Eight patients with BL + HIV were treated (6M/2F) with a median age 40.25 years (range 24–64). Five remain in complete remission (CR) at 65 months (range 13–109 months), three patients died, two of progressive disease and one of treatment-associated hepatotoxicity in CR. Five patients with BL-DH were included; (3M/2F), age 47.8 years (range 42–55 years); and all patients died of progressive disease, 4 on RCRI therapy and a further patient despite an allogeneic transplantation.
Conclusion
These results confirm that RCRI is an effective treatment in adults with BL and BL + HIV and remains the gold standard against which other regimens should be compared. We confirm the poor prognosis found in BL-DH, indicating new treatment approaches are needed for this sub-group which should be identified at diagnosis by FISH analysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burkitt D (1958) A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children. Br J Surg 46(197):218
Kelemen K, Braziel RM, Gatter K, Bakke TC, Olson S, Fan G (2010) Immunophenotypic variations of Burkitt lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol 134:127–138
Thomas DA, O’Brien S, Faderi S et al (2011) Burkitt lymphoma and atypical or Burkitt-like lymphoma: should these be treated as different diseases? Curr Hematol Malig Rep 6:58–66
Blum KA, Lozanski G, Byrd JC (2004) Adult Burkitt leukaemia and lymphoma. Blood 104(10):3009–3020
Perkins AS, Friedberg JW (2008) Burkitt lymphoma in adults. ASH Hematology 2008:341–348
Magrath I, Adde M, Shad A et al (1996) Adults and children with small non-cleaved-cell lymphoma have a similar excellent outcome when treated with the same chemotherapy regimen. J Clin Oncol 14(3):925–934
Mead GM, Sydes MR, Walewski J et al (2002) An international evaluation of CODOX-M and CODOX-M alternating with IVAC in adult Burkitt’s lymphoma: results of United Kingdom Lymphoma Group LY06 study. Ann Oncol 13(8):1264–1274
Zoufaly A, Stellbrink HJ, an der Heiden M et al (2009) Cumulative HIV viremia during highly active antiretroviral therapy is a strong predictor of AIDS-related lymphoma. J Infect Dis 200:79–87
Foot NJ, Dunn RG, Geoghegan H, Wilkins BS, Neat MJ (2011) Fluorescence in situ hybridisation analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections in the diagnostic work-up of non-Burkitt high grade B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: a single centre’s experience. J ClinPathol. 64(9):802–808
Wu D, Wood BL, Dorer R, Fromm JR (2010) “Double-Hit” mature B-cell lymphomas show a common immunophenotype by flow cytometry that includes decreased CD20 expression. Am J Clin Pathol 134:258–265
Elkins CT, Wakely PE (2011) Cytopathology of “Double-Hit” non-Hodgkins lymphoma. Cancer Cytopathol 119(4):267–271
Mohamedbhai SG, Sibson K, Marafioti T et al (2011) Rituximab in combination with CODOX-M/IVAC: a retrospective analysis of 23 cases of non HIV-related B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma with a proliferation index >95. Br J Haematol 152(2):175–181
Dunleavy K, Little RF, Pittaluga S et al (2010) The role of tumour histogenesis, FDG-PET, and short-course EPOCH with dose-dense rituximab (SC-EPOCH-RR) in HIV-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 115(15):3017–3024
Dunleavy K, Pittaluga S, Shovlin M et al (2013) Low-intensity therapy in adults with Burkitt’s lymphoma. New Engl J Med 369:1915–1925
Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME et al (2007) International harmonization project on lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25(5):579–586
Ferra C, De Guzmao BM, Morgades M et al (2012) Lack of impact of human immunodeficiency virus infection on the outcome of lymphoma patients transferred to the intensive care unit. Leuk Lymphoma 53(10):1966–1970
Johnson NA, Savage KJ, Ludkovski O et al (2009) Lymphomas with concurrent BCL2 and MYC translocations: the critical factors associated with survival. Blood 114(11):2273–2279
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smyth, L., Browne, P.V., Conneally, E. et al. Burkitt leukaemia/lymphoma: R-CODOX-M/R-IVAC remains gold standard treatment in BL. Ir J Med Sci 185, 773–777 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1288-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1288-3