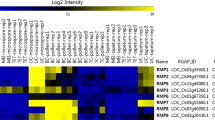
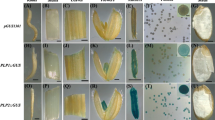
Abstract
Tissue-specific promoters are a very useful tool for manipulating gene expression in a target tissue or organ; however, their range of applications in other plant species has not been determined, to date. In this study, we identified two late pollen-specific rice promoters (ProOsLPS10 and ProOsLPS11) via meta-anatomical expression analysis. We then investigated the expression of both promoters in transgenic rice (a homologous system) and Arabidopsis (a heterologous system) using ProOsLPS10 or ProOsLPS11::GFP-GUS constructs. As predicted by microarray data, both promoters triggered strong GUS expression during the late stages of pollen development in rice, with no GUS signals detected in the examined microspores and sporophytic tissues. Interestingly, these promoters exhibited different GUS expression patterns in Arabidopsis. While in Arabidopsis, the OsLPS10 promoter conferred GUS expression at the uni- and bi-cellular pollen stages, as well as at the shoot apical region during the seedling stage, the OsLPS11 promoter was not active in the pollen at any stage, or in the examined sporophytic tissues. Furthermore, by performing a complementation analysis using a sidecar pollen (scp) mutant that displays developmental defects at the microspore stage, we found evidence that OsLPS10 promoter, which can be applied in Arabidopsis, is useful for directing gene expression in the early stages of pollen development. Our results indicate that the OsLPS10 and OsLPS11 promoters can drive the expression of target genes during the late stages of pollen development in rice, but not in Arabidopsis. Our results also emphasize the necessity of confirming the applicability of an established promoter to heterologous systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albani D, Robert LS, Donaldson PA, Altosaar I, Arnison PG, Fabijanski SF (1990) Characterization of a pollen-specific gene family from Brassica napus which is activated during early microspore development. Plant Mol Biol 15:605–622
Albani D, Altosaar I, Arnison PG, Fabijanski SF (1991) A gene showing sequence similarity to pectin esterase is specifically expressed in developing pollen of Brassica napus. Sequences in its 5′ flanking region are conserved in other pollen-specific promoters. Plant Mol Biol 16:501–513
Albani D, Sardana R, Robert LS, Altosaar I, Arnison PG, Fabijanski SF (1992) A Brassica napus gene family which shows sequence similarity to ascorbate oxidase is expressed in developing pollen. Molecular characterization and analysis of promoter activity in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant J 2:331–342
Azria D, Bhalla BL (2011) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Australian rice varieties and promoter analysis of major pollen allergen gene, Ory s1. Plant Cell Rep 30:1673–1681
Bae HK, Kang HG, Kim GJ, Eu HJ, Oh SA, Song JT, Chung IK, Eun MY, Park SK (2010) Transgenic rice plants carrying RNA interference constructs of AOS (allene oxide synthase) genes show severe male sterility. Plant Breed 129:647–651
Bate N, Twell D (1998) Functional architecture of a late pollen promoter: pollen-specific transcription is developmentally regulated by multiple stage-specific and co-dependent activator elements. Plant Mol Biol 37:859–869
Cao P, Jung KH, Choi D, Hwang D, Zhu J, Ronald PC (2012) The rice oligonucleotide array database: an atlas of rice gene expression. Rice 5:17
Chao J, Jin J, Wang D, Han R, Zhu R, Zhu Y, Li S (2014) Cytological and transcriptional dynamics analysis of host plant revealed stage-specific biological processes related to compatible rice-Ustilaginoidea virens interaction. PLoS One 9:e91391
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Cosgrove DJ (2000) Loosening of plant cell walls by expansins. Nature 407:321–326
Cosgrove DJ, Bedinger P, Durachko DM (1997) Group I allergens of grass pollen as cell wall-loosening agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6559–6564
Gupta V, Khurana R, Tyagi AK (2007) Promoters of two anther-specific genes confer organ-specific gene expression in a stage-specific manner in transgenic systems. Plant Cell Rep 26:1919–1931
Han MJ, Jung KH, Yi G, Lee DY, An G (2006) Rice Immature Pollen 1 (RIP1) is a regulator of late pollen development. Plant Cell Physiol 47:1457–1472
Han SY, Shin D, Moon SJ, Jeon SA, Byun MO, Kim BK (2012) Optimization of Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in Japonica-type rice Oryza sativa L. cv. Dongjin for high efficiency. Korean J Breed Sci 44:221–228
Higo K, Ugawa Y, Iwamoto M, Korenaga T (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database. Nucleic Acids Res 27:297–300
Jeon JS, Chung YY, Lee S, Yi GH, Oh BG, An G (1999) Isolation and characterization of an anther-specific gene, RA8, from rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Mol Biol 39:35–44
Jeong HJ, Jung KH (2015) Rice tissue-specific promoters and condition-dependent promoters for effective translational application. J Integr Plant Biol. doi:10.1111/jipb.12362
Jiang SY, Ramachandran S (2011) Functional genomics of rice pollen and seed development by genome-wide transcript profiling and Ds insertion mutagenesis. Int J Biol Sci 7:28–40
Khurana R, Kapoor S, Tyagi AK (2013a) Spatial and temporal activity of upstream regulatory regions of rice anther-specific genes in transgenic rice and Arabidopsis. Transgenic Res 22:31–46
Khurana R, Kathuria H, Mukhopadhyay A, Kapoor S, Tyagi AK (2013b) 286 bp upstream regulatory region of a rice anther-specific gene, OSIPP3, confers pollen-specific expression in Arabidopsis. Biotechnol Lett 35:455–462
Lee Y, Kende H (2001) Expression of β-expansins is correlated with internodal elongation in deepwater rice. Plant Physiol 127:645–654
Liu Y, Cui S, Wu F, Yan S, Lin X, Du X, Chong K, Schilling S, Theissen G, Meng Z (2013) Functional conservation of MIKC*-Type MADS box genes in Arabidopsis and rice pollen maturation. Plant Cell 25:1288–1303
Nicol AF, Drouaud J, Haouazine N, Pelletier G, Guerche P (1999) Isolation of rapeseed genes expressed early and specifically during development of the male gametophyte. Plant Mol Biol 40:857–872
Oh SA, Park KS, Twell D, Park SK (2010) The SIDECAR POLLEN gene encodes a microspore-specific LOB/AS2 domain protein required for the correct timing and orientation of asymmetric cell division. Plant J 64:839–850
Oo MM, Bae HK, Nguyen TD, Moon M, Oh SA, Kim JH, Soh MS, Song JT, Jung KH, Park SK (2014) Evaluation of rice promoters conferring pollen-specific expression in a heterologous system, Arabidopsis. Plant Reprod 27:47–58
Park JI, Hakozaki H, Endo H, Takada Y, Ito H, Uchida M, Okabe T, Watanabe M (2006) Molecular characterization of mature pollen-specific genes encoding novel small cysteine-rich proteins in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 25:466–474
Paupière MJ, van Heusden AW, Bovy AG (2014) The metabolic basis of pollen thermo-tolerance: perspectives for breeding. Metabolites 4:889–920
Perez M, Ishioka GY, Walker LE, Chesnut RW (1990) cDNA cloning and immunological characterization of the rye grass allergen Lol p I. J Biol Chem 265:16210–16215
Rogers HJ, Bate N, Combe J, Sullivan J, Sweetman J, Swan C, Lonsdale DM, Twell D (2001) Functional analysis of cis-regulatory elements within the promoter of the tobacco late pollen gene g10. Plant Mol Biol 45:577–585
Ross EJ, Stone JM, Elowsky CG, Arredondo-Peter R, Klucas RV, Sarath G (2004) Activation of the Oryza sativa non-symbiotic haemoglobin-2 promoter by the cytokinin-regulated transcription factor, ARR1. J Exp Bot 55:1721–1731
Sato Y, Takehisa H, Kamatsuki K, Minami H, Namiki N, Ikawa H, Ohyanagi H, Sugimoto K, Antonio BA, Nagamura Y (2013) RiceXPro version 3.0: expanding the informatics resource for rice transcriptome. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D1206–D1213
Sharma N, Russell SD, Bhalla PL, Singh MB (2011) Putative cis-regulatory elements in genes highly expressed in rice sperm cells. BMC Res Notes 4:319
Sheoran IS, Saini HS (1996) Drought-induced male sterility in rice: changes in carbohydrate levels and enzyme activity associated with the inhibition of starch accumulation in pollen. Sex Plant Reprod 9:161–169
Suwabe K, Suzuki G, Takahashi H, Shiono K, Endo M, Yano K, Fujita M, Masuko H, Saito H, Fujioka T, Kaneko F, Kazama T, Mizuta Y, Kawagishi-Kobayashi M, Tsutsumi N, Kurata N, Nakazono M, Watanabe M (2008) Separated transcriptomes of male gametophyte and tapetum in rice: validity of a laser microdissection (LM) microarray. Plant Cell Physiol 49:1407–1416
Swapna L, Khurana R, Vijaya-Kumar S, Tyagi AK, Rao KV (2011) Pollen-specific expression of Oryza sativa indica pollen allergen gene (OSIPA) promoter in rice and Arabidopsis transgenic systems. Mol Biotechnol 48:49–59
Tien DN, Oo MM, Soh MS, Park SK (2013) Bioengineering of male sterility in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Breed Biotech 1:218–235
Toki S, Hara N, Ono K (2006) Early infection of scutellum tissue with Agrobacterium allows high-speed transformation of rice. Plant J 47:969–976
Tsuchiya T, Toriyama K, Ejiri S, Hinata K (1994) Molecular characterization of rice genes specifically expressed in the anther tapetum. Plant Mol Biol 26:1737–1746
Twell D, Wing R, Yamaguchi J, McCormick S (1989) Isolation and expression of an anther-specific gene from tomato. Mol Gen Genet 217:240–245
Twell D, Yamaguchi J, McCormick S (1990) Pollen-specific gene expression in transgenic plants: coordinate regulation of two different tomato gene promoters during microsporogenesis. Development 109:705–713
Wei LQ, Xu WY, Deng ZY, Su Z, Xue Y, Wang T (2010) Genome scale analysis and comparison of gene expression profiles in developing and germinated pollen in Oryza sativa. BMC Genom 11:338
Welchen E, Gonzalez DH (2006) Overrepresentation of elements recognized by TCP-domain transcription factors in the upstream regions of nuclear genes encoding components of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation machinery. Plant Physiol 141:540–545
Xu H, Theerakulpisut P, Goulding N, Suphioglu C, Singh MB, Bhalla PL (1995) Cloning, expression and immunological characterization of Ory s 1, the major allergen of rice pollen. Gene 164:255–259
Xu H, Goulding N, Zhang Y, Swoboda I, Singh MB, Bhalla PL (1999) Promoter region of Ory s 1, the major rice pollen allergen gene. Sex Plant Reprod 12:125–126
Xu J, Yang C, Yuan Z, Zhang D, Gondwe MY, Ding Z, Liang W, Zhang D, Wilson Z (2010) The ABORTED MICROSPORES regulatory network is required for postmeiotic male reproductive development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 22:91–107
Yanagisawa S (2004) Dof domain proteins: plant-specific transcription factors associated with diverse phenomena unique to plants. Plant Cell Physiol 45:386–391
Yue YZ, Sun J, Huang X, Peng H, Liu GF, Hu HR (2014) Characterization of a novel anther-specific gene encoding a leucine-rich repeat protein in petunia. Gen Mol Res 13:9889–9898
Zhang Q, Li Z, Yang J, Li S, Yang D, Zhu Y (2012) A calmodulin-binding protein from rice is essential to pollen development. J Plant Biol 55:8–14
Zou JT, Zhan XY, Wu HM, Wang H, Cheung AY (1994) Characterization of a rice pollen-specific gene and its expression. Am J Bot 81:522–561
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Next-Generation BioGreen21 Program, of the Rural Development Administration in the Republic of Korea (The National Center for GM Crops, Grant No. PJ01128401; Plant Molecular Breeding Center No. PJ008137), and the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2013R1A1A2006040 to KHJ, and NRF-2014R1A1A2005312 to SAO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
T. D. Nguyen and M. M. Oo contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11816_2015_365_MOESM3_ESM.jpg
Supplemental Figure 3. Complementation analysis of scp-2 homozygotes (a-j). Pollen phenotypes in scp-2hm. a- normal tricellular pollen; b- uninucleate pollen; c, d- binucleate pollen; e- larger tricellular pollen; f-i- four-nucleate pollen with (g-i) or without (f) the extracellular compartment marked with an arrowhead; j- aborted pollen. Pollen images were all taken at the same magnification. (k-m) Confirmation of T-DNA insertion in the ProOsLPS10-SCP:dHA lines. (n) 1,316 bp SCP-dHA fragment was amplified from the DNA of fourteen transgenic lines (lane 1-14) using gene-specific primers (SCP forward and reverse). (o) scp-2 allele was detected using the LBb1 and LOBRP primer set. (p) SCP wild-type gene was checked in scp-2 hm background and transgenic lines using the LBb1 and 47870-R primers. scp- 2 hm and Col were used as the control. (JPEG 278 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.D., Oo, M.M., Moon, S. et al. Expression analysis of two rice pollen-specific promoters using homologous and heterologous systems. Plant Biotechnol Rep 9, 297–306 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-015-0365-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-015-0365-4