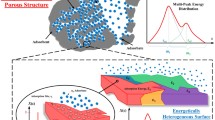
Abstract
The equilibrium adsorption isotherm has a crucial effect on various characteristics of the solid adsorbent (e.g., pore volume, bulk density, surface area, pore geometry). A historical paradox exists in conventional estimation of adsorption isotherm parameters. Traditionally, the total amount of adsorb material (total adsorption isotherm) has been considered equivalent to the local adsorption isotherm. This assumption is only valid when the corresponding pore size or energy distribution (PSD or ED) of the porous adsorbent can be successfully represented with the Dirac delta function. In practice, the actual PSD (or ED) is far from such assumption, and the traditional method for prediction of local adsorption isotherm parameters leads to serious errors. Up to now, the powerful combination of inverse theory and linear regularization technique has drastically failed when used for extraction of PSD from real adsorption data. For this reason, all previous researches used synthetic data because they were not able to extract proper PSD from the measured total adsorption isotherm with unrealistic parameters of local adsorption isotherm. We propose a novel approach that can successfully provide the correct values of local adsorption isotherm parameters without any a priori and unrealistic assumptions. Two distinct methods are suggested and several illustrative (synthetic and real experimental) examples are presented to clearly demonstrate the effectiveness of the newly proposed methods on computing the correct values of local adsorption isotherm parameters. The so-called Iterative and Optima methods’ impressive performances on extraction of correct PSD are validated using several experimental data sets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Guntuka, National University of Singapore, M.Sc. Thesis (2006).
A. Shahsavand and M. Niknam Shahrak, Colloids Surf.. A., 378, 1 (2011).
A. Shahsavand and M. Niknam Shahrak, Chem. Eng. J., 171, 69 (2011).
A. Malek and S. Farooq, AIChE J., 42, 11 (1996).
I. Langmuir, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 38, 11 (1916).
J.H. De Boer, The Dynamical Character of Adsorption, Second Ed., Oxford University Press, London (1968).
A. L. Myers and J. M. Prausnitz, AIChE J., 11, 1 (1965).
M. M. Dubinin, Chem. Rev., 60, 235 (1960).
D.M. Ruthven, Principles of Adsorption and Adsorption Processes, Wiley, New York (1984).
K. Y. Foo and B.H. Hameed, Chem. Eng. J., 156, 2 (2010).
W.H. Press, S.A. Teukolsky, W.T. Vetterling and B.P. Flannery, Numerical recipes in FORTRAN: The art of scientific computing, Cambridge University Press (1992).
D.D. Do, Adsorption Analysis: Equilibria and Kinetics, Imperial College Press, London (1998).
O. Solcova, L. Matejová and P. Schneider, Appl. Catal. A-Gen., 313, 167 (2006).
P. H. Merz, J. Comp. Phys., 38, 64 (1980).
W. A. House, M. Jaroniec, P. Brauer and P. Fink, Thin. Solid. Films, 87, 323 (1982).
S. K. Bhatia, Chem. Eng. Sci., 53, 18 (1998).
V.M. Gun’koa and D.D. Do, Colloid. Surface. A., 193, 71 (2001).
J. Keller and R. Staudt, Gas adsorption equilibria: Experimental methods and adsorption isotherms, Springer Science Press, U.S. (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Husseinzadeh, D., Shahsavand, A. Reliable estimation of adsorption isotherm parameters using adequate pore size distribution. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 32, 925–933 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0294-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-014-0294-x