Abstract
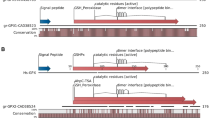
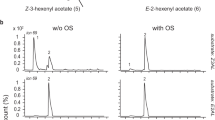
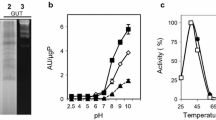
Polygalacturonase (PG), an enzyme that degrades pectin within the plant tissue cell wall, has been postulated as the chemical cause of damage to plants by the mirid Lygus hesperus. Micro-injection of two pure recombinant Aspergillus niger PG II protein forms, the wild type enzymically active and the mutant inactive one, into alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) florets, demonstrates that the enzymatic activity rather than the PG protein structure per se elicits damage symptoms. A PG gene family has been described for the tarnished plant bug, L. lineolaris. Here we report cloning members of the L. hesperus PG gene family, Lhpg2, obtained with L. lineolaris PG-specific primers and a novel Lhpg4, amplified with degenerate primers that were designed based, in part on the N-terminal sequence from an active, partially purified L. hesperus salivary gland PG protein. Proteomic analyses revealed that the salivary gland PGs encoded by Lhpg2 and Lhpg4 are detected in a diet into which L. hesperus has extruded its saliva when feeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agblor A, Henderson HM, Madrid FJ (1994) Characterization of alpha-amylase and polygalacturonase from Lygus spp. (Heteroptera; Miridae). Food Res Int 27:321–326
Allen ML (2007) Expressed sequenced tags from Lygus lineolaris (Hemiptera: Miridae), the tarnished plant bug. Genet Mol Res 6:206–213
Allen ML, Mertens JA (2008) Molecular cloning and expression of three polygalacturonase cDNAs from the tarnished plant bug, Lygus lineolaris. J Insect Sci 8:27
Annis SL, Goodwin PH (1997) Recent advances in the molecular genetics of plant cell wall-degrading enzymes produced by plant pathogenic fungi. Eur J Plant Pathol 103:1–14
Armand S, Wagemaker MJM, Sanchez-Torres P, Kester HCM, van Santen Y, Dijkstra BW, Visser J, Benen JAE (2000) The active site topology of Aspergillus niger endopolygalacturonase II as studied by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem 275:691–696
Celorio-Mancera MP, Greve LC, Teuber LR, Labavitch JM (2009) Identification of endo- and exo-polygalacturonase activity in Lygus hesperus (Knight) salivary glands. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 70(2). doi:10.1002.arch.20282
Doostdar H, McCollum TG, Mayer RT (1997) Purification and characterization of an endo-polygalacturonase from the gut of West Indies sugarcane rootstalk borer weevil (Diaprepes abbreviatus L.) larvae. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochemi Mol Biol 118:861–867
D’Ovidio R, Mattei B, Roberti S, Bellincampi D (2004a) Polygalacturonases, polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins and pectic oligomers in plant–pathogen interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteomics 1696:237–244
D’Ovidio R, Raiola A, Capodicasa C, Devoto A, Pontiggia D, Roberti S, Galletti R, Conti E, O’Sullivan D, De Lorenzo G (2004b) Characterization of the complex locus of bean encoding polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins reveals subfunctionalization for defense against fungi and insects. Plant Physiol 135:2424–2435
Ebel J, Mithöfer A (1998) Early events in the elicitation of plant defence. Planta 206:335–348
Esser K, Lemke PA (eds) (1994) The mycota: a comprehensive treatise on fungi as experimental systems for basic and applied research, vol 5. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Ferrari S, Vairo D, Ausubel FM, Cervone F, De Lorenzo G (2003) Tandemly duplicated Arabidopsis genes that encode polygalacturonase-inhibiting proteins are regulated coordinately by different signal transduction pathways in response to fungal infection. Plant Cell 15:93–106
Frati F, Galletti R, De Lorenzo G, Salerno G, Conti E (2006) Activity of endo-polygalacturonases in mirid bugs (Heteroptera: Miridae) and their inhibition by plant cell wall proteins (PGIPs). Eur J Entomol 103:515–522
Furman-Matarasso N, Cohen E, Du QS, Chejanovsky N, Hanania U, Avni A (1999) A point mutation in the ethylene-inducing xylanase elicitor inhibits the beta-1-4-endoxylanase activity but not the elicitation activity. Plant Physiol 121:345–351
Gatehouse JA (2008) Biotechnological prospects for engineering insect-resistant plants. Plant Physiol 146:881–887
Girard C, Jouanin L (1999) Molecular cloning of cDNAs encoding a range of digestive enzymes from a phytophagous beetle, Phaedon cochleariae. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 29:1129–1142
Habibi J, Backus EA, Coudron TA, Brandt SL (2001) Effect of different host substrates on hemipteran salivary protein profiles. Entomol Exp Appl 98:369–375
Keller A, Nesvizhskii AI, Kolker E, Aebersold R (2002) Empirical statistical model to estimate the accuracy of peptide identifications made by MS/MS and database search. Anal Chem 74:5383–5392
Laurema S, Varis AL (1991) Salivary amino-acids in Lygus species (Heteroptera, Miridae). Insect Biochem 21:759–765
Leigh TF, Jackson CE, Wynholds PF, Cota JA (1977) Toxicity of selected insecticides applied topically to Lygus hesperus. J Econ Entomol 70:42–44
Li RG, Rimmer R, Yu M, Sharpe AG, Seguin-Swartz G, Lydiate D, Hegedus DD (2003) Two Brassica napus polygalacturonase inhibitory protein genes are expressed at different levels in response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Planta 217:299–308
Markovic O, Janecek S (2001) Pectin degrading glycoside hydrolases of family 28: sequence-structural features, specificities and evolution. Protein Eng 14:615–631
Mithöfer A, Boland W (2008) Recognition of herbivory-associated molecular patterns. Plant Physiol 146:825–831
Mueller SC, Summers GG, Goodell PB (2003) Key features of common Lygus species in the central San Joaquin Valley. http://www.anrcatalog.ucdavis.edu/pdf/8105.pdf
Nesvizhskii AI, Keller A, Kolker E, Aebersold R (2003) A statistical model for identifying proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 75:4646–4658
Pickersgill R, Smith D, Worboys K, Jenkins J (1998) Crystal structure of polygalacturonase from Erwinia carotovora ssp. carotovora. J Biol Chem 273:24660–24664
Powell ALT, van Kan J, ten Have A, Visser J, Greve LC, Bennett AB, Labavitch JM (2000) Transgenic expression of pear PGIP in tomato limits fungal colonization. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:942–950
Rodriguez-Saona C, Crafts-Brandner SJ, Williams L, Pare PW (2002) Lygus hesperus feeding and salivary gland extracts induce volatile emissions in plants. J Chem Ecol 28:1733–1747
Roper MC, Greve LC, Warren JG, Labavitch JM, Kirkpatrick BC (2007) Xylella fastidiosa requires polygalacturonase for colonization and pathogenicity in Vitis vinifera grapevines. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:411–419
Schaefer CW, Panizzi AR (eds) (2000) Heteroptera of economic importance. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Shackel KA, Celorio-Mancera MP, Ahmadi H, Greve LC, Teuber LR, Backus EA, Labavitch JM (2005) Micro-injection of Lygus salivary gland proteins to simulate feeding damage in alfalfa and cotton flowers. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 58:69–83
Shen Z, Denton M, Mutti N, Pappan K, Kanost MR, Reese JC, Reeck GR (2003) Polygalacturonase from Sitophilus oryzae: possible horizontal transfer of a pectinase gene from fungi to weevils. J Insect Sci 3:1–9
Shevchenko A, Wilm M, Vorm O, Mann M (1996) Mass spectrometric sequencing of proteins from silver stained polyacrylamide gels. Anal Chem 68:850–858
Strong FE (1970) Physiology of injury caused by Lygus hesperus. J Econ Entomol 63:808–814
Strong FE, Kruitwagen EC (1968) Polygalacturonase in salivary apparatus of Lygus hesperus (Hemiptera). J Insect Physiol 14:1113-1119
Taylor G, Secor G (1988) An improved diffusion assay for quantifying the polygalacturonase content of Erwinia culture filtrates. Phytopathology 78:1101–1103
ten Have A, Mulder W, Visser J, van Kan JAL (1998) The endopolygalacturonase gene Bcpg1 is required for full virulence of Botrytis cinerea. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:1009–1016
Varis AL, Laurema S, Miettinen H (1983) Variation of enzyme-activities in the salivary glands of Lygus rugulipennis (Hemiptera, Miridae). Ann Entomol Fenn 49:1–10
Williams L, Tugwell NP (2000) Histological description of tarnished plant bug (Heteroptera: Miridae) feeding on small cotton floral buds. J Entomol Sci 35:187–195
Zheng SJ, Dicke M (2008) Ecological genomics of plant–insect interactions: from gene to community. Plant Physiol 146:812–817
Zhu-Salzman K, Koiwa H, Salzman RA, Shade RE, Ahn JE (2003) Cowpea bruchid Callosobruchus maculatus uses a three-component strategy to overcome a plant defensive cysteine protease inhibitor. Insect Mol Biol 12(2):135–145
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Dr. Carl Bergman at the Complex Carbohydrate Research Center for providing the A. niger PG II wild type and D202N samples. Thanks to Sandy Briesacher for providing us with L. hesperus eggs from her colony at the University of Missouri, Columbia. This work was supported by University of California Institute for Mexico and the United States, National Council of Science and Technology (CONACyT), University of California Davis (Plant Sciences Departmental Graduate Research Award and Jastro Shields Award), Cotton Incorporated and the California Cotton State Support Committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Henryk Czosnek
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de la Paz Celorio-Mancera, M., Allen, M.L., Powell, A.L. et al. Polygalacturonase causes lygus-like damage on plants: cloning and identification of western tarnished plant bug (Lygus hesperus) polygalacturonases secreted during feeding. Arthropod-Plant Interactions 2, 215–225 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-008-9050-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11829-008-9050-7